* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Road to World War II
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Kriegsmarine wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
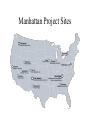
The Road to World War II The World Economic Conference: June 1933 • • • • Cause US leaves Gold Standard Failure Reciprocal Trade Agreements Act of 1934 Recognizing the Soviet Union • • • • Diplomatic Recognition “Socialism in One Country” Restrain Japan Roosevelt Litinov Accord: 1933 The Good Neighbor • Hoover drops Dollar Diplomacy • 7th International Conference of American States • Consultation • Cuba • Mexico • Reciprocation Neutrality and the Road to War • • • • • Morris Commission: 1934 1935 Neutrality Act 2nd 1935 Neutrality Act 1937 Neutrality Act: “Cash and Carry” Arming of the Chinese Rise of Fascism • Nationalist Disgruntlement + Faltering Economies • Mussolini (1922-43) • Adolph Hitler (1934-45) • Francisco Franco (1936-1975) Hitler and the Rise of Nazi Germany • • • • 1933: Hitler becomes Chancellor 1936: Remilitarization of the Rhineland 1937: The Axis forms 1938: Austria and Munich and the Sudetenland • Kristallnacht (October 28, 1938) World War II Begins • • • • • • Blitzkreig Invasion of Poland (September 1, 1939) Phony War Norway (Spring 1940) France falls (Summer 1940) Battle of Britain (Summer-Fall 1940) From Neutrality to Undeclared War, 1939-41 (I) • • • • • Pro-Neutral America: 85% oppose war September 1939: Declaration of Panama November 1939: Cash and Carry 1940: Destroyer deal 1940: FDR vs Wendell Wilkie, 27.3 to 22.3 million, 449 to 82 EV From Neutrality to Undeclared War, 1939-41 (II) • • • • Lend-Lease (March 1941) Submarine Warfare May 21, 1941: The Robin and Convoys Summer 1941: Into Russia The Atlantic Charter (August 1941) • 1. no territorial gains sought by the United States or the United Kingdom; • 2. territorial adjustments must conform to the people involved; • 3. the right to self-determination of peoples; • 4. trade barriers lowered; • 5. postwar disarmament; • 6. freedom from want and fear; • 7. freedom of the seas; • 8. an association of nations. Japan • Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere • 1931: Manchuria • 1937: Invasion of China – Rape of Nanking: 300,000 Chinese killed • 1939-41: US cuts off trade with Japan • December 7, 1941: Pearl Harbor Mobilization of Industry • America Under Attack: 1,662 ships lost in 1942 to Nazi subs • War Production Board • War Manpower Commission • War Labor Board • Office of Price Administration • 5 Million Women Go to Work • Migration The Citizen Army • 20 million Americans in military (344,000 in 1939) • Gis • Term of Service • Army Women: 350,000 • Indians: 25,000 – Code-Talkers Increased Spending • 321 billion dollars spent on war= Twice government spending from 1789 to 1941 • GNP + 75% • Prices up 32% • Higher Living Standard Manhattan Project Sites Manhattan Project • Starts in late 1941 • Entire SECRET towns created to house facilities: Oak Ridge, TN and Richland, WA • K-25 Purification Plant: 44 acres • Trinity, New Mexico: July 16, 1945 Home Experiences • • • • Prosperity Rationing Higher Incomes Discrimination: – Japanese: Internment Camps – Blacks suffer from racism, military segregation Entertainment • Film and Radio • Superheroes and the Rise of the Comic Book • Archie • Pulp Adventure • Science Fiction The Early War in the Pacific • Halsey’s Counterattack • Coral Sea (May 4-May 8, 1942) and Midway (June 4, 1942 to June 7, 1942) • Guadalcanal: August 7, 1942-February 1943 • Race Hatred The War in Europe: 1942-3 • Russian Front (1941-3) – Stalingrad (1942-3) • • • • Africa (1942) Italy (1943) Hitler’s Last Offensive in East (July 1943) Tehran Conference (Fall 1943) The War in Europe: 1944 • Russians Push West • Bombing • D-Day: June 6, 1944--Operation OVERLORD • Balkans • Battle of the Bulge (December 16, 1944December 26, 1944) • Discovery of the Holocaust War in the Pacific • Two Pronged Strategy: Island Hopping (Navy) and Guineas--Solomons--Indonesia-Phillipines (Army) • Battle of the Philippine Sea (June 19 and June 20, 1944) Battle of Leyte Gulf • MacArthur Lands in Philippines: 10-8-44 • Battle of Leyte Gulf: 23 October to 26 October 1944-Largest in Naval History • US: 17 aircraft carriers, 18 escort carriers, 12 battleships, 24 cruisers, 141 destroyers, Many other ships, PT boats, and submarines, About 1,500 planes. US loses 3,500 dead; 1 light aircraft carrier, 2 escort carriers, 3 destroyers sunk • Japan: 4 aircraft carriers, 9 battleships, 19 cruisers, 34 destroyers, About 200 planes. 10,000 dead; 4 aircraft carriers, 3 battleships, 8 cruisers, 12 destroyers sunk Iwo Jima • • • • February, 1945 4200 marines killed, 15,000 wounded bloodiest battle in Marines history Iconic Image Yalta • 1944: Roosevelt defeats Dewey • February 1945: Yalta – – – – – Roosevelt: Wants Russia vs. Japan Churchill: Money and enlarge empire Stalin: Buffer zone in Europe Partition of Germany Planned Russia agrees to help vs. Japan once Europe is done Trinity Test Site War’s End • • • • • Fall of Okinawa (April 1945) April 12, 1945: Roosevelt dies April 27, 1945: Hitler’s suicide May 7, 1945: German Surrender August 1945: Dropping of the Atomic Bombs at Hiroshima and Nagasaki • 6: Hiroshima • 9: Nagasaki • 10: Japan surrenders. Total Casualties – Americans • Killed: 292,000 • Prisoners of War: 100,000 • Wounded: 691,000 – Global: • Total Dead: 72,155,800 – Military: 25,037,500 – Civilian: 41,363,400 – Jewish Holocaust Deaths: 5,754,400 Why Allied Victory? • • • • • Superior Production Control of Raw Materials Superior Manpower Technology Superior Appeal