* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Unit: MA1G3, MM1G3 Study Guide for Test 1 Yes/No
Survey
Document related concepts
Rule of marteloio wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
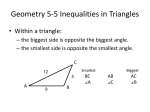
Geometry Unit: MA1G3, MM1G3 Study Guide for Test 1 Yes/No Indicate whether you agree with the statement. Properties of Triangles Side Relationships of a Triangle Determine whether each set of segment lengths can form a triangle. ____ 1. 4 in., 6 in., 10 in. ____ 2. 2 m, 20 m, 21 m Completion Complete each statement. Properties of Triangles Points of Concurrency Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement. 3. A(n) __________________ is a line that divides a segment into two smaller segments of equal length. 4. The ________________ of a triangle is the point at which the three medians intersect. 5. Three or more lines that intersect at a common point are called ___________________. 6. A(n) __________________ of a triangle is a line segment that connects a vertex to the midpoint of the side opposite the vertex. 7. The ___________________ of a triangle is the point at which the three perpendicular bisectors intersect. 8. The point at which three or more lines intersect is called the ___________________. 9. A(n) _________________ is a segment bisector that is also perpendicular to the line segment. 10. The _________________ of a triangle is the point at which the three angle bisectors intersect. 11. To divide an angle into two smaller angles of equal measure is to _________________. 12. A perpendicular line segment that is drawn from a vertex to the opposite side is called an _______________. 13. A(n) _________________ is a line that divides an angle into two smaller angles of equal measure. 14. The __________________ of a triangle is the point at which the three altitudes intersect. 15. To divide a segment into two smaller segments of equal length is to _________________. Properties of Triangles Direct and Indirect Proof Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement. 16. The _________________________________________ says an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the two remote interior angles of the triangle. 17. The ______________________________________ says that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles of the triangle. 18. The ______________________________ means assuming the opposite of the conclusion. Matching Properties of Triangles Angle Relationships in a Triangle Vocabulary Match each word with its definition. a. an angle formed by one side of a triangle and an extension of another side b. The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than the measure of either of its remote interior angles. c. a triangle with three equal angles d. a triangle with three acute angles e. a triangle that has one right angle f. a triangle with one obtuse angle g. the two angles of a triangle that are not supplementary to a given exterior angle ____ 19. acute triangle ____ 20. obtuse triangle ____ 21. right triangle ____ 22. equiangular triangle ____ 23. exterior angle ____ 24. remote interior angles ____ 25. Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem Short Answer Classify each triangle by its angles. Then classify the triangle by its sides. 26. 27. 28. Determine the theorem or postulate that proves each pair of triangles are congruent. 29. 30. 31. Use a compass and a straightedge to construct the centroid of the triangle. Determine the theorem or postulate that proves each pair of triangles are congruent. 32. Classify each triangle by its angles. Then list the sides from shortest to longest. 33. Classify each triangle by its sides. Then list the angles from smallest to largest. 34. 35. Use the diagram to calculate and Determine whether a triangle could be formed from each set of segment lengths. 36. 7 inches, 15 inches, 8 inches 37. 8 feet, 3 feet, 6 feet 38. Sketch the perpendicular bisector of segment AB. Classify each triangle by its angles. Then list the sides from shortest to longest. 39. Classify each triangle by its sides. Then list the angles from smallest to largest. 40. 41. What is the value of x in the diagram? 42. Describe the possible values for the length of 43. Jamal needs to attach a yield sign to a pole, and he only has one bolt left. He decides to make the hole for the bolt at the incenter of the triangular yield sign. Use your compass and a straightedge to locate the incenter and label it with a B. 44. Use a compass and a straightedge to construct the bisector of the angle shown. Write the theorem or postulate that can be used to prove that each pair of triangles are congruent. Then write a congruence statement. 45. 46. Properties of Triangles Angle Relationships in a Triangle Identify the exterior angle of each triangle. 47. Properties of Triangles Angle Relationships in a Triangle Solve for x in each triangle. 48. 49. Properties of Triangles Angle Relationships in a Triangle Use the Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem to describe the angles of each triangle. 50. Properties of Triangles Side Relationships of a Triangle Vocabulary Define each term in your own words. 51. scalene triangle 52. isosceles triangle 53. equilateral triangle Properties of Triangles Side Relationships of a Triangle Identify the smallest and largest angle in each triangle. Identify any angles that have the same measure. 54. Properties of Triangles Points of Concurrency Compare the parts of the given types of triangles. 55. Compare the placement of the incenter and circumcenter for acute, obtuse, and right triangles. 56. Compare the placement of the incenter and centroid for acute, obtuse, and right triangles. 57. Compare the placement of the incenter and orthocenter for acute, obtuse, and right triangles. 58. Compare the placement of the circumcenter and centroid for acute, obtuse, and right triangles. 59. Compare the placement of the circumcenter and orthocenter for acute, obtuse, and right triangles. 60. Compare the placement of the centroid and orthocenter for acute, obtuse, and right triangles. Properties of Triangles Direct and Indirect Proof Problem Set For the triangle shown, use a direct proof to prove each statement. 61. Statements Reasons 1. Angle ABD is an exterior angle of triangle BCD. 1. Given 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. 6. 6. 7. 7. Wind Triangles Proving Triangles Congruent: ASA and AAS Problem Set Use the ASA Postulate to show that each pair of triangles is congruent. 62. Wind Triangles Proving Triangles Congruent: ASA and AAS Use the AAS Theorem to show that each pair of triangles is congruent. 63.