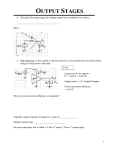
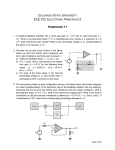
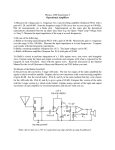
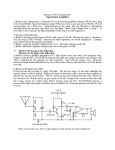
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Free Documents
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Subject Basic Electronic Devices Credits Branch El, EC, EE Code EC Sem I UNIT Introduction to semiconductor physics Crystalline solids, Band theory of solids, Insulators, Semiconductors and Metals. UNIT Transport phenomenon in semiconductors Mobility and conductivity, Electron and holes in an intrinsic semiconductor, Donor and acceptor impurities, Charge densities in a semiconductor, The Hall effect, Conductivity modulation, Generation and recombination of charges. Diffusion, Injectedminority carrier charges. UNIT Junction diode characteristics The open circuited pn junction, The pn junction as an rectifier, Form factor, Average voltage and current, Half wave and full wave rectifier, The current components in a pn junction diode, The VoltAmpere Characteristics, The temperature dependence of the V/I characteristics, Diode resistance, Space charge or Transition, Capacitance C, Charge control description of the diode, Diffusion capacitance, Junction diode switching times, Zener diode and its application. Bipolar Junction Transistor The junction transistor, Transistor configuration CE, CC and CB currentvoltage characteristics. UNIT Introduction to vacuum tubes Diodes, Triodes and Introduction to CRT Text books . Integrated Electronics, Analog and Digital circuit and system Miliman amp Halkias TMH N. Delhi . Electronic Principles Malvino TMH N. Delhi Subject Electromagnetic Theory Credits Branch EC, El, EE Code EC Sem III UNIT Elements of Vector calculus Coordinate system, differential volume, surface amp line elements, gradient, divergence, curl and deloperator. UNIT Review of static electric field Coulombs Law, Electric fieldintensity, electric flux and flux density, Gausss Law, Conservative properties of electrostatic field, Electric potential, Energy and work in electric field, Current, current density and conductor capacitance amp dielectric materials, Polarization relative permittivity, Multiple dielectric capacitors, Energy stored in a capacitor. UNIT Review of magnetic field Faradays Law, Lenzs Law, Biot savarts Law, Amperes Law, Magnetic flux density, Vector Magnetic potential, Stokes theorem, Magnetic force, Displacement current, Self, Internal and Mutual Inductance. UNIT Maxwells, Laplaces and Poissons Equation and Boundary conditions Introduction and its applications. UNIT Electromagnetic waves Introduction and solutions for partially conducting perfect dielectric and good conductor mediums, Skin depth, Interface conditions at normal incidence, Oblique incidence and Snells laws, Perpendicular and Parallel Polarization, Standing wave, Power and the Pointing vector. UNIT Transmission Lines Wave equation for ideal Transmission line, Characteristic impedance, Propagation amp Reflection, VSWR, Impedance, Transformation, Smith Chart, Parallel and Coaxial Transmission lines, Impedance Matching Single and double stub matching, Impedance measurement, Motion of charged particles in an Electric amp Magnetic Field. Text books . Electromagnetic John D. Kraus . Schaums outline series on Electromagnetic Joseph A. Edinister Mc Graw Hill Inc. . Engineering Electromagnetic Haytt, Kemmerly. . Electromagnetic wave and radiating system Jordan, Balmain . Engineering Electromagnetic William Haytt. The heat developed in a current carrying conductors. Hall effect amp carrier density. The atomic interpretation of the dielectric constant of nonatomic gases. Qualitative amp quantitative analysis of the dielectric constant of nonatomic gases. Diamagnetism. Antiferromagnetic materials. III UNIT. The internal fields in solids amp liquids.Magnetic properties of materials Classification of magnetic materials. Nature of the chemical bond amp classification of solids. Some properties of ferroelectric materials.Behavior of dielectrics in alternating fields Frequency dependence of the electronic polarizability. UNIT.Subject Electronic Engineering Materials Credits Branch EC amp EI Code EC Sem. The energy gap. UNIT. Electron scattering amp resistivity of metals. The density of carriers in intrinsic semiconductors. The electron configuration of atoms. Spontaneous polarization. Qualitative amp quantitative analysis of the dielectric constant of poly atomic molecules. Nomenclature pertaining to electronic states. UNIT.Dielectric properties of insulators in static fields Polarization amp dielectric constant. The origin of permanent magnetic dipoles in matters.The conductivity of metals Relaxation time. UNIT. Ferrimagnetic materials. Some properties of ferromagnetic