* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PRAG
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
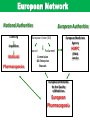
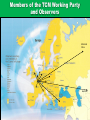
The Global Challenge The Role of the European Pharmacopoeia for TCM Globalisation Gerhard FRANZ, Chairman of the Pharmacognosy group DAB University of Regensburg, Regensburg/Germany Content - TCM Herbal Medicinal Products in Europe - Quality standards set by the European Pharmacopoeia - Elaboration of TCM herbal drug monographs - Problems with processing of herbal drugs - Outlook for the future Acceptance of TCM in Europe • High acceptance of Complementary Medicine • Phytomedicine well established in the EU • Good educational background in most countries of the EU • Historical good connections with the Far East • Present in many specialised Pharmacies as prescription medicines for TCM practitioners Actual Problems with TCM in Europe • No specific regulation existing for TCM Products • European new legislation on Traditional Herbal Medicines difficult for CMM registration • No animal or mineral products allowed • Officially no Pinyin names and Sinograms allowed TCM product classification as: - Medicinal Products Nutraceuticals Dietary -Supplements Cosmetics TCM in the European Union Products not to be licensed: - Tradidional crude (processed) herbal drugs - Decoction pieces - Granules for prescription Products to be licensed: - Chinese patent medicines - Granules for prescriptions complex formulas - New TCM Phytomedicines Categories of Herbal Products Medicinal products Dietary supplements Food Concept - No clear guidance relating to quality for most of the dietary supplements : GMP?, Safety?, Efficacy? - No claims for Therapeutic Indication - Easy access to market as: Botanicals – Dietary Supplements Functional Foods, Nutraceuticals Not relevant for Traditional Chinese Medicine in most European countries Content - Herbal Medicinal Products in Europe -Quality Standards set by the European Pharmacopoeia - Elaboration of Ph Eur TCM herbal drug monographs - Problems with Processing of herbal drugs - Outlook for the future European Network National Authorities Licensing European Authorities European Union (EU) Inspection Council National Pharmacopoeias European Medicines Agency Parliament Commission DG Enterprise Brussels European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines European Pharmacopoeia HMPC (EMA) London Herbal Medicinal Products in Europe All HMP‘s can only be markted in the EU demonstrating : HMPC Monographs Safety Efficacy Quality Ph Eur Monographs Purpose of the European Pharmacopoeia To promote public health by the provision of recognised common standards for use by health-care professionals and others concerned with the Quality of Medicines: Safeguard Users of Traditional Chinese Medicines ! Criteria Impact of the Ph Eur The standards apply to all medicines regardless of their origin: - chemical - biological - herbal, included TCM - method of production - mode of application (homeopathic medicines). - Actual situation: more than 2400 Monographs out of which : ~ 280 Herbal Monographs ~ 300 General Methods In future editions: more than 100 TCM Monographs Herbal – Monographs in the Ph Eur General Monographs: – Herbal drugs – Herbal drug preparations – Herbal teas – Extracts – Essential oils – Methods in Pharmacognosy (22) Technical Requirements apply to the entire class! Scope of Ph Eur Herbal Drug Monographs QUALITY SAFETY minimize the risk potential by clear Defintions, Identifications, Tests and Assay EFFICACY: HMPC/ LONDON, EMA 9th : 2017 60 TCM Monographs published Content - Herbal Medicinal Products in Europe - Quality standards set by the European Pharmacopoeia - Elaboration of Ph Eur TCM herbal drug monographs - Problems with processing of herbal drugs - Outlook for the future TCM herbal drugs in the World •Growing interest worldwide •Exportation from China has increased •Few legally binding quality standards •Knowledge on TCM herbal drugs is limited outside China •Quality problems have been observed • Future: Granules instead of Herbals? ©2009 EDQM, Council of Europe, All rights reserved 20 TCM Standards/Monographs in various countries of the World Pharmacopoeia/Monographs Authority legal status Chinese Pharmacopoeia European Pharmacopoeia SFDA EU ,EDQM official official Hong Kong Chinese Materia Medica Standards DHKK China official Japanese Pharmacopoeia PA Japan official British Pharmacopoeia BPC, UK official German Pharmacopoeia BfArM official American Herbal Pharmacopoeia Australian Guidelines for Complementary Medicines private non official TGA Australia official What is actually needed for a good TCM practice? • better knowledge about the impact of TCM on pharmaceutical practices and public health • balanced information for the public about TCM potential health risks • more information about safety issues due to the absence of qualified reporting systems for undesirable effects caused by TCM Why specific Ph Eur Monographs on TCM? • Imported TCM herbal drugs: often quality problems observed - Problems with correct Identification - Confusion between related species - Contamination with heavy metals, microbes pesticides • Addition of synthetic compounds to fake pharmacological effects History of the Activities: Quality Monographs on CMM for the EU Member States • About 20 years ago TCM became known and more and more popular