* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Similar Shapes 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Similar Shapes MENU
Enlargements
Similar Triangle
Calculations
Scale Factors and
VOLUME questions
What makes
shapes similar ?
Similar Triangle
questions
Congruency
Match up the
Similar rectangles
Scale Factors
and AREA
Congruency
questions
What makes
Triangles similar ?
Scale Factors and
AREA examples
Match up the
Similar triangles
Scale Factors and
AREA questions
Similar Shape
Calculations
Scale Factors
and VOLUME
Similar Shape
questions
Scale Factors and
VOLUME examples
1
Main menu
Enlargements MENU
Basic
Fractional
Enlargements
Negative Scale
Factor
Enlargements
Fractional
Enlargements
questions
Negative Scale
Factor
questions
Describing
Fractional
Enlargements
Describing
Negative
Enlargements
Basic questions
Positive Whole
Scale Factor
Enlargements
Positive Whole
Scale Factor
Enlargement
questions
Describing Positive
Whole Scale Factor
Enlargements
2
Similar Shapes Menu
3
Menu
Twice
asyou
big.to
That’s
a Scale
Factor = 2
I want
enlarge
the rectangle.
You know exactly what I mean !
How
many
bigger
you
want
?!
Do you mean
O.K.
twice
Youtimes
the
mean
AREA
twice
or do
the
twice
line
the
lengths
lineitlengths
?
4
Menu
What are the DIMENSIONS of the following enlargements ?
S.F. = 2
S.F. = 2
S.F. = 3
5
Menu
Copy the following shapes onto squared
paper and sketch their enlargements.
2)
1)
3)
S.F. = 3
S.F. = 3
4)
S.F.= 2
5)
S.F.= 4
S.F.= 3
6
Menu
7
Menu
I will fix the position of the ‘image’ by using a Centre of
All
of
theis
‘light
rays’
from
and
lead prefer
If
I
wanted
enlarge
aoriginate
shape
say
a Scale
If the enlargement
carried
out
on the
a by
grid
then
Enlargement
intothe
same way
that
position
of you
a lensmay
fixes the
back to
the
Centre
of
Enlargement.
Factor
=
2
I
could
draw
it
anywhere
!
position
an image.
to ‘count
theofsquares.’
Scale Factor = 2
x
x
x
x
C of E
87
4
x
=8
x 2x=214
7.284.47
x 2 = x14.56
2 = 8.94
8
Menu
If the enlargement is carried out on a grid then you may prefer
to ‘count the squares.’
Scale Factor = 2
C of E
x
x
x
x
7
4 left7and
left
4 left
2 down
x x2 2= =148 left
left
x 2x and
=and
2 14
= 844left
left
down
down
x
9
Menu
x
2.2 x 3 = 6.6
Object
2.2
x
Scale Factor = 3
x
Image
2.2 x 3
= 6.6
or
2.2
1.4
x
1.4 x 3 = 4.2
x
x
x
2
11right
rightand
and12down
up
x3=3
6 right and 3
6 down
up
x
10
Menu
Scale Factor = 2
x
x
x
x
3.6 x 2 = 7.2
3.6 2.2
3.2
x
x 2.21.4x 2 = 4.4
3.2 x 2 = 6.4
1.4 x 2 = 2.8
x
x
x
x
11right
right
3 3left
left
and
and
and
and
121down
up
2down
up
xx 22x==26
22=left
right
right
6 left
and
and
and
and
2 4down
24up
down
up
11
Menu
Enlarge the following shapes by the given Scale Factors.
1)
x
S.F. = 2
2)
4) X
3)
S.F. = 3
X
S.F. = 3
x
S.F. = 2
12
Menu
Answers
Fully describe each Enlargement : Give the Scale Factor and the
coordinates of the Centre of Enlargement (Each square = 1 unit)
x (-9,7)
S.F. = 2
1)
y
2)
(3,4)
Object
x
Object
Image
Image
S.F. = 3
x
3) x
(-4,-2)
S.F. = 4
Object
Image
13
Menu
Answers
14
Menu
Scale Factor = 1/2
½ of 16.1 = 8.05
½
of
10.2
=
5.1
16.1
10.2
C of E
x
x
Object
Image
x
x
x
10.2
½ of 10.2 = 5.1
16.1
10
10
16
left
left
left
left
and
and
and
and
222
down
2down
up
up
½ of 16.1 = 8.05 ½ of 10 16
left and ½ of 2 up = 5 left and 1 up
½ of
½16
of ½
left
10ofleft
and
16and
left
½ of
½
and
2ofdown
½
2 down
of 2= up
8 =left
=5 8left
and
leftand
1and
down
1 1down
up
Scale factors less than 1 will produce
You may prefer to count squares !
images smaller than their objects.
x
x
Object
Image
x
x
x
15
Menu
Enlarge the following shapes by the given Scale Factors.