materials. Superconductivity.The mechanism of conduction in semiconductors Classifying materials as semiconductors. Paramagnetic spin systems. Dielectric losses. UNIT. Conductivity. Electrical Engineering Materials A. Ionic polarization as a function of frequency. Text book . The chemical bond in Si amp Ge and its consequences. Dielectric relaxation. Piezoelectricity.J. The thermal conductivity of metals. The static dielectric constant of solids. Collision time amp mean free path.Atoms amp aggregates of atoms Introduction. Dekkar . HTL. Implementation of Boolean function with multiplexer and decoder. QuineMcCluskey Tabulation Method. DTL. D. CMOS. Encoder. EE. MCA Code EC. Counter with unused states. ROM. Asynchronous Sequential logic circuit. Error detection. Theorems and their properties. UNIT Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates Basic of Boolean Algebra and logic operations. Dual slope.Subject Digital Electronics Credits Branch EC. Totem pole and Open collector concept. Counter Asynchronous Counter/Ripple Counter Binary up amp down counter. Triggering of FlipFlop. Synchronous counter. Variable entered mappingVEM. EI. SR. Dontcare condition. Floatingpoint representation. MOS. PLD. ECL. Error correction. Code convertor BCD. PLA. Number system. Parallel adder/substractor. NAND and NOR implementation amp other minimization method. Plotting amp Reading Theory. D latch. Master Slave. Flipflops JK. A/D converter Ramp type. Decoder. D/A Converter Weighted register. Successive approximation and Flash type. Number base conversion. Logic Gates Basic. Characteristics table. UNIT Registers and Counters Loading of register. Jain . Analysis of Synchronous Sequential Circuit. KMap method upto six variables. IL. Gray. UNIT Combinational Circuits Design of combinational logic circuit using different chips/gates. Multiplexer. State reduction techniques. TTL. A/D amp D/A Converter RTL. POS and SOP simplification. segment decoder/driver. UNIT Logic Families. ExOR amp ExNOR Gate. Look ahead carry generator. Design steps for sequential circuits State diagram. Modern digital electronics R. Johnson counter. Ring counter. DeMultiplexers. Complements. UNIT Sequential Logic Circuit Latches RS Latch. truth table. CSIT. Alphanumeric codes. UNIT Minimization Techniques Canonical and Standard form. Comparison of logic families. Excessthree. Full and Half adder/substractor.P. Parity bit checker/generator. Sem IV UNIT Digital Numbers and Codes Introduction to digital system. Racearound condition. Concept of Flipflop conversion. Universal. RR Ladder. Text books . T. Codes Weighted amp Nonweighted binary code. Morris Mano . Digital logic and computer design M. Divide by N counter. Frequency convolution theorem. Dirac delta function amp its properties. Sampling function. Types of signals. Normal and Gaussian distribution. EI. Graphical amp analytical methods of convolution. Lathi . Nyquist rate amp Nyquist interval. Band pass filters. Digital communication systems Taub amp Schilling . Energy amp Power spectral densities of signals. Amplitude. Fourier Transform of some useful functions. Digital principles and application Malvino amp Leach . Time invariant amp LTI system. Natural sampling. CDF and their properties. UNIT Convolution of signals. Communication systems Simon Haykins . Filter characteristics of linear systems. CS amp EE Code EC Sem IV UNIT Fourier analysis of signals. Orthogonality of functions. Time convolution theorem.. Auto correlation. Communication systems Singh amp Sapre . Low pass filters. Cross correlation. Recovery from sampled signal. Impulse response. Phase amp Power spectrum. Text books . Modern Digital amp Analog System B. Causal systems. Band stop filters. Flat top sampling. Fundamental of digital electronics Barttee Subject Signal amp Systems Credits Branch EC. UNT Systems amp Filters Linear system. Laplace Transform of some useful functions. Aliasing. Sampling theorem time domain amp frequency domain. Singularity functions amp its properties. PDF. Aperture effect. P. UNIT Random variables and probability theory. UNIT Power amp Energy signals. High pass filters. Foster seely discriminators. Double tuned discriminators. noise figure. S/N in DSBSC receiver. Principles of communication system Taub amp Shilling . Communication system Simon Haykin . Communication systems B. SSBSC. Unit Demodulation of FM or frequency discriminators Single tuned discriminators. Frequency modulation amp phase modulation DSBAM. S/N in SSBSC receiver. Unit Noise SNR signal to noise ratio. EI Code EC Sem V Unit Modulation process Definition of amplitude modulation.Subject Analog Communication Systems Credits Branch EC. Text books . Communication system Singh amp Sapre .e. Armstrong method of frequency modulation. Direct method of FM reactance