* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 5 - Wednesday Training Net
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Continuous-wave radar wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Radio direction finder wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Active electronically scanned array wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Beams wikipedia , lookup
Amateur radio repeater wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Radio receiver wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Direction finding wikipedia , lookup
FM broadcasting wikipedia , lookup
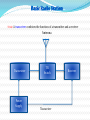
G. West Your First Radio p. 73 Your Computer goes Digital p. 119 Multi-mode Radio Excitement p. 127 Run Some Interference Protection p. 137 Amateur Radio equipment ARRL: Ch. 2.3, 3.3, 5 G. West Your First Radio p. 73 Your Computer goes Digital p. 119 Multi-mode Radio Excitement p. 127 Run Some Interference Protection p. 137 Generalized Transceiver Categories • Single Band • Dual Band • Multimode • Multiband • Handheld (HT) Basic Station Organization • Station Equipment – – – – Transmitter Receiver Antenna Power Supply • Accessory Station Equipment T7A02 A transceiver combines the functions of a transmitter and a receiver Antenna Transmitter Power Supply TR Switch Transceiver Receiver What Happens During Radio Communication? • Transmitting (sending a signal): – Information is converted to electronic form. Transmitter Info What Happens During Radio Communication? • Receiving end: Receiver front end Our Basic Building Blocks Converts a radio signal from one frequency to another. T7A03 Mixer T7A05 Oscillator Produces a steady signal at a single frequency Detector Amplifier Filters Modulator Demodulator Converts modulated RF directly into data or voice Makes signals stronger Detects CW & SSB Removes or blocks unwanted signals Puts information on the RF signal T7A08 Product Detector Frequency Discriminator Removes information from modulated RF Removes information from FM signals The Superheterodyne Receiver Block Diagram The mixer combines two signals to To convert one frequency to another, T7A03 One mixer = single conversion Two mixers = double conversion T4Bo4 Memory controls Microphone connector T4A01 Some include PTT and mic voltage. Mode Select Quick access to favorite frequencies. VFO, Tuning Knob, T4B02 Used for frequency entry Band select Antenna tuner Carrier Squelch – Mutes the receiver audio by the presence Noise blanker T4B05, or absence of a RF T4B09 signal. Filters, T2B03 2.4 kHz for SSB Help to eliminate T4B10 500 Hz for CW noise T4B08 Some variable. Squelch T2B03 , T4B03 Mutes receiver output when no signal. RIT Receive incremental tuning T4B07. change receive freq. Tuning control Select memory CH or Frequency ARO Automatic Repeater Offset Squelch T7A07 “PTT” Push to talk Microphone F + Select type of tone F + Select tone frequency Memory or VFO operation T7A10 An RF power amp can be used to increase power out Direct frequency entry In VFO operation Increase Handheld output power T7A10 • • • • • Extra battery packs. Drop-in, fast charger. Extended antenna. External microphone and speaker. Headset. Receivers Selectivity / Sensitivity Selectivity – The receivers ability to Discriminate between multiple signals. T7A04 Sensitivity – The ability to receive and detect the presence of a signal. T7A01 Increase Sensitivity Pre Amplifier Receiver T7A11 Transverter Transverter is used to extend the the frequency Capabilities of a HF transceiver. 222MHz HF Transceiver On 28 MHz Antenna connection 28 MHz in and out Transverter 222 MHz T7A06 Example 1: A Transverter is being used to allow the HF transceiver to operate on the 222MHz band. Amateur Radio Station T7B03 Fundamental overload Harmonics Spurious Emissions Extra signals produced by all transmitters If it is related to electricity, it produces noise. Good station practice. Ensure your station is not producing interference. Part 15 rules, Covers un-Licensed devices that use RF communications. • May not cause interference to licensed equipment • Must accept interference caused by licensed equipment operating properly under FCC rules T7B05 Overload interference by amateur to television T7B04 Interference by amateur to telephone, RF Filter T4A04 T7B08 