* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II – Victory for the United Nations (1939
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Britain (film) wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
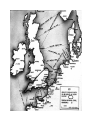
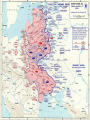
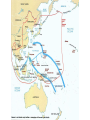
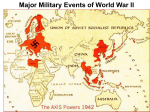
WWII divided into two periods • 1939-1942 – Hitler and Axis Domination • 1943-1945 Allies on the Offensive Major Turning Points during WWII • • • • Stalingrad, November, 1942 El Alamein, Summer 1942 Battle of the Coral Sea, May 1942 Midway, June, July 1943 World War II – Victory for the United Nations (1939-1945) • May 1940, France out of the War – Vichy France • Battle of Britain – an obvious strategy would have been for a landing, but the Germans had made no preparations for amphibious warfare • The decision was then made by Hitler and Air Marshall Goring to do the job solely with air power Two Main Phases to the Battle of Britain • August and September 1940, daylight bombing raids to wipe out merchant convoys, airports and fighter planes • Almost a success for the Germans, but losses were so high that on September 17 Hitler postponed any invasion • Shift in German strategy to bombing British cities • Winston Churchill; -- “The nations finest hour” • Air attacks continued until 1942, but the aerial battle of Britain was over Equally Critical was the Battle of the Atlantic • Importance of convoys getting through to Britain • After the sinking of the Bismarck the British controlled the ocean’s surface, the Germans beneath the waters with their submarines The fateful decision to invade Russia – Spring, 1941 • The idea that Russia could be conquered by winter • Russia would add considerable lebensraum or space to the German Reich • The plan almost worked • Millions of Russians captured or killed • But when winter closed in, neither Leningrad nor Moscow was captured • Between December 1941 and May 1942 the German army in Russia literally froze to death U.S. Enters WWII • American government took steps to freeze Japanese credits in the U.S. to halt access of raw materials – summer and autumn of 1941 • Force Japan to withdraw from China • Pearl Harbor, December 7, 1941, a “day of infamy” • Because of treaty with Japan, Germany declared war on America on December 11, 1941 Japan had many initial advances • • • • • • Philippines Guam Wake Island Malaya Indonesia Borneo The last two years of the war the Axis was on the defensive • Attack on Germany and Italy came from three directions • By the Russians from the east • By the British, French and Americans from the South and West Finishing the War in the Pacific • “Island Hopping” – Tarawa – Eniwetok – Guam – Okinawa – Iwo Jima China Theater Larger Islands – Solomons, New Guinea,Phillippines The Sudden End – the Manhattan Project • Hiroshima and Nagaski, August 6 and 9, 1945 • September 2, 1945 Japanese Surrender, Tokyo Bay