* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 13765_2016_148_MOESM1_ESM
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Ligand binding assay wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Anthrax toxin wikipedia , lookup
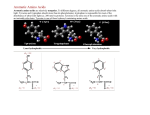
Supplementary material Biological Features, Drug-likeness, Pharmacokinetic Properties, and Docking of 2-Arylidenehydrazinyl-4-arylthiazole Analogues Mohammad Sayed Alam1 ⋅ Junaid Uddin Ahmed2 ⋅ Dong-Ung Lee1,* 1 Division of Bioscience, Dongguk University, Gyeongju 780-714, Republic of Korea 2 Department of Chemistry, Jagannath University, Dhaka 1100, Bangladesh (A) (B) (C) (D) ALA246 ALA246 5.38 2.10 GLY152 MET207 ALA246 VAL212 VAL212 ILE156 ALA216 ALA216 ALA216 MET207 ILE156 2.99 GLY209 VAL212 MET207 ILE156 GLY209 GLY209 5.17 TRP32 TRP32 TRP32 Fig. 1 (A) Binding model of compound 3c into E. coli FabH (Protein Data Bank entry: 1HNJ). The green dotted lines show the hydrogen bond, the blue dotted lines show -alkyl interactions, and the yellow dotted lines show -sulfur interactions. (B) 2D ligand interaction diagram with E. coli FabH using Discovery Studio program with the essential amino acid residues at the binding site are tagged in circles. The purple circles show the amino acids which involve in electrostatic and covalent interactions and the green circles show the amino acids which participate in the van der Waals interactions. (C) Hydrogen bond interaction showing donor (pink) and acceptor surfaces (green). (D) Hydrophobic interaction showing hydrophobic surface (brown) (A) ALA246 (B) (C) (D) ALA246 PHE213 ALA246 PHE213 PHE213 4.26 3.07 ASN247 ASN247 2.21 2.03 GLY209 5.09 5.49 GLY209 GLY209 ILE156 ILE156 MET207 ASN247 MET207 ILE156 MET207 4.82 ARG151 ARG151 ARG151 Fig. 2 (A) Binding model of compound 3j into E. coli FabH (Protein Data Bank entry: 1HNJ). The green dotted lines show the hydrogen bond, the blue dotted lines show -alkyl interactions, and the yellow dotted lines show -sulfur interactions. (B) 2D ligand interaction diagram with E. coli FabH using Discovery Studio program with the essential amino acid residues at the binding site are tagged in circles. The purple circles show the amino acids which involve in electrostatic and covalent interactions and the green circles show the amino acids which participate in the van der Waals interactions. (C) Hydrogen bond interaction showing donor (pink) and acceptor surfaces (green). (D) Hydrophobic interaction showing hydrophobic surface (brown) (A) (B) (C) Fig. 3 Energy map of compound 3c into the binding site E. coli FabH. (A) The green, red and blue color regions are energetically favorable for steric, negative electrostatic and positive electrostatic interactions, respectively. (B) The yellow and cyan color regions are energetically favorable for H-bond donor and acceptor interactions, respectively. (C) Pharmacophore model of protein-ligand interactions (A) (B) (C) Fig. 4 Energy map of compound 3j into the binding site E. coli FabH. (A) The green, red and blue color regions are energetically favorable for steric, negative electrostatic and positive electrostatic interactions, respectively. (B) The yellow and cyan color regions are energetically favorable for H-bond donor and acceptor interactions, respectively. (C) Pharmacophore model of protein-ligand interactions (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) Fig. 5 Field patterns and physicochemical properties of compound 3c. (A) The cyan, red, yellow, gold points indicating negative, positive, surface and hydrophobic fields, respectively which are potentially involve in the interactions. (B) White smoke areas indicates solvent-accessible surface. (C) Positive field (red color) points like to interact with negatives/H-bond acceptors on a protein receptor. (D) Negative field (cyan color) points like to interact with positives/H-bond donors on a protein receptor. (E) van der Waals surface filed (yellow color) points involve in the vdW interactions. (F) Hydrophobic field (gold color) points describing the regions with high polarizability/hydrophobicity (A) (D) (B) (E) (C) (F) Fig. 6 Field patterns and physicochemical properties of compound 3j. (A) The cyan, red, yellow, gold points indicating negative, positive, surface and hydrophobic fields, respectively which are potentially involve in the interactions. (B) White smoke areas indicates solvent-accessible surface. (C) Positive field (red color) points like to interact with negatives/H-bond acceptors on a protein receptor. (D) Negative field (cyan color) points like to interact with positives/H-bond donors on a protein receptor. (E) van der Waals surface filed (yellow color) points involve in the vdW interactions. (F) Hydrophobic field (gold color) points describing the regions with high polarizability/hydrophobicity.