* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
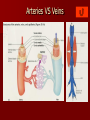
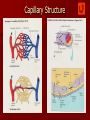
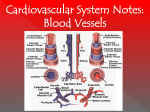
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Vessels and Blood Pressure Chapter 15 Topics 4 - 7 Differences Between the Vessels Arteries arterioles capillaries venules veins Arteries - carry blood away from heart – Round Cross Section – Tough and Elastic Elastic recoil helps keep blood flowing – 3 Layers: Tunica Adventitia – Outer – CT to connect arteries in place Tunica Media – middle – Smooth muscle Vasoconstriction sympathetic N.S. Vasodilation inhibition of sympathetic NS – Elastic CT – pulse Tunica Intima – inner endothelium – Needs to be smooth DIAGRAM Differences Between the Vessels Arterioles – small arteries – Precapillary sphincters – open and close capillary beds – Metaterioles – Major part of vasodilation and vasoconstriction Veins – carry blood toward heart (atria) – 3 layers Tunica adventitia Tunica Media – less developed Tunica Intima – one way valves – Blood Resevoir – Skeletal Muscles help move blood Venules – small veins DIAGRAM CAPILLARIES Smallest; walls one cell thick – Largest total cross sectional area Connect arteriole and venous systems Capillary permeability varies DIAGRAM – Muscle tissue cap small – Gland, intestinal cap. Larger – Liver, spleen and bone marrow cap. Largest sinusoids Capillary Arrangement – Nearly every tissue has associated cap. Bed – High metabolic extensive cap. Bed – Can be shut off or opened up Precapillary sphincters CAPILLARIES Only place for exchange – Diffusion At Tissues: O2, nutrients out; CO2, wastes in At alveoli (lungs): CO2 out; O2 in Sm. Intestines: Nutrients in Lipid soluble and small molecules diffuse easily Plasma Proteins remain in blood – Filtration – hydrostatic pressure Pressure decreases as distance increases Filtration greater at arteriole end Water is lost DIAGRAM – Movement depends on osmotic and hydrostatic pressures – Lymph system returns fluid Arteries VS Veins Capillary Structure Fluid Pressure at Capillaries