1) x
2)
S.F.= 1/2
S.F.= 1/4
3)
4)
x
x
x
S.F.= 2/3
.
S.F.= 1 5
16
Menu
Fully describe each Enlargement : Give the Scale Factor and the
coordinates of the Centre of Enlargement (Each square = 1 unit)
1)
Object
2)
S.F. = 1/3
S.F. = 1/2
C of E at ( 3 , 2 )
Image
3)
x
x
C of E at ( - 6 , 0 )
Image
C of E at ( - 1 , - 1 )
x
Image
S.F. = 1/4
Object
Object
17
Menu
18
Menu
The lens in your eye produces an image using a Negative
As with the other enlargements
youFactor
could! have carried out these negative
Scale
enlargements by counting squares in the opposite directions.
x
x
Scale Factor = - 2
2.83 x -2 = - 5.66
Image
x
Object
x
2.83 x -2 = - 5.66
4.47 x -2 = - 8.94
19
Menu
Enlarge the following shapes by the given Scale Factors.
1)
S.F. = - 2
x
2)
X
S.F. = - 0.5
20
Menu
Fully describe each Enlargement : Give the Scale Factor and the
coordinates of the Centre of Enlargement (Each square = 1 unit)
1)
Enlargement, Scale Factor = - 3
Object
Centre of Enlargement at ( - 7 , 4 )
Enlargement, Scale Factor = - 1/4
x
2)
Centre of Enlargement at ( 5 , - 1 )
Image
Image
x
Object
21
Menu
22
Menu
Two shapes are said to be SIMILAR when one is an
ENLARGEMENT of the other.
4
2
1
2
For shapes to be similar they must :
1)
Have identical angles.
2)
Have their sides in the same proportion.
=2
=2
23
Menu
Match up the PAIRS of Similar Shapes.
1)
3
2
6÷3=2
10
3)
4)
10 ÷ 2 = 5
6)
2
Rectangles NOT drawn to scale.
6
7
7 ÷ 2 = 3.5
2)
3
2
3 ÷ 2 = 1.5
5)
14
4
7)
3
14 ÷ 4 = 3.5
15
15 ÷ 3 = 5
4
8)
10
8
8÷4=2
15
15 ÷ 10 = 1.5
24
Menu
25
Menu
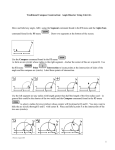
Same angles so automatically
Similar Triangles.
0
40
0
40
0
0
50
50
For 2 Triangles to be Similar to each other you
only need to check whether or not they have
the same angles.
If their angles are the same then their sides will
automatically be in the same proportions.
26
Menu
Match up the PAIRS of Similar Triangles.
Triangles NOT drawn to scale.
1)
2)
3)
40°
80°
30°
60°
70°
4)
20°
70°60°
5)
6)
60°
8)
50°
60°
7)
20°
60°
40°
27
Menu
28
Menu
Bob decides to enlarge a poster of himself.
How wide will the enlargement be ?
10 cm
15 cm
30 ×
=
x cm
× 30
x = 10 × 30 30 cm
15
x = 300
15
x = 20 cm
29
Menu
Bob’s work rival decides to reduce the poster so
that it is only 3 cm wide. How long will it be ?
20 cm
3×
=
×3
3 cm
x cm
x = 30 × 3
20
30 cm
x = 90
20
x = 4.5 cm
30
Menu
Calculate the missing lengths.
{ Each pair of shapes are similar }
1)
x
3
2)
15
5
9
9.6
10
8
12
x
3)
8
x
9
16.87
5
17.64
7
5)
15
9
4)
115°
15
5
115°
17
8.75
8
x
6)
6
x
14
5
130°
20
130°
12
x
4
8
31
Menu
32
Menu
How high is the church spire ?
Common to both triangles
Corresponding Angles
Parallel
Both are Right Angles
1)
Hammer a stick into the ground.
2)
Line up the top of the stick with the top of the spire.
{You will need to put your eye to the ground}
3)
We now have 2 Similar Triangles because …
33
Menu
How high is the church spire ?
50 ×
× 50
=
x = 2 × 50
4
x = 25 m
2
x
4
2m
4m
50 m
4)6)
Measure
height
of the
stick.
Let the the
height
of the
spire
be called x.
5)7)
Measure
You may
the
well
distances
find it easier
from the
seeing
‘eye’them
to the
asstick
two separate
and the
‘eye’
triangles
to the church.
