* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World Geography Facts PP
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
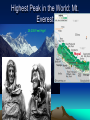
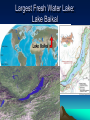
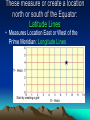
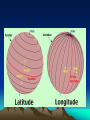
World Geography Themes, Fact, and the Basics! 5 Major Themes of Geography • Location: Most geographic study begins with learning the location of places. Location can be absolute or relative. – Absolute: Absolute location provides a definite reference to locate a place. The reference can be latitude and longitude, a street address, or even the Township and Range system. – Relative: Relative location describes a place with respect to its environment and its connection to other places. Place • Place: Place describes the human and physical characteristics of a location. • Physical characteristics include a description such things as the mountains, rivers, beaches, topography, and animal and plant life of a place. • Human characteristics include the human-designed cultural features of a place, from land use and architecture to forms of livelihood and religion to food and folk ways to transportation and communication networks. Movement • Movement: Humans move, a lot! In addition, ideas, fads, goods, resources, and communication all travel distances. This theme studies movement and migration across the planet. Human-Environment Interactions • Human-Environment Interactions: This theme considers how humans adapt to and modify the environment. Humans shape the landscape through their interaction with the land; this has both positive and negative effects on the environment. Regions: Region divides the world into manageable units for geographic study. Regions have some sort of characteristic that unifies the area. Regions can be formal, functional, or vernacular. • Formal: are those that are designated by official boundaries, such as cities, states, counties, and countries. For the most part, they are clearly indicated and publicly known. • Functional: are defined by their connections. For example, the circulation area for a major city area is the functional region of that paper. • Vernacular: are perceived regions, such as "The South," "The Midwest," or the "Middle East;" they have no formal boundaries but are understood in our mental maps of the world. World Facts!!! Age of the Earth: 4.6 Billion Years old! Circumference of the Earth: 25,000 miles (Diameter: 8,000 mi) Speed of the Earth making Revolution: 700 mph The Water area found on the surface of the Earth: 361,132,000 sq km ; 70% Surface Area of the Earth • We would Freeze if we did not Have??? CO2 (Ozone) and the Sun of Course! Name of all one Continent? • Pangaea The Land we find on the Earth’s Surface? • Tectonic Plates: Earth's crust is broken into huge plates that move apart or push together at about the rate our fingernails grow. Convection of semi-molten rock in the upper mantle helps drive plate tectonics. (50 Miles thick!) Reason For Continents to Move… • 3 ways-cause earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains etc.. – A) Hit each other head on-Subduction: Ural Mts., Himalayas; Mariana Trench (35, 827 feet deep!) FOLDS – B) Move away from each other-Diverging: African Great Rift Valley, Atlantic Mountains – C) Slide against one another- NeutralCalifornia-Moving Towards Alaska. Continent in all 4 Hemispheres? • Africa Windiest and Driest Continent? • Antarctica! Largest Island In the World: Greenland What do we call Global Winds? • Polar Easterlies: 60 to 90 Degrees Latitude • Prevailing Westerlies: 30 to 90 Degrees Latitude • Tropical Easterlies: 0 to 30 Degrees Latitude Where are Doldrums Located? Around the Equator • Sailors noticed the stillness of the rising (and not blowing) air near the equator and gave the region the depressing name "doldrums." The doldrums, usually located between 5° north and 5° south of the equator, are also known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone or ITCZ for short. The trade winds converge in the region of the ITCZ, producing convectional storms that produce some of the world's heaviest precipitation regions. Highest Peak in the World: Mt. Everest 29,035 Feet High! Highest Peak in U.S.: Mt. Denali 20,320 feet Largest inland Sea? Caspian Sea Largest Salty Lake: Caspian Sea Largest Fresh Water Lake: Lake Baikal Lowest Point on Earth? The Dead Sea , Israel-Jordan Average Global Temperature: •58 Degrees Where on the Earth’s Surface can we find Life? • Everywhere from the Poles to the Equator=> Up to 11 mile High Warm water along the Coast which in turns Changes climate patterns: •El Nino Direction winds or ocean currents move in the Northern Hemisphere: • Clockwise! Largest Rainforest: Amazon We are losing up to 5% per year! ½ of all the Earth’s Oxygen comes From the Amazon! Longest Day: June 21st (Summer Solstice) • Equinoxes are the time of the year when the Day’s and Night’s are approximately the same length. Map Making: Cartography These measure or create a location north or south of the Equator: Latitude Lines • Measures Location East or West of the Prime Meridian: Longitude Lines Start by creating a grid • Latitude measures the north-south position of locations on the Earth's surface relative to a point found at the center of the Earth (Figure 2b-2). This central point is also located on the Earth's rotational or polar axis. The equator is the starting point for the measurement of latitude. The equator has a value of zero degrees. A line of latitude or parallel of 30° North has an angle that is 30° north of the plane represented by the equator (Figure 2b-3). The maximum value that latitude can attain is either 90° North or South. These lines of latitude run parallel to the rotational axis of the Earth. • Longitude measures the west-east position of locations on the Earth's surface relative to a circular arc called the Prime Meridian (Figure 2b-2). The position of the Prime Meridian was determined by international agreement to be in-line with the location of the former astronomical observatory at Greenwich, England. Because the Earth's circumference is similar to circle, it was decided to measure longitude in degrees. The number of degrees found in a circle is 360. The Prime Meridian has a value of zero degrees. A line of longitude or meridian of 45° West has an angle that is 45° west of the plane represented by the Prime Meridian (Figure 2b-3). The maximum value that a meridian of longitude can have is 180° which is the distance halfway around a circle. This meridian is called the International Date Line. Designations of west and east are used to distinguish where a location is found relative to the Prime Meridian. For example, all of the locations in North America have a longitude that is designated west. Some parts of this are language, religion, government, education, etc: •Culture! First Person to Reach the South Pole: • Norwegian Explorer. Roald Engelbregt Graving Amundsen American Robert E. Peary was the First to the North Pole! The air we breath… • 10 gases…Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, Carbon Dioxide, Neon, Helium, Methane, Krypton, Hydrogen, and Xenon • Physical Map: Shows names and relative locations of natural features such as: Mountains, Forests, Deserts, and Rivers/Lakes. • Political Maps: Show boundaries between states, countries or providences. Usually includes names, capitals, and major cities. 4 Different Types of Maps • Thematic Maps: Show single topics such as population, rainfall, land use, climate, etc… • Regional Maps: Provide a close up view of certain areas. Gives detailed information of that area.