* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Environmental, social and corporate governance wikipedia , lookup
Stock trader wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
History of investment banking in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis of 2007–2008 wikipedia , lookup
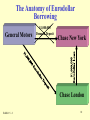
Financial crisis wikipedia , lookup
Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 15 Financial Innovation ©2000 South-Western College Publishing Financial Innovation •The creation of new financial instruments, markets, and institutions in the financial services industry •New ways for people to spend, save, and borrow funds •Changes in the operation and scope of activity by financial intermediaries 2 Glass-Steagall Act of 1933 •Banking legislation enacted in response to the Great Depression •Established Regulation Q ceilings •Separated commercial and investment banking •Created the FDIC 3 Regulation Q Interest rate ceilings on deposits at commercial banks established during the Great Depression and phased out after 1980 4 Fungible means... A characteristic referring to the ease with which a financial instrument can be converted to another 5 Disintermediation The removal of funds from a financial intermediary 6 The Reasons for Financial Innovation in the Past 35 Years Costs Fell Computer and telecommunications technology reduced the transactions costs of moving and monitoring funds Benefits Increased The rise in inflation and interest rates caused disintermediation and increased the profits of getting around certain regulations such as Regulation Q Increased global and domestic competition from other financial intermediaries increased the benefits of innovation to meet and beat the competition Increased volatility caused the development of innovations to hedge the risks of losses from increased uncertainty Exhibit 15 - 1 7 Nondeposit Liabilities Borrowed funds, such as Eurodollar borrowings, fed funds, and repurchase agreements, that are not deposits and not subject to reserve requirements 8 Regulation D A regulation that prescribed reserve requirements on some deposits 9 The Anatomy of Eurodollar Borrowing General Motors $1,000,000 Demand Deposit Chase New York Chase London Exhibit 15 - 2 10 Deregulation The dismantling of existing regulations 11 Depository Institutions Deregulation and Monetary Control Act of 1980 • Phased out Regulation Q • Established uniform and universal reserve requirements • Increased the assets and liabilities depository institutions could hold • Authorized NOW accounts • Suspended usury ceilings 12 Usury Ceilings Maximum interest rates that FIs are allowed to charge borrowers on certain types of loans 13 Universal Reserve Requirements Reserve requirements established by the Fed to which all depository institutions would be subject 14 Uniform Reserve Requirements The same reserve requirements across all depository institutions would apply to particular types of deposits 15 Garn-St. Germain Depository Institutions Act of 1982 Additional deregulation act that authorized money market deposit accounts and Super Now accounts 16 Reregulation Imposing new regulations in response to innovations that weakened existing regulations 17 Securitization •The process whereby relatively illiquid financial assets are packaged together and sold off to individual investors •Result in Pass-through Securities 18 Financial Market Changes in the 1990s Geographic barriers to deposit taking, loan granting and other services are reduced Banks are relying on fee income as their share of intermediation declines Fls are making extensive use of derivatives and other instruments to unbundle risks Fls are less specialized because of mergers with other financial services firms and because of engaging in other activities Financial Market Changes Fls and payment mechanisms are automated Interest rate ceilings are eliminated increasing competition and reducing profit margins Securitization is increasing and spreading from the mortgage market to many other markets Collateralized mortgage obligations allow prepayment risks to be different classes of bondholders 19 Exhibit 15 -2