* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pediatric Radiography Pediatric Restorative Dentistry
Focal infection theory wikipedia , lookup
Remineralisation of teeth wikipedia , lookup
Periodontal disease wikipedia , lookup
Crown (dentistry) wikipedia , lookup
Tooth whitening wikipedia , lookup
Special needs dentistry wikipedia , lookup
Dental anatomy wikipedia , lookup
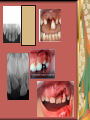
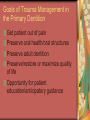
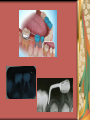
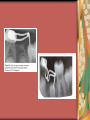
Primary Dentition: Trauma & Space Management Dr. Ha T. Jacklynn Thai Board Certified Pediatric Dentist Associate Professor, University of California, San Francisco Department of Pediatric Dentistry HRSA Program: Pediatric Dentistry in Hygiene Dentistry 24700 Calaroga Ave. Suite 104 ~ Hayward, CA 94545 ~ 510.785.9295 Trauma Explore the Problem Find out the story Who What When Where Why How Prioritize medical status/condition(s) Primary vs. permanent dentition How to Address the Problem Medical evaluation Glascow Coma Scale Behavior/mental status Clinical exam Radiographic exam Types of traumas Common types of trauma Fracture Tooth Root Alveolar bone Concussion – tenderness Movement of tooth position Subluxation – increased mobility but not been displaced. Bleeding from gingival sulcus Extrusion Intrusion Lateral luxation Avulsion Cut lip or other soft tissue Avulsed Teeth How was it brought to you? How long has it been out of the mouth? Primary teeth Do NOT reimplant Permanent teeth Patient age – is apex open or closed? How long as it been out of the mouth? Splint Possible sequelae Necrosis Tooth discoloration Pulpal obliteration Ankylosis Loss of tooth Rule Out Child Abuse Does the story make sense? Are there repeated occurrences? Goals of Trauma Management in the Primary Dentition Get patient out of pain Preserve oral health/oral structures Preserve adult dentition Preserve/restore or maximize quality of life Opportunity for patient education/anticipatory guidance Space Management They’re Just Baby Teeth Know the exfoliation and eruption table – at least a rough estimate Rule of 3 Types of Space Maintenance Appliances Band and loop Distal shoe Bilateral – Permanent Teeth Upper: Nance/TPA Lower: Lingual Holding Arch Goals of Space Management Prevent loss of arch length, width, and perimeter by maintaining the relative position of the existing dentition Space maintenance is NOT space gain Space maintenance does not rule out future orthodontics Few Thoughts to Walk Away With Regarding Pediatric Dental Care Health Professional Service Proper consent Definition of a household Co-parent – amicable or not? MINOR MUST BE 15 YEARS OF AGE OR OLDER LAW CONFIDENTIALITY AND/OR INFORMING OBLIGATION OF THE HEALTH CARE PROVIDER GENERAL MEDICAL CARE “A minor may consent to the minor's medical care or dental care if all of the following conditions are satisfied: (1) The minor is 15 years of age or older. (2) The minor is living separate and apart from the minor's parents or guardian, whether with or without the consent of a parent or guardian and regardless of the duration of the separate residence. (3) The minor is managing the minor's own financial affairs, regardless of the source of the minor's income.” (Cal. Fam. Code § 6922(a)).