modulator Unit Demodulation I detection process Demodulation of AM waves Diode detection Average detection and Envelope detection. Superhetrodyne receiver. DSBSCAM.Lathi .P. preemphasis and deemphasis. using linear modulation and nonlinear modulation. Unit Linear modulation Collector modulator or Plate modulator and Base modulator. Ratio detectors and phase locked loop PLL demodulator. noise temperature of a cascaded system. Unit Generation of frequency modulation Indirect method of FM i. Principles of communication George Kennedy . S/N in FM receiver. Unit Nonlinear modulation Balanced modulator amp Ring modulator. Maxwell equation. Electromagnetic wave equation in dielectrics and conductors. smart antenna. field from oscillating dipole. Radio frequency band.Subject Antenna amp Wave propagation Credits Branch EC Code EC. beam efficiency. plasma antenna . sky wave propagation. Reflector antenna. Radiation of dipole of finite length. Terahertz antenna. Radiation pattern. Wide band antenna. Typical sources of errors in antenna measurements. Gain. Phase front. Antenna D. polarization.embedded antenna Unit Antenna Measurement Introduction. Ground or surface wave propagation. Unit Fundamental of Antenna Basic antenna parameter. Helical antenna. effective height. Sem V Unit Introduction Antenna fundamental and definition. Radiation from elementary source. Kraus TMH . Antenna Engineering Rajeshwari . beam area. Antenna J. Tropospheric scatter propagation Text books . Boundary condition in electromagnetic field. antennas field zones. slot and micro strip antenna. space wave propagation. Basic concept. directivity. Horn antenna. Lens antenna. Measurements of different antenna parameters Input and mutual impedance. Antenna Fusco Pearson Education . Loop antenna. Unit Theory of Radio wave radiation and reception Current across closed surface. antenna aperature. Biconical antenna. Polarization. radiation intensity. patterns. The influence of the earth and metal bodies on antenna radiation.Pozar PHI . Unit Types of Antenna devices Thin linear Antenna. cylindrical antenna. Unit Radio Wave Propagation Propagation characteristics of electromagnetic wave. Electromagnetic spectrum.D. frequency independent antenna. DC supply. Composite video signal. TV channel. High fidelity Audio system. Block diagram of TV transmitter. Synchronization. Black amp white TV Rx. LCD tunes with alarm. Colour TV signal. Inverter. Cellular telephone. Stereo sound system.Subject Consumer Electronics Credits Branch EC. CCTV. HDTV. Radio and TV Transmission amp Reception. An electronic guessing game. Decorative Lighting. Block diagram of VCR. Audio signal modulation. Battery telephone. CCTRB System. Monochrome picture tube. Audio compact disc system. Unit Miscellaneous Devices Digital watch. Bandwidth of TV signal. VHS.R. Cable TV. Block diagram of TV receiver. Tape transport mechanism. Persistence of vision. Tape recorder. Feeder cable. scanning. Colour TV Rx. public address system. UPS. Cordless Telephone. TV camera tube. study of VCD amp DVD. EI Code EC Sem V Unit Audio System Microphones. Gupta . loudspeaker. compatibility. PAL signal. Unit Video Cassette Recorder VCR Principle of video recording on magnetic tapes. Microwave oven. Battery charger. Text books . Consumer Electronics B. Balun T/F. Mobile telephone. Calculators. Television studies and Equipment. magnetic sound recording. DC supply operational amplifier. Television Rx antenna. Battery Eliminator. Antenna for TV transmitter. IC regulator. Unit Television Introduction. ShannonFano. EI Code EC Sem VI UNIT Introduction to Digital Communication. Different Signals. ASK. Reception of signals.Glover . Hamming distance. Quantization error. Adaptive Delta Modulation. Digital Modulation Techniques BPSK. Sampling process. Optimum filter and matched filter. Error correcting code. Error control code. PCM. PCM Building blocks. Entropy. Signal recovery through holding. Coding efficiency.A. UNIT Information Theory. Convolutional codes. Communication System Taub amp Schilling . Companding.Subject Digital Communication System Credits Branch EC. Communication Systems Simon Haykins . T Digital System. Text books . Line Coding. ASK. Transfer functions calculation. UNIT Quantization of signals. Block codes. Multiplexing PCM Signals. PAM. Integrator Response. DPSK. UNIT Delta Modulation. Bandwidth S/N tradeoff. Slope Overloading. Probability of error calculation for matched filter. Principles of Communication George Kennedy . Natural amp Flat Top samplings. Expansion. Equalization. Linear block code. Aperture effect. Noise calculation in PCM amp DM System. Transmitter amp Receiver. Conditional and Joint entropy schemes. Coding techniques. Noise free channel. Correlation reception of signals. Bit rate. Capacity of