in some European Countries with the consequence that CMM with often doubtful Definition/Identity and Quality were imported and sold to the patient. Intoxications occured and several National Authorities became alert. • Consequence by the EU in 2005: Decision in the EU: Ph Eur Commission 2005 ‘Monographs on Herbal Drugs used in Traditional Chinese Medicine should be developed to give a modern quality standard according to European Pharmacopoeia principles and to facilitate and encourage use by practitioners for safe products’ 25 Inclusion Criteria of CMM in the TCM Herbal Drug Working Program EP - existance of a monograph in the Ch Ph - volume of use in the EU member states - documented problems of quality - documented problems of toxicity - risk of substitution with toxic herbal drugs - risk of documented contaminations Number of items on the TCM Work Programme ? - the average European TCM practitioner is prescribing about 300 TCM Herbal Drugs in daily practice - commercial importers provide up to 400 TCM Herbal Drugs to the EU market - the average number of CMM used in Chinese TCM Clinics is around 500 - how many Quality Monographs are needed in the future for the EU? Transfer of Monographs • • adapt/adopt??? •who does the work ? • where is it done ? • how is it done ? ANSWERS • Adapt/adopt not possible due to different technical requirements Ch P/ Ph Eur • Who does the work: TCM Working Party • Close collaboration with China • Where is it done? By the respective Experts in EU Member States and China • How is it done? Examination/Modification, Validation of all methods published in Ch P TCM Working Party Ph Eur Commission 2016 Chairman Prof. Dr. G. Franz Country: AT: AT: AT. B: CH: CH: CH: CH: D: D: FR: FR: GB: IT: NL: PL: TR: Prof. Dr. R.Bauer Dr. R. Laenger Mag. E. Stoeger Prof.Dr. P. Duez Dr. I.M. Bruentrup Dr.Th. Lehmann Dr.E.Reich Dr.Sh. Wang-Tschen Dr. M.Gasser Dr.K.Wuthold Prof.Dr.I.Fouraste M. R.Soussain Mr M.Whaley rof.Dr.A.R.Bilia Dr. M. Wang Prof. Dr. K. Glowniak Prof.Dr. S. Harput University EMA Industry University Industry OMCL Industry Industry Industry Industry University OMCL NPA University University University University Observers: AU: CN: Prof.Dr.K.Chan SATCM/NKL University Analytics Microscopy Analytics Analytics TLC/HPTLC Analytics Analytics Microscopy Analytics Analytics Analytics Members of the TCM Working Party and Observers Mainland China Australia Elaboration procedure of Monographs The Ph Eur Commission decides to elaborate/revise a new Monograph Start Working Party: Rapporteur prepares a draft Monograph which is evaluated by the Group 1. Publication draft Monograph: PHARMEUROPA National Authorities comment on the published draft Monograph Working Party examines the comments and revises the draft Monograph The draft monograph is proposed for adoption :Commission Commission adopts the Monograph The Monograph is published The monograph will be implemented Time frame: average two years Structure of Ph Eur Herbal Drug Monographs • Definition • Identification ( Morphology, Histology, HPTLC/TLC – fingerprinting ) • Tests ( foreign matter, water content, pesticides, heavy metals, aflatoxins, mineral ash, ariostolochic acid …..) • Assay ( quantification of defined marker compounds) • Storage Structure of Ch P Monographs • • • • • • • Description Identification Tests Assay Action and use: legal requirement for TCM Dosage and Usage: legal requirement for TCM Storage: legal requirement for all monographs Ch P 2010 Latin Differences: - root tuber versus -tuberous root Chinese Ph Eur 2016 Differences: - no family - no collection period -minimum content given English English Latin Chinese title missing Guide for the Elaboration of Monographs on Herbal Drugs (Ph Eur) A monograph on a Herbal Drug is drafted with the same overall structure as a Monograph on a chemical substance The latest versions of the Technical Guide for the Elaboration of Mongraphs and of the Style Guide apply to monographs on Herbal Drugs All Tests and Assay methods described in a monograph must be validated according to the procedures stated in the Technical Guide. Consequence: Apply for all TCM Herbal Drugs! Assay Chemically defined Substance 1% impurities 99 % chemical substance Herbal Drug ~ 2 % active principle 98 % inert matrix Constituents to be determined in an Assay of a TCM Monograph • constituents with documented therapeutic actvity • constituents with a toxicological risk which have to be limited • distinguish closely related species if not possible by identification A,B and C • constituents as technical markers (proper harvesting, drying, storage, adulterations…) Constituents with therapeutic Activity Definition: ‘Chemically defined substances or groups of substances which are generally accepted to contribute substantially to the therapeutic activity of a herbal drug or herbal drug preparation‘ Assay essential for the Safety of the Patient • • • • • • • TCM herbal drugs containing: Aconite alkaloids Pyrrolizidine alkaloids ß- Asarone Furano cumarines Aristolochic acid In these cases acceptable limits for toxic compounds must be set Content - Herbal Medicinal Products in Europe - Quality standards set by the European Pharmacopoeia - Elaboration of Ph Eur TCM herbal drug monographs - Problems with Processing of TCM herbal drugs - Outlook for the future Reasons of Processing • Main purpose: • Detoxification or Reducing Side Effects • Modifying/ Reinforcing