* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
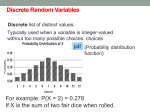
Accelerated GSE Pre-Calculus Unit Six Information Curriculum Map: Probability Concept 1: Rules of Probability Concept 2: Calculate & Use Expected Values Concept 3: Use Probabilities to Make Decisions Content from Frameworks: Probability Unit Length: Approximately 25 days 20152016 TCSS – Accelerated GSE Pre-Calculus – Unit 6 Curriculum Map Big Idea / Unit Students will use calculate, interpret and use probabilities and expected values to make decisions. Unit Essential Questions: How do you calculate, apply and interpret probabilities? Prerequisites: As identified by the GSE Frameworks Length of Unit Understand the basic nature of probability Determine probabilities of simple and compound events Understand the Fundamental Counting Principle Organize and model simple situations involving probability Concept 1 Rules of Probability 25 Days Concept 2 Concept 3 Calculate & Use Expected Values Use Probabilities to Make Decisions GSE Standards MGSE9-12.CP.8 (+) Apply the general Multiplication Rule in a uniform probability model, P(A and B)=[P(A)] x [P(B│A)] = [P(B)] x [P(A│B)], and interpret the answer in terms of the model. MGSE9-12.S.CP.9 (+) Use permutations and combinations to compute probabilities of compound events and solve problems. GSE Standards GSE Standards MGSE9-12.S.MD.1(+) Define a random variable MGSE9-12.S.MD.5(+) Weigh the possible for a quantity of interest by assigning a numerical outcomes of a decision by assigning probabilities value to each event in a sample space; graph the to payoff values and finding expected values. corresponding probability distribution using the MGSE9-12.S.MD.5a(+) Find the expected same graphical displays as for data distributions. payoff for a game of chance MGSE9-12.S.MD.2(+) Calculate the expected MGSE9-12.S.MD.5b(+) Evaluate and compare value of a random variable; interpret it as the mean strategies on the basis of expected values of a probability distribution. MGSE9-12.S.MD.6(+) Use probabilities to make MGSE9-12.S.MD.3(+) Develop a probability fair decisions (e.g., drawing by lots, using a distribution for a random variable defined for a random number generator). sample space in which theoretical probabilities can MGSE9-12.S.MD.7(+) Analyze decisions and be calculated; find the expected value strategies using probability concepts (e.g., product MGSE9-12.S.MD.4(+) Develop a probability testing, medical testing, pulling a hockey goalie at distribution for a random variable defined for a the end of a game). sample space in which probabilities are assigned empirically; find the expected value Supporting Standards MGSE7.SP.8 Find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulation. MGSE9-12.S.CP.2 Understand that two events A and B are independent if the probability of A and B occurring together is the product of their probabilities, and use this characterization to determine if they are independent. MGSE9-12.S.CP.3 Understand the conditional probability of A given B as P(A and B)/P(B), and interpret independence of A and B as saying that the conditional probability of A given B is the same as the probability of A, and the conditional probability of B given A is the same as the probability of B. MGSE9-12.S.CP.6 Find the conditional probability of A given B as the fraction of B’s outcomes that also belong to A, and interpret the answer in terms of the model. MGSE9-12.S.CP.7 Apply the Addition Rule, P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A and B), and interpret the answer in terms of the model. TCSS 7/27/2015 2 TCSS – Accelerated GSE Pre-Calculus – Unit 6 Lesson Essential Question How do I use the General Multiplication Rule to calculate probabilities? How do I determine when to use a permutation or a combination to calculate a probability? Vocabulary General Multiplication Rule Conditional Probability Combinations Permutations Resources – Concept 1 Combinations and Permutations Overview with Practice Combination calculator activity These tasks were taken from the GSE Frameworks. Permutations and Combinations Task Testing Learning Task Differentiated Activities Concept 1 TCSS Lesson Essential Question How do I identify a random variable? How do I graphically display the probability distribution of a random variable? How do I calculate the expected value of a random variable? How do I calculate theoretical and empirical probabilities of probability distributions? How do I represent and calculate payoff values in a game of chance? How do I use expected values to make decisions? How do I explain the decisions I make using expected values? Vocabulary Random Variable Expected Value Sample Space Theoretical Probabilities Empirical Probabilities Vocabulary Pay off Odds Resources – Concept 2 Discrete Random Variables Expected Value Practice Expected Value Worksheet These tasks were taken from the GSE Frameworks. Please Be Discrete Task Resources – Concept 3 Statistics Review These tasks were taken from the GSE Frameworks. Lottery Learning Task Mega Millions Practice Task Design a Lottery game Project Differentiated Activities Concept 2 Medical Testing FAL Differentiated Activities Concept 3 7/27/2015 Representing Conditional Probabilities 2 FAL 3 TCSS – Accelerated GSE Pre-Calculus – Unit 6 Unit 6 Checklist – Probability Good luck to ________________________Date_______ Period___ Keep this list handy and refer to it periodically to see how you are doing. If you know how to each of these you should do well on an exam. In this unit I : sort of really can calculate probabilities using the general Multiplication Rule in a probability model. can use permutations and combinations to calculate probabilities of compound events and to solve problems. given a probability situation, theoretical or empirical, understand how to define a random variable, assign probabilities to its sample space, and graph the probability distribution of the random variable. can calculate the expected value of a random variable can develop a theoretical and empirical probability distribution and find the expected value. can develop a probability distribution for a random variable representing payoff values in a game of chance. can make and explain decisions based on expected values. TCSS 7/27/2015 4