34
Menu
Calculate the missing lengths x
1)
5.83
5
x
2)
9.17
17
6
15
11
7
18
11.7
3)
5
x
14
4)
10.8
9
6
x
20
x
18
16
12
35
Menu
Harder Problems
Calculate the missing lengths x
12.5
1)
2)
6
5
12
x
x
>
3
1.5
3
4
>
3)
20
A
x
B 4) Prove that triangles
and
CDE in
^ ABC
^ (Vertically
ACB
= DCE
opposite angles)
^ = BAC
^ (Alternate 3
CDE
angles)
question
are similar.
^ ^
26.7 >
10
6
E
5
C
3
>
8
CED = ABC (Alternate angles)
D
36
Menu
37
Menu
Each
rectangle
is Areas
enlarged
using
Scale
Factor = 2 ?
Work
In
each
out the
case
how of
has
each
theaof
Area
theincreased
rectangles
S.F. = 2
2
1
1×2=2
2×3=6
4
5 × 6 = 30
10
7
7 × 10 = 70
2×4=8
4 × 6 = 24
12
6
5
4
6
3
2
2
Diagrams not drawn to scale.
10
10 × 12 = 120
20
14 14 × 20 = 280
×4
2 8
×4
6 24
×4
30 120
×4
70 280
38
Menu
Each
is Areas
enlarged
Factor = 3?
Work
Inrectangle
each
out case
the
how has
of using
each
the aArea
ofScale
theincreased
rectangles
S.F. = 3
2
1
1×2=2
2×3=6
6
5 × 6 = 30
10
7
7 × 10 = 70
3 × 6 = 18
6 × 9 = 54
18
6
5
6
9
3
2
3
Diagrams not drawn to scale.
15
15 × 18 = 270
30
21 21 × 30 = 630
×9
2 18
×9
6 54
×9
30 270
×9
70 630
39
Menu
Each
is Areas
enlarged
Factor = 4?
Work
Inrectangle
each
out case
the
how has
of using
each
the aArea
ofScale
theincreased
rectangles
S.F. = 4
2
1
1×2=2
2×3=6
8
5 × 6 = 30
10
7
7 × 10 = 70
4 × 8 = 32
8 × 12 = 96
24
6
5
8
12
3
2
4
Diagrams not drawn to scale.
20
20 × 24 = 480
40
28 28 × 40 = 1120
× 16
2 32
× 16
6 96
× 16
30 480
× 16
70 1120
40
Menu
(
What is the connection
between the
2
Scale
Factor
Increase
in?Area
Scale Factor
and )the=increase
in Area
Scale Factor
2
Increase in Area
( Area multiplier )
×4
3
×9
4
× 16
41
Menu
Example 1
( Scale Factor )2 = Area multiplier
32 = 9 times
Area = ?
Area = 8
New Area = 8 × 9
cm2
= 72 cm2
5 cm
S.F. = 15 ÷ 5 = 3
15 cm
Example 2
( Scale Factor )2 = Area multiplier
Area multiplier = 250 ÷ 10
Area =
10
cm2
4 cm
= 25 times
Area = 250 cm2
x Scale Factor = Area multiplier
S.F. = 25
S.F. = 5
New base : 4 × 5 = 20 cm
Menu
42
Work out the following : {All of the shapes are Similar}
1)
96
2)
cm2
5 cm2
Area = ?
Area
Area
Area = ?
= 45 cm2
= 6 cm2
2 cm
8 cm
4 cm
12 cm
3)
4)
Area
8m
Area
Area
= 180 m2
= 100 m2
= 20 m2
Area
= 25 m2
15 m
x
5m
16 m
x
43
Menu
44
Menu
Each
CUBOID
is enlarged
using
a Scale
Factor
=2 ?
InWork
each
case
how
has the
Volume
increased
out the
Volume
of
each
cuboid.
Diagrams not drawn to scale.
S.F. = 2
11 × 1 × 2
1 =2
2
1 1×2×3
2
=6
3
2
2
2
4
4
2×4×6
= 12
4
3
2×3×4
= 24
4
2 16
×8
6 48
= 48
×8
4
2×2×3
2
3
= 16
×8
6
2
2
2×2×4
4
6
4×4×6
12 96
= 96
6
4×6×8
= 192
8
×8
24 192
45
Menu
Each
is enlarged
using
a Scale
Factor
=3 ?
InWork
eachCUBOID
case
how
has the
Volume
increased
out the
Volume
of
each
cuboid.
Diagrams not drawn to scale.