therapeutic Effects • Others such as dissipating odours and taste, facilitating storage ……. Processed versus Unprocessed • Processing reduces the toxicty of many drugs • Processing enhances the activty of drugs • No uniform Processing Methods in China (regional differences) • No objective criteria (SOP) for the use of excipients • No standardised criteria for excipients in the actual Ch P Methods of Processing (Pao Zhi) according to Ch P 2010 - cleaning: O.K. with Ph Eur - cutting : O.K. with Ph Eur -special processing methods not in line with Herbal Drug Preparations all unknown for Ph Eur, need to be standardised and acknowledged by the Ph Eur Technical Guide stir frying stir frying with solid or liquid materials ca lcining steaming/ boiling torrefication grinding with water Processing of Crude Drugs: Excipients used for different Processing Techniques ChPh 2010 For all PhEur Monographs, the quality of excipients must be specified: - Wine: use yellow rice wine (% alcohol?) -Vinegar: use rice vinegar (acidity?) -Salt water: salt dissoved in an appropriate quantity of water ? -Ginger juice: squeezed juice of fresh Ginger (content of ingredients ?) -Honey: refined honey (quality according to PhEur?) -Fat: sebum fat (quality parameters?) What we need to do - Clarifying the Processing Mechanisms to guide the establishment of Standard Processing Techniques -Applying modern analysis techniques combining with chemical/analytical , pharmaco-dynamics, molecular biology and toxicology studies Content - Herbal Medicinal Products in Europe - Quality standards set by the European Pharmacopoeia - Elaboration of Ph Eur TCM herbal drug monographs - Problems with Processing of herbal drugs - Outlook for the future Outlook • Interest in TCM is permanently growing in many EU countries • This should be reflected by the National Authorities to propose additional CMM to the Commission of the European Pharmacopoeia • Consequently, the Work Programme of the TCM Working Party • must accept additional items to be worked on in the future • The efficiency and quality of this Work Programme must be optimised by a close collaboration of EDQM/ Ph Eur/ Ch P/ SATCM NKI • The Working Programme of the Ph Eur TCM WP should be considered for the further planning of the Ch P 2020 • Consequently, Ph Eur Commission should be informed about the future plans of Ch P ROUNDTABLE 3: REGULATORY AND LEGISLATION Marketing of Herbal Products • Products Legislation • Herbal Medicinal Product Medicinal Product • Full marketing authorization CD 2001/83 EC as amended by • • Well established use Traditional use CD 2004/24 EC & CD 2004/27/EC • Herbal Food Supplement Food Supplements • • Herbal Novel Food CD 2002/46 EC & DC 2006/C80E Novel Foods Regulation 258/97 • Herbal Cosmetic • Cosmetics Regulation CD76/768 Pharmacovigilance Consumer information; labeling;advertising Efficacy new trials bibliographic Safety new tests bibliographic Traditional use expert report bibliographic new tests Quality Control Good Manufacturing Practices Good Agricultural and Collection Practices ( GACP) new 52 well-established traditional HMPC-Scheme: Access to the market http://www.ema.europa.eu European quality guidelines for approval of herbal medicinal products • Public Statement on Good Agricultural and Collection Practice for starting materials of herbal origin (GACP) • Guideline on Quality of Herbal Medicinal Products / Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products • Specifications: Test procedures and Acceptance Criteria for Herbal Drugs, Herbal Drug Preparations • Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products • Guideline on Quality of Combination Herbal Medicinal Products / Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products • Guideline on Stability Testing Criteria for Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products (Directive 2004/24/EC) - limited therapeutic indications - specified strength and posology - oral, external or inhalation preparations - period of traditional use has elapsed at least 30 years, out of which at least 15 years in the EU - sufficient data on traditional use Consequences: - legal use for OTC - no treatment of severe diseases - high quality documentation required - no innovative products possible EU Directive 2004/24/EC on Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products it does not cover the treatment of severe diseases efforts on quality are still high does not allow innovative products (IPR difficult) the legal use for OTC For modernized TCM products for „well established“ use or „new“ products should be developed Summary and Conclusions • Depending whether used for health or desease treatment, herbal products can be marketed in Europe as food supplements or as medicines. • In both cases corresponding regulations need to be considered. • Medicinal products can be approved as new, well established, or traditional products. • In order to guarantee safety and efficacy, herbal medicinal products must undergo serious quality control, which should be based on Pharmacopoeia Monographs. • For well established and traditional herbal medicinal products proof of efficacy and safety can be based on bibliographic data, and corresponding monographs should be established. • More research is necessary to improve clinical evidence and our knowledge on relevant constituents and mechanism of action. Many thanks for your kind attention!