* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Control Systems in Plants
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
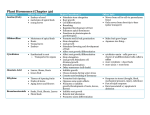
Control Systems in Plants Etioloation and Deetiolation Plant Hormones • What is a Plant hormone? • Compound produced by one part of an organism that is translocated to other parts where it triggers a response in target cells and tissues. Experiments on Phototropism Discovery of Hormones • 1. Darwin and Darwin – Removed the tip of the coleoptile of a grass seedling, and it failed to grow toward light. • 2. Boysen-Jensen – Put block of gelatin on coleoptile tip to allow chemical diffusion – Auxin purified later by Thimann • 3. Went – Modified Boysen-Jensen experiments – Extracted the chemical messenger responsible Functions of Plant Hormones • Control plant growth and development by affecting division, elongation, and cell differentiation • Effect depends on size of action, stage of plant growth and hormone concentration • Hormonal signal is amplified by gene expression, enzyme activity, or membrane properties Five Classes of Plant Hormones • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Auxins Cytokinins Gibberellins Abscissic acid Ethylene Which hormones cause the following…. • • • • • • • • • • • Apical dominance from apical bud Abscission Stimulates growth of axillary buds Root growth Stimulates closing of stomata Causes fruit ripening Stimulates seeds to break dormancy and germinate Growth inhibitor Cell division and differentiation Cell elongation Seedless fruit Which hormone is made at each location? • Made in roots and transported upwards • Found in meristems of apical buds and seed embryos • Found in tissues of ripening fruit • Leaves stems, roots and green fruit Which hormone caused the following? Opposing hormones • Which two hormones act in opposition to one another regarding apical dominance, cell division and differentiation? • Which two hormones work in opposition regarding seed dormancy? Phototropism Acid Growth Hypothesis Plant Movement • A. Tropisms: – growth response toward or away from stimuli • 1. Phototropism – cells on darker side of shoot elongate faster than cells on bright side due to auxin distribution – auxin move laterally across the tip from the bright to dark side by an unknown mechanism. – Cells on the dark side grow • 2. Gravitropism (geotropism) – gravity – roots --> positive geotropism – stems---> negative geotropism • Statoliths – starch grains in root cap cells, they trigger calcium redistribution which results in auxin movement in root – auxin inhibits cell elongation – upperside of root elongates faster than bottom • • • • 3. Thigmotropism growth in response to touch tendrils contacts solid and coils increased production of ethylene • 4. Hydrotropism • growth toward water • willow tree Circadian Rhythms and the Biological Clock • Circadian Rhythm- a physiological cycle with a frequency of about 24 hours that persists even when an organism is sheltered from environmental cues. • Photoperiodism – a physiological response to DAY length – seasonal events • Photoperiods Control of Flowering – the amount of night length controls flowering • 1. Short day plants – late summer, fall and winter • 2. Long day plants – late spring and summer • 3. Day- Neutral plants – unaffected by photoperiods Critical Night Length • Night (dark) actually causes flowering not light – Leaves detect the photoperiod while buds produce flowers • Florigen– scientists believe this unidentified hormone is produced in the leaves and moves to buds. Phytochrome • Protein containing chromophore (lightabsorbing component) responsible for a plant’s response to photoperiod – Pr - red absorbing – Pfr- Far red absorbing • Plants synthesize Pr in dark – if phytochrome illuminated then Pr both types of light are seen Pfr since • Pfr triggers many plant responses to light • In darkness Pfr goes back to Pr Response to Stress • • • • • • Water deficit Oxygen deprivation Salt Stress Heat Stress Cold Stress Herbivores… Defense Against Pathogens • Gene for Gene relation between plant and pathogen • Coevolution between plant and pathogen Short Day Plant Short Day Plant • Spinach Long Day Plant Spinach Long Day Plant Which wavelength of light causes phototropism? Auxins IAA indoleactetic acid: natural auxin • Promotes elongation & secondary growth • Apical meristem is the major site of auxin production • Inhibits lateral growth • Induces female floral parts & fruit Cytokinins • Move from the roots to tissues by moving up xylem • Works with auxin to promote differentiation • Stimulates protein synthesis • Made in roots • Function: – 1. Cell division and differentiation – 2. Apical dominance – 3. Anti-aging hormones • slow protein deterioration Observe Apical Dominance Gibberellins • Stimulate elongation of cells • Inhibits root growth • Stimulate flower part developmentbolting(large internode) • Works with auxin for fruit development • Signals seeds to break dormancy and germinate Abscisic Acid (ABA) • Growth inhibitor • returns seeds to dormancy • inhibits cell division in vascular cambium • causes rapid closing of stoma during dry periods • promotes positive geotropism Ethylene • • • • Gaseous hormone high [auxin] induce release of ethylene fruit ripening (positive feedback) Apoptosis: – Senescence (aging) – Abscission – leaves falling