S.F. = 3
11 × 1 × 2
1 =2
2
1 1×2×3
2
=6
3
3
3
3
6
6
3×6×9
= 12
6
3
2×3×4
= 24
4
× 27
6 162
= 162
6
2×2×3
2
3
= 54
× 27
2 54
9
2
2
3×3×6
6
9
6×6×9
× 27
12 324
= 324
9
6 × 9 × 12
= 648
12
× 27
24 648
46
Menu
Each
CUBOID
is enlarged
using
a Scale
Factor
=4 ?
InWork
each
casethe
how
has the
Volume
increased
out
Volume
of
each
cuboid.
Diagrams not drawn to scale.
S.F. = 4
11 × 1 × 2
1 =2
2
1 1×2×3
2
=6
3
4
4
4
8
8
4 × 8 × 12
= 12
3
2×3×4
= 24
4
× 64
6 384
= 384
8
2×2×3
2
3
= 128
× 64
2 128
12
2
2
4×4×8
8
8
12
8 × 8 × 12
× 64
12 768
= 768
12
8 × 12 × 16
= 1536
16
× 64
24 1536
47
Menu
What is the connection
between the Scale
3 = Increase
( Scale
Factor
)
in Volume
Factor and the increase in Volume ?
Scale Factor
Increase in Volume
( Volume multiplier )
2
×8
3
× 27
4
× 64
48
Menu
Example 1
5m
Volume
10 m
( Scale Factor )3 = Volume multiplier
23 = 8 times
Volume
=?
= 50 m3
New Volume = 50 × 8
= 400 m3
Scale Factor = 2
Example 2
( Scale Factor )3 = Volume multiplier
Volume
Volume
= 20 m3
= 540 m3
4m
Volume multiplier = 540 ÷ 20
= 27 times
x
3
Scale Factor = Volume Multiplier
New width : 4 × 3 = 12 m
3
S.F. = 27
S.F. = 3
49
Menu
Work out the following : {All of the shapes are Similar}
1)
6
120
Volume
2)
m3
12
Volume
30 m3
Volume
=?
= 3750
= 15 m3
20
3)
18 m
Volume
m3
4)
= 40
6
4
9m
Volume
m3
=?
Volume
= 1080 m3
Volume
x
x
Volume
36
= 12800 m3
= 200 m3
50
Menu
51
Menu
Shapes are said to be CONGRUENT when they
have the same angles and their sides are the
same length.
They are identical.
They would fit perfectly over each other.
100° 110°
80°
70°
70°
80°
110° 100°
70°
110°
100°
80°
52
Menu
For Triangles to be CONGRUENT ( hence identical )
they have to fulfil one of four conditions :
1)
If their sides are all the same length
then the triangles are identical ( Congruent ).
Side Side Side
S.S.S
53
Menu
For Triangles to be CONGRUENT ( hence identical )
they have to fulfil one of four conditions :
The INCLUDED angle lies between the 2
pairs of equal length sides.
40°
40°
2)
If 2 of their sides are the same length
and their INCLUDED angles are the same then
the triangles are identical ( Congruent ).
Side Angle Side
S.A.S
54
Menu
For Triangles to be CONGRUENT ( hence identical )
they have to fulfil one of four conditions :
A corresponding side lies opposite to
one of the identical angles.
OR
40°
3)
70°
40°
70°
If 2 of their angles are the same and also 1
of their corresponding sides are the same
then the triangles are identical ( Congruent ).
Angle Angle Side
A.A.S
55
Menu
For Triangles to be CONGRUENT ( hence identical )
they have to fulfil one of four conditions :
OR
4)
If they both have Right angles, they both have
the same Hypotenuse and one other side is
the same length then the triangles are
identical ( Congruent ).
Right angle
Hypotenuse
Side
R.H.S
56
Menu
Summary of conditions for Congruent Triangles.
Side Side Side S.S.S
Angle Angle Side A.A.S
Side Angle Side S.A.S
Right angle Hypotenuse Side
R.H.S
57
Menu
Which triangles are Congruent to the RED triangle.
You must give reasons. ie SSS, AAS, SAS, RHS
Triangles not drawn to scale.
1)
9.8
9.8
A.A.S
60° 40°
2)
15
80°
60°
6)
80°
13.2
60°
40°
5)
15
3)
9.8
80°
80°
S.S.S
13.2
40°
13.2
15
4)
40°
9.8
15
40°
S.A.S
13.2
58
Menu
R.H.S problems
Which triangles are Congruent to the RED triangle.
You must give reasons. ie SSS, AAS, SAS, RHS
Triangles not drawn to scale.
37°
5
4
A.A.S
5
37°
53°
3
3
R.H.S
5
3
5
37°
3
53°
Menu
5
3
5
53°
S.A.S
or
R.H.S
or
A.A.S
59
End of Similar Shapes Presentation.
Return to previous slide.
60