Gaussian channel. Cyclic code. BEC channel. Binary. Probability of error of Different Modulation Techniques. Absolute. Rate of information. Digital Communication I. Channel with independent input amp output channel capacity. DPCM. Electronics Communication Dennis Reddy amp John Cooten . Shannon Hartley theorem. QPSK. Binary symmetric channel. Channel BW for PAM signals. UNIT Data Transmission. Huffman coding. Mutual information. Basic building blocks. Communication System Singh amp Sapre . principles. design of FIR filter. EE amp CSIT Code EC Sem VI UNIT Discrete time signals amp systems Discretetime signals. design of IIR filters from analog filters.Proakis amp Dimitris G. UNIT Design of digital filters General considerations. One sided Z transform. Inversion of Ztransform. UNIT Implementation of discretetime systems Structures of the realization of discretetime systems. Properties of Discrete Fourier transform. Linear filtering methods based on DFT. Analysis of discretetime linear systeminvariant systems. Manolakis PHI . Digital signal processing Alan V. Application of FFT algorithms. UNIT Discrete Fourier transforms Its properties amp applications Discrete Fourier Transform. algorithms and applications John G. Digital signal processing. Structures of FIR systems. Structures of IIR systems.Schafer . discrete time systems. Properties of Ztransform. Introduction to digital system processing Roman Kuc Mc Graw Hill International Editions . UNIT Efficient computation of the DFT Fast Fourier Transform FFT algorithms.Subject Digital Signal Processing Credits Branch EC. UNIT The Ztransform The Ztransform. Text books . El. Oppenheim amp Ronald W. Photo resist. Xray masks. Xray sources.S. UNIT Metallization Vacuum evapouration amp Cathode sputtering. V. NMOS.M. . V. CMOS.Botkar Khanna Publisher . Silicon processing. Integrated Electronics K. Electron beam lithography Resists. Processing technology. Doping processes Diffusion amp Ion implantation.S. electron optics. UNIT Oxidation.L. Printing techniques. Design Analog amp Digital Technique Geiger Publisher McGraw Hill .S.R. Technique S. Molecular beam epitaxy. UNIT Fabrication process sequence for Bipolar. Xray lithography Xray resist.L. Photo etching. printing techniques. Text books .Subject Microelectronics Credits Branch EC Code EC Sem VI UNIT Introduction to monolithic silicon integrated circuits. Comparison of various lithographys. Synchrotron radiation.I. UNIT Photolithography Photo mask fabrication.I.Publisher McGraw Hill. Crystal growth. Etching Processes Wet etching amp Dry etching or Plazma etching. Ion beam lithography. Isolation techniques pn junction isolation amp dielectric isolation. Reactive plazma etching apparatus. Vapour phase epitaxy. Chemical vapour deposition. Range and precision of Standard Loran .The Goniometer .Recent Developments.Solid State RF Power Sources .Pulse Doppler Radar Other Doppler Radar Topics.The Omega .Other Tracking Radar Topics Comparison of Trackers . Hyperbolic Systems of Navigation Loran and Decca .Range and Accuracy of Direction Finders Radio Ranges .Automatic Tracking with SurveillanceRadarsADT.Four methods of Navigation Radio Direction Finding .Tracking with Radar Monopulse Tracking Conical Scan and Sequential Lobing .Subject RADAR and Navigational Aids Credits Branch EC Unit Introduction to RADAR Code EC Sem VI Basic Radar The simple form of the Radar Equation.Adcock Direction Finders .Detection of Signals in Noise.FrequencyScan Arrays Radar Transmitters.Duplexers and Receiver Protectors.The Radar Antenna .Decca Receivers .Nonstandard Propagation .Receiver Noise and the SignaltoNoise RatioProbability Density FunctionsProbabilities of Detection and False Alarm.LoranC .Delay Line Cancelers.Other aspects of Radar Transmitter.VOR Receiving Equipment Range and Accuracy of VOR .ConstantFalseAlarm Rate Receivers . Unit MTI and Pulse Doppler Radar Introduction to Doppler and MTI Radar.Introduction Linear Beam Power Tubes .Radar Cross Section of Targets.An Aural Null Direction Finder .The Commutated Aerial Direction Finder .Transmitter PowerPulse Repetition FrequencyAntenna ParametersSystem losses Other Radar Equation Considerations.VHF Omni Directional RangeVOR .LoranA .MTI from a Moving Platform AMIT .Limitations to Tracking Accuracy .The LF/MF Four course Radio Range .Digital MTI Processing .Radar Displays.Moving Target Detector Limitations to MTI Performance .Direction Finding at Very High Frequencies .Receiver noise Figure .The Radar Receiver .Signal Management Propagation Radar Waves .LowAngle Tracking .Radar Block Diagram.Phase Shifters .The Decca Navigation System .Errors in Direction Finding .Electronically Steered Phased Array Antennas .The Radar operator . Unit Introduction . Unit Detection of Signals in Noise Introduction Matched