* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Attack or Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
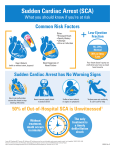
Heart Attack or Sudden Cardiac Arrest? Source: Sudden Cardiac Arrest Association HEART ATTACK • A heart attack, or myocardial infarction (MI), is caused by a circulation or plumbing problem of the heart, when one (or more) of the arteries delivering blood to the heart is severely reduced or blocked. Oxygen in the blood cannot reach the heart muscle, and the heart muscle becomes damaged. • This damage to the heart muscle can lead to a malfunction of the heart’s electrical system, causing dangerously fast or slow heart rhythms that can cause SCA. • Many SCAs occur in patients with coronary heart disease. If the patient suffers a heart attack, there is a higher risk for SCA. • Symptoms of an impending heart attack include chest pain, radiating pain (left arm, between shoulder blades, jaw), difficulty breathing, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and profuse sweating. SUDDEN CARDIAC ARREST • Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a condition that occurs when the heart abruptly ceases to function due to an electrical problem. The signals that control the heart’s pumping ability suddenly become rapid and irregular, and blood is no longer pumped to the rest of the body. • There are also mechanical occurrences (with a normal electrical signal) that may precipitate SCA. Sometimes SCA is caused by severe hemorrhage and other issues. • There are often no warning signs or symptoms.