* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download After School Physiology review 2013
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
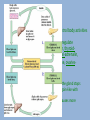
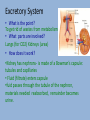
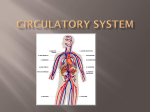
Physiology Overview Respiratory System • What is the point? get oxygen to muscles and carbon dioxide out • Where does gas exchange happen? In the lungs-between alveoli (air sacs) and capillaries (small blood vessels) • What parts are involved, in order? Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs • What does the diaphragm do? Contracts to bring air in, relaxes for air to go out • What is the epiglottis? Flap that prevents food from going down trachea (wind pipe) Circulatory system • What is the point? To get oxygen and nutrients to all cells and wastes out • What moves the blood around? The heart pumps the blood through arteries to capillaries, and returns via veins • How many chambers does the heart have? What are they called? 4-right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle • What do valves do? Prevent back flow Digestive System • What is the point? To break down food and provide nutrients for the cells • Where are complex sugars broken down? In the mouth, and chewing breaks down food here toomechanical digestion • What happens in the stomach? Acids break down proteins • What happens in the small intestine? Where MOST nutrient absorption takes place, lipids are broken down here • What do the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas do? Liver-make bile to break down fat, Gall bladder-store bile, pancreas-make chemicals for digestion in small intestine • What does the large intestine do? Mostly absorb water Immune system • What is the point? To prevent infection and illness • What is the first line of defense? Skin! • What are the main cell types and their jobs? Macrophages-eat invaders and interact with helper Ts Helper T Cells-Tell others what to do B-cells-Make antibodies to tag invaders Memory B-cells-remember past invaders Killer T Cells-kill tagged invaders • How do vaccines work? Inject coat of virus with antigens on it (no DNA), body makes antibodies and memory B cells, so ready when get real virus Nervous system • What is the point? For brain to interact with body and environment • What are the cells called? Neurons-sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons • How do they work? Stimulus hits dendrite, causes voltage gates ion channels to open on axon, sodium goes into cell, changing gradient, spreading signal down axon to synapse-goes to next cell • What is a synapse? Space between one neuron and the next. Neurotransmitters (chemicals) carry the signal across • What is a reflex? Signal that goes to spin and directly to motor neuron, no brain involved Endocrine System • What is the point? Send chemical messages (hormones) to control body activities • Which glands are involved? Hypothalamus-regulate pituitary, pituitary-regulate adrenals, thyroid, growth, ova and sperm, thyroidmetabolism, parathyroid-calcium, adrenal-adrenalin, pancreas-blood glucose, testes-testosterone, ovariesestrogen • How are they controlled? Negative feedback loops-when a lot is made, the gland stops making it, then too little, starts making it again-like with glucose and insulin Positive feedback-less common, production causes more production-oxytocin and childbirth Excretory System • What is the point? To get rid of wastes from metabolism • What parts are involved? Lungs (for CO2) Kidneys (urea) • How does it work? •Kidney has nephrons- is made of a Bowman’s capsule: tubules and capillaries • Fluid (filtrate) enters capsule •fuid passes through the tubule of the nephron, materials needed reabsorbed, remainder becomes urine. Skeletal/Muscular • What is the point? Structure and movement • How are bodies organized from small to big? Cells-tissues-organs-organ systems-organisms • What are the parts of a bone? Compact bone (outside), spongy bone (inside) bone Marrow (where blood cells made), and blood vessels • What are ligaments? Tendons? Ligaments-connect bone to bone, tendons-bone to muscle • What are the three types of muscles? 1. Smooth-organs, involuntary 2. Cardiac-heart, involuntary 3. Striated-arms, legs, voluntary • How do muscles contract? Actin slides across mysoin using ATP and calcium