Filter Receiver Detection Criteria Detectors Automatic Detector Integrators .Superheterodyne Receiver .Automatic Direction Finders .Loop Input Circuits .Reflector Antennas .Crossed Field Amplifiers Other RF Power Sources .Atmospheric Refraction Standard propagation .Tracking in Range .The Loop Antenna .Integration of Radar Pulses.Magnetron .Range and Accuracy of Decca .Staggered Pulse Repetition Frequencies Doppler Filter Banks .Radar cross Section Fluctuations.Radar Frequencies Applications of Radar The Origins of Radar The Radar Equation Introduction.LoranA Equipment . Radar Receivers . TACAN Equipment.Doppler Spectrum Components of the Doppler Navigation System . Skolnik TMH .Earth Coordinate Mechanization .Ground Controlled Approach System . Satellite Navigation System . Aids to Approach and Landing .System.Navigation Over the Earth Components of an Inertial Navigation System .Track Stabilization .Navstar Global Positioning System GPS Text books .StrappedDown Systems .Accuracy of Inertial Navigation Systems.TACAN . Introduction to Radar Systems Merrill I.Principles of Operation .Doppler range Equation .Microwave Landing SystemMLS Doppler Navigation .Operation of DME .Distance Measuring Equipment .Instrument Landing System .Accuracy of Doppler Navigation Systems.Beam Configurations Doppler Frequency Equations . Unit DME and TACAN .The Doppler Effect . Inertial Navigation . Navigation Nagrajan .The Transit System . Asynchronous Analysis. UNIT Sequential Machine Fundamentals The Need for Sequential Circuits. Shift Register Sequences. Basic Architectural Distinctions between Combinational and Sequential Circuits. Approaches to the Design of Synchronous Sequential Finite State Machines. VEM Reading theory. The Binary Cell. Scope. The Design of Asynchronous Machines. An Engineering Approach to Digital Design William I. Types of Modeling and Fundamental to VHDL Programming Text books .Subject Digital System Design Credits Branch EC Code EC. Digital Design Morris Mano PHI . VariableEntered Mapping. UNIT Asynchronous Finite State Machines Why Asynchronous Circuits. UNIT Introduction to VHDL Introduction to Hardware Descriptive Languages. Fundamental Differences between Sequential Machines. Design Steps for Traditional Synchronous Sequential Circuits. State Reduction. Five and Six Variable Maps. VEM Plotting Theory. Prime and Essential Implicants. The Karnaugh Map. FlipFlop Conversion from one type to another. Tabulation Method. The FlipFlop. Sem VII UNIT Digital Design Fundamentals amp Design of Combinational Circuits Hardware Aspects Related to ASSERTED and NOTASSERTED conditions. Analysis of Synchronous Sequential Circuits. Shift Register. Fletcher PHI . Concept of Memory. Counters. UNIT Traditional Approaches to Sequential Analysis and Design Introduction. Basic NMOS NOR logic circuit. . other shift register. VLSI Design amp circuits Geige Publisher Mc. Sizing. Dynamic MOS storage circuit. Multi input NAND amp NOR logic circuit. Decode and selector circuit. Select time delay calculation. Static RAM. Super buffer NMOS NAND and NOR delay. CMOS inverter logic levels. Clock CMOS logic. Storage cell. CMOS noise margin. EPROM. NMOS pass transistor. CMOS NOR logic gate. UNIT Structured gate layout. Memory organization. Philip E. CMOS logic delay. VLSI Design Puknill . Depletion MOS Transistor. Logic fan out delay. UNIT Semiconductor memory. Capacitive noise coupling. NMOS power dissipation. NMOS noise margin. Graw Hill .Allen amp Noel R. Basic inverter device. Capacitive loading. Interconnection characteristics. Resistive noise coupling. Basic NMOS NAND logic circuit. Evalute logic.Subject VLSI Design amp Circuits Credits Branch EC Code EC Sem VII UNIT MOS transistor. CMOS NAND logic gate. Enhancement load verses load inverters. UNIT Ratio logic model. Sense amplifier. CMOS Transmission gate.Starder. Distributive drivers. ROM design. Enhancement MOS Transistor. VLSI Design amp circuits Shoji . Stick rules amp diagrams. Domino CMOS. Text books . Simple shift register. Process characteristics time constant. Inverter pair delay. Optimum precharge voltage concept. Design technique for Analog and Digital circuits L. Dynamic RAM cell. Enhancement v/s depletion load.Geizer. EEPROM. Inverter device sizing. Logic gate arrays. CMOS power dissipation. Multiinput CMOS logic gate. UNIT A basic CMOS inverter. Photo transmitter. Demodulation schemes. Semiconductor photodiode. Intrinsic amp Extrinsic absorption. UNIT. VII UNIT. Optical detection principles.Applications and future developments Military applications.Transmission Characteristics of optical fibers Attenuation.Optical fiber systems Basic system. Fiber attenuation measurements. Injection LASER characteristics. Acceptance angle. Public network application. Skew rays. The general