What should you do if a "Part 15" device in your neighbor’s home is causing harmful interference to your amateur station? Work with your neighbor to identify the offending device B. Politely inform your neighbor about the rules that require him to stop using the device if it causes interference C. Check your station and make sure it meets the standards of good amateur practice D. All of these choices are correct A. 22 T7B12 (D) What might be the first step to resolve cable TV interference from your ham radio transmission? A. Add a low pass filter to the TV antenna input B. Add a high pass filter to the TV antenna input C. Add a preamplifier to the TV antenna input D. Be sure all TV coaxial connectors are installed properly Protocol A method for encoding, packaging, exchanging, and decoding digital signals Packet PSK31 MFSK RTTY Keyboard to Keyboard ✔ Many of the digital modes use error detection and correction. T8D11 ARQ. Automatic Repeat Request T8D08 Packet includes in the transmission Check Sum for error detection Header for sender and receiver information Automatic repeat request in case of errors. Most popular in the HF Bands Found at the bottom of the bands just above CW PSK31 most used mode on HF. Phase Shift Keying 31 baud T8D06 Sends Data at a slow rate T8D07 Automatic Packet Reporting System T8D02 Basically a packet station connected to a GPS Global Positioning System T8D03 The code used when sending CW in the amateur bands is International Morse. T8D09 The following devices can be used to transmit CW in the amateur bands: T8D10 Straight Key Electronic Keyer Computer Keyboard 28 28 T4A06 TNC connects computer with radio T4A07 An interface is needed if connected directly to sound card T8C11 A gateway is used to connect other amateur radio stations to the internet A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. T6D05 A regulator is part of a power supply to maintain a stable voltage. T4A03 Voltage fluctuations are prevented form entering radio equipment. T4A11 A fused connection in both the positive and negative leads should be connected directly to the vehicle's battery. T5A06 Mobile radio equipment uses a 12 volt power source. T2C02 A 12V. vehicle battery can be charged by connecting it to a vehicle battery, and running the vehicle. T0A09 A lead acid vehicle battery can produce explosive hydrogen gas while being charged. T0A10 A vehicle battery can get hot and give off hydrogen gas if charged, or discharged too quickly. Power Ground Safety Ground Wall Outlets Tools RF Ground Keeping all station equipment at the same RF voltage Audio distortion RF Burns Erratic computer operation T7B11 RF feedback can cause distorted transmit audio Connect all radio equipment to a common bus. Connect the bus to a good earth ground. Solid copper strap is best for grounding. T4A08 Keep Connections short. http://www.cruiser.co.za/radionet.asp Maritime Mobile http://www.mmsn.org/ Maratime Mobile http://hamuniverse.com/ A little of everything http://www.hamuniverse.com/repeater.html Ladies http://www.pinkhamsters.com/ Blogging About Amateur Radio From a Feminine Perspective! www.ylrl.org/ http://www.ylsystem.org/ T4A04 Where must a filter be installed to reduce harmonic emissions? Between the transmitter and the antenna B. Between the receiver and the transmitter C. At the station power supply D. At the microphone A. 37 T4A08 Which type of conductor is best to use for RF grounding? Round stranded wire B. Round copper-clad steel wire C. Twisted-pair cable D. Flat strap A. 38 T4A09 Which would you use to reduce RF current flowing on the shield of an audio cable? Band-pass filter B. Low-pass filter C. Preamplifier D. Ferrite choke A. 39 T4A10 What is the source of a high-pitched whine that varies with engine speed in a mobile transceiver’s receive audio? The ignition system B. The alternator C. The electric fuel pump D. Anti-lock braking system controllers A. 40 Study flash cards www.hamexam.org Radio Fundamentals Lesson 1 • T1B • T3B • T8A Rules & Regs. Lesson 2 • T1A • T1C • TID • T1E • T1F Comm. w/ Others Antennas Propagation Equipment Electricity Safety Lesson 3 • T2A • T2B • T2C • T8B • T8C Lesson 4 • T3A • T3C • T9A • T9B • T7C Lesson 5 • T4A • T4B • T7A • T7B • T8D Lesson 6 • T5A • T5B • T5C • T5D • T6A • T6B • T6C • T6D • T7D Lesson 7 • T0A • T0B • T0C