* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download …And Energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
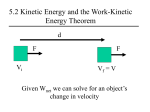
…And Energy Work – Measured in Joules Energy – Measured in Joules Power – Measured in Watts Work and Energy are both measured in Joules. Are they the same thing? What do you think??? Work (W) • Work is the Transfer of Energy • Force exerted over a distance • W = Fd – F = Magnitude of Force (Newtons) – d = Magnitude of Displacement (distance - m) Remember displacement? W=F (Newton) x displacement (Meters) So 1 Joule = 1 Newton x 1 Meter Energy of a body is its Capacity to do Work Energy There’s 3 Types! Kinetic Energy (KE or K) • The Energy of Motion • KE = ½ mv² – m = mass of the object – v = velocity of the object Gravitational Potential Energy • The stored energy an object has due to with its position above earth’s surface • PE = mgh – m = mass of the object – g = acceleration of gravity – h = height of the object relative to earth (or some other zero level) Elastic Potential Energy (PEs) • Energy a Spring has by virtue of being stretched or compressed • PEs = ½ kx² – k = Spring Constant – Measures the strength of the spring in N/m – x = Distance the spring is stretched or compressed Are Work and Energy related? Remember: Work is the transfer of Energy Energy is the ability to do work Work and Energy • Work exerted on an object is equal to the difference between an object’s initial and final Energies. • Or… W=Ef-Ei WKE = KEf – KEi = mv²f - ½ mv²i Wgravity = PEf – PEi = mghf – mghi WPEs = PEsf – PEsi = ½ kx²f - ½ kx²i Mechanical Energy – the ability to do work Mechanical energy is the energy that an object has due to its motion (kinetic energy) or its position (potential energy. • (ME or E) of an object is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of that object Etotal= KE + PE KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf …In this case, KE and PE can be transformed into one another as the object moves. But, the energy is never lost or gained, it is only transformed… Ei = E f KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf Power • The Rate at which Work is done • P = Work/time or • P = Force x velocity • remember Work = Force x Displacement • Force =ma • Measured in Watts (W) = J/s Time to Practice! Find the work exerted on a suitcase if the suitcase is being pulled with a force of 16.0 N and the displacement of the suitcase is 63.0 cm. W = Fd W = (16.0N)(0.63m) W = 5.64 J An archer pulls a bowstring back a distance of 0.470m and then releases the arrow. The bow and string act like a spring whose spring constant is 425 N/m. What is the elastic potential energy of the system? PE = ½kx² PE = ½(425N/m)(0.470m)² PE = 46.9 J A motorcyclist is trying to leap across a canyon by driving horizontally off the cliff at a speed of 38.0 m/s. Ignoring air resistance, find the speed at which the motorcycle strikes the ground on the other side. The motorcycle starts at a height of 70.0m and will end at a height of 35.0m. KEf + Pef = KEi + PEi ½ mv² + mgh = ½mvi² + mghi (mass cancels out) ½v² + (9.8m/s²)(35.0m) = ½(38.0m/s)² + (9.8m/s²)(70.0m) V = 46.2 m/s