system. UNIT. UNIT. Modulation formats. Optical emission from semiconductors. Intrinsic absorption.Optical fiber waveguides Total internal reflection. Advantage of optical fiber communication. Fluoride glass fibers. Computer applications. Linear amp nonlinear scattering. Photo conductive detectors. Local area networks.Optical fibers and cables Preparation of optical fibers. Medical applications. UNIT. Optical receiver. Mie scattering.Optical sources LASER. Stimulated Brillouin scattering. Step index fibers. UNIT. Phase and group velocity. Senior PHI . LED characteristics.Subject Optical Fiber Communication Code EC Credits Branch EC Sem. Optical fiber cable. Graded index fibers. Optical fiber communication Keiser Publisher Mc. Midinfrared photo diodes. Reflection and optical return loss.Optical detectors Device types.Chand amp Company Ltd . Optical fiber communication John M.Introduction Historical development. UNIT. Quantum efficiency. Graw Hill . Optical transmitter. Liquid phase melting techniques. Numerical aperture. Vapour phase deposition techniques. Modes in planer guides. Stimulated Raman scattering. Mid infrared and far infrared transmission. Cylindrical fiber Modes. Optical fiber. Dispersion. Mode coupling. Optical fibers and fiber optic communication systems Subir Kumar Sarkar Publisher S. Optical power budgeting. Stability of the fiber transmission characteristics. Modulation. UNIT. UNIT. Fiber bend loss. Basic concepts of LASER. Rayleigh scattering.Optical Fiber Measurements Fiber numerical aperture measurements. Text Book . Field measurement. V. Interaction b/w electron and fields. Transmission line parameters. Megnetron. MFETs. Smith chart. Waveguide junctions. MMICs. Isolators and circulators. Optical communication systems J. Trapatt diode. Attenuators. Mitatt diode. slotted line.K. Text books . Unit Semiconductor Microwave Devices amp Integrated circuits Parametric amplifier. Jain Publisher Narosa publishing house Subject Microwave Engineering Credits Code EC. Peniotron. Windows. Low frequency v/s Microwaves frequency. Waveguide Rectangular and circular. Rotating joints. Strip lines and micro strip lines . Unit Microwave Measurements Network analysis. Klystron. Collin . Unit Transmission Media. Gun diode. Microwave power measurements. Barritt diode. Microwave Engineering Annapurna Das Sisir K Das .quarter wave transformer. PIN diode. Gyrotron.E. CFA. Cavity Resonators. Transmission line and Waveguides Transmission line propagation modes. Spectrum analysis. TWT. Scattering matrix. Comparison of microwave tubes. Microwave Engineering Lio . and Frequency counter. Directional couplers. Hybrid ring. Unit Microwave Components Coupling probes and loops. Microwave Engineering DPozar . Noise measurements. Microwave signal propagation. Microwave Engineering R. Tunnel diode. Advantages and application of microwave.. Sem VII Branch EC Unit Introduction to Microwave Microwave. Franz. Impact diode. Wave meters. microwave filters Unit Microwave Tubes Limitation of gridded tubes at high frequency. BWO. Phase shifters. Waveguide flanges. Mathematical analysis of propagation modes and cutoff wavelength. Directive gain. UNIT. Prasad . half wave dipole. Pointing vector amp power flow. UNIT. Effective height amp radiation resistance. Bionomial array. Text books .Subject Antenna Engineering Credits Branch EI Code EI Sem. Keith G. Short monopole. Antenna parameters. Antenna aperture. Helical antenna. Turnstile antenna. Power gain. Jordan.Elements of Antenna Theory Antenna action. Antennas J D Kraus . Loop amp Bicanonical antenna. Rhombic antenna. Electromagnetic Waves amp radiating system Edward C. Gain.Antenna measurements Effective area. Power amp field pattern. Log periodic antenna and Parabolic reflectors. Antenna resistance and its efficiency. Radiation from a short dipole.Antenna arrays Two element array Broad side array. UNIT. Total resistance of Ariel. Antenna amp Wave propagation K.Types of antennas Folded dipole. Hertizen dipole. Balmain . Chebyshev array and YagiUda array. end fire array. Linear arrays multiplication of patterns. VII UNIT. D. Inverse Filtering. Transform frequency. Components of an Image Processing System.Subject Digital Image Processing Credits Branch EC Code EC. Cosine transform. Jain . Description and Recognition Introduction of Image Representation amp Description. Digital Image Processing Rafael C. Some Basic Morphological Algorithms. Noise Models. RegionBased Segmentation. Optimum transform. Detection of Discontinuities. UNIT Image Representation. Opening and Closing. Some Basic Relationships Between Pixels. UNIT Image Restoration and Image Compression A Model of Image Degradation/Restoration Process. Histogram Processing. Fundamental of Image Compression. Lossy Compression. Regional