* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem Mathemagics Page
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Group action wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
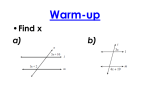
1. Types of Angles Vertical angles: ________________________ Congruent or Supplementary Alternate Interior: _____________________ Congruent or Supplementary Same-side Interior: ____________________ Congruent or Supplementary Alternate Exterior: _____________________ Congruent or Supplementary Same-side Exterior: _____________________ Congruent or Supplementary Corresponding: _________________________ Congruent or Supplementary 2. Formulas Angle Sum of a Triangle Exterior Angles of a Triangle Interior Angle Sum of a Polygon (define variables) Exterior Angles of a Polygon (in words) Pythagorean Theorem (define variables) The Distance Formula (define variables) 3. Parts of a Right Triangle – label all sides using “a”, “b”, and “c” in the boxes and then name the sides using the lines. ____________________________ ___________________________ Stop Sign - The stop sign shown is a regular octagon. Answer the following questions showing all work. 4. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles. 5. Find the measure of an interior angle. 6. Find the measure of an exterior angle. 7-8. Solve using Pythagorean Theorem – show all work. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 7. 8. 9-10. Plot the points. Then use the Distance Formula to find distance between the points. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 9. 10. 11. Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem (fill in the blanks) a. If c2 = a2 + b2 then ΔABC is _____________ b. If c2 < a2 + b2 then ΔABC is _____________ c. If c2 > b2 + a2 then ΔABC is _____________