Descriptors. KL transforms and their properties. UNIT Image Morphology and Image Segmentation Introduction of Morphological Image Processing. UNIT Image Transform Orthogonal and unitary transforms. Minimum Mean Square Error Wiener Filtering. The HitsorMiss Transformation. Slant transform. DFT. Harr transform. Fundamental steps in Digital Image Processing. Sharpening Frequency Domain Filters. Properties of unitary transforms. Sine transform. Filtering in the Frequency Domain. Origins of Digital Image Processing and its Applications. Some Basic Level Transformations. Sem VIII UNIT Digital Image Processing Fundamentals amp Image Enhancement Introduction of Digital Image Processing. Woods . Boundary Descriptors. Edge Linking and Boundary Detection. Dilation and Erosion. Smoothing Spatial Filters. Dimensional and two Dimensional. Sharpening Spatial Filters. Digital Image Processing Anil Kr. Thresholding. Text books . ErrorFree Compression.Gonzalez amp Richard E. Hadamard transform. Object Recognition. Image Compression Models. Brief History of Satellite Communication. Basic antenna theory. Eclipse effect. Antenna noise temperature.Subject Satellite Communication Credits Branch EC Code EC. George Kennedy . Current State of Satellite Communication. Agarwal . Power systems. Electronic Communication System. Range variation. Space qualification. Orbit determination. Attitude and orbit control system. Describing the orbit. Orbital effects in Communication system performance Doppler Shift. TDM system. Digital transmission of voice. Design of small earth station antennas. Uplink design. Orbital Perturbations Effects of earths oblateness. Bostian. Locating the satellite in the orbit. Satellite Communication Timothy Pratt amp Charles W. Text books . Transponders. UNIT Earth station technology Earth station design for low system noise temperature. UNIT Orbital Aspects of Satellite Communication The equations of the orbit. Sem VIII UNIT Introduction Origin of Satellite Communication. Satellite Communication D. . Orbital elements. Large earth station antennas. Locating the satellite with respect to the earth. Sun transit outage. Effects of sun amp moon. UNIT Spacecraft Space craft subsystems. Design of downlinks. Telemetry tracking and command. UNIT Modulation and multiplex techniques for satellite links Analog television transmission. FDM system.C. UNIT Satellite link design Basic transmission theory. System noise temperature and G/T ratio. outdoor and indoor propagation models. IS CDMA Vijay K Garg . TDMA. Wireless Communication Theodore S Rappaport . Text books . comparison of various wireless comm. handoff strategies . third and fourth generation wireless networks. WLAN. Systems. maximal ratio combiner. cordless telephone systems. multipath fading frequency dispersive. Comparison of various multiple access techniques. Mary FSK. channel assignment . examples of wireless comm. paging systems. QPSK. Unit Digital modulation techniques for wireless communication Performance analysis of BPSK. delay spread and coherence band with Unit Diversity and basic Combining methods Diversity and types of Diversity time Diversity. DPSK. modern wireless communication systems second. systems. PAN. Bluetooth. digital cellular systems. Unit Introduction to cellular mobile systems Spectrum allocation. WLL. frequency reuse. capacity of cellular systems Unit Multiple Access Techniques Introduction to multiple access techniques FDMA. equal gain combiner. frequency Diversity. OFDM for Wireless transmission. MSK. Communication Systems Simon Haykins . freespace propagation model. CDMA. Performance of CDMA systems. antenna Diversity. operation of cellular systems. Unit Fading Propagation path loss. time dispersive and frequency dispersive channels. Combining methods selection combiner.performance criteria. QAM. RAKE receiver. analog cellular systems.Subject Mobile Communication Credits Branch EC Code EC Sem VIII Unit Introduction to wireless communication Evolution of mobile radio communication. basic cellular systems . UNIT Output system with continuous actuators. . architecture. Operator interface. Family of PCs. UNIT Signals. Digital signal conditioning. Backplane bus. Computer languages. Hardware and software of personal computers Sanjay K Bose. Brey . UNIT Low cost multifunctional DA and C card. The Intel microprocessors. UNIT Plugincards. IEEE GPIB. Chidambaram. Input/output devices. Computer control of processes M. Interfacing input signals. . Basic I/O interface. Microprocessor. Parallel I/O ports. VME bus. Analog signal conditioning. Programming and interfacing Barry B. PCI bus. Timing circuits. Motherboard.Hall. Personal computer. Interfacing to the IBM personal computer Lewis C Eggerbrecht SAMS Publication . Plug in slots. Serial I/O ports. SCXI. Text books . Analog to digital converters.Subject PC Interfacing Credits Branch EC Code EC Sem VIII UNIT Introduction to computer. UNIT Communication with external devices. Cabling. Input signal buffering and amplification. Microprocessors and interfacing programming and Hardware Douglas V. Standard addoncards. VXI bus microcontrollers. Software from transducer to control room. Operating system. . The memory. Electromechanical relay. UNIT Computer interfacing for data acquisition and control. Digital to analog converter. Programmability and Program Execution. Interrupts of TMSOCXX processors. Chand amp Co. . Architectures amp Features Lapsley et al. Unit Computational accuracy in DSP implementations Number formats for signals and coefficients in DSP systems. Branching effects. Unit Execution control and pipelining Hardware looping. Relative Branch support. Unit Interfacing memory and I/O peripherals to programmable DSP devices Memory space organization. Venkata Ramani and M. D/A Conversion Errors. Programming and Applications B. Digital filters. Digital Signal Processors. and Pipeline Programming models. Interpolation Filters. S. A/D Conversion errors. . Text books . Program Control. Address Generation Unit. Srinivasan. Dynamic Range and Precision. . Programmed I/O. Features for External interfacing. DSP Computational Building Blocks. FIR Filters. Memory interface. Parallel I/O interface. DSP Computational errors. . Stacks. Decimation Filters. DSP Processor Fundamentals. Pipeline Depth. Digital Signal Processing Avtar Singh and S. Digital Signal Processing Jonatham Stein. Pipeline Operation of TMSOCXX Processors. linear timeinvariant systems. . A Digital signalprocessing system. Discrete Fourier Transform DFT and Fast Fourier Transform FFT. Data Addressing Capabilities. Sources of error in DSP implementations. Architecture. Decimation and interpolation. Bhaskar. . Bus Architecture and Memory. Unit Programmable digital signal processors Commercial Digital signalprocessing Devices. IIR Filters. Pipelining and Performance. John Wiley. PID Controller. D Signal Processing. TMSOCSXX instructions and Programming. OnChip Peripherals. Interlocking. Compensating filter. Unit Architectures for programmable DSP devices Basic Architectural features. Interrupts. Direct memory access DMA. Interrupts and I/O. External bus interfacing signals. Discrete time sequences. TMH. . Adaptive Filters. Data Addressing modes of TMSOCXX Processors. The sampling process. Interrupt effects. Data Addressing modes of TMSOCXX DSPs. Speed Issues. Thomson Publications.Subject DSP Processors and Architecture Credits Branch EC Code EC Sem VIII Unit Introduction to digital signal processing Introduction. Unit Implementations of basic DSP algorithms The Qnotation. Memory space of TMSOCSXX Processors. On wafer Sparameter of active devices. UNIT MMIC process. UNIT Metal semiconductor functions and their characteristics.Subject Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuit Credits Branch EC UNIT History of Monolithic Integrated Circuits. UNIT Optical control of MMICs. Lumped and distributed passive elements. Sparameter General concept. Code EC Sem VIII UNIT Monolithic circuit components Planar transmission lines. UNIT Sparameter measurement and their use in GaAs MESFET circuit design. GaAs MESFET. Measurement of Sparameters of active devices. Sparameter in circuit design. Utilization. On wafer Sparameter measurements. Other active devices. . EI EC. EI. OF COPIES LIST OF SUBJECTS IN EVEN SEMESTER SR.Faculty of Engineering amp Technology M. Rohilkhand University. CS EC.EE EC.J. EI EC EC. Bareilly DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING LIST OF SUBJECTS IN ODD SEMESTER SR. YEAR I II II III III III III III IV IV IV IV IV SEM II IV IV VI VI VI VI VI VIII VIII VIII VIII VIII PAPER CODE EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC PAPER NAME Basic Electronics Devices Signals and Systems Digital Electronics Digital Signal Processing Digital Communication Systems Radar amp Navigational Aids Microelectronics Elements Of Communication Engineering Mobile Communication Satellite Communication Digital Image Processing Microwave Communication DSP Processors and Architecture BRANCH CH. ME. EI. YEAR II II III III III III IV IV IV IV SEM III III V V V V VII VII VII VII PAPER CODE EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC EC PAPER NAME Electronics Engineering Materials Electromagnetic Theory Analog Communication System Antenna and Wave Propagation Consumer Electronics Signals and Systems VLSI Design And Circuits Microwave Engineering Optical Fiber Communication Digital System Design BRANCH EC.P. CS EC. NO. NO.EI. EI EC EC EE EC EC Pool Elective Pool Elective Pool Elective NO. CS EC. EI EC.CS. OF COPIES . EI EE EC EC EC Pool Elective NO.