* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Physics - Partners4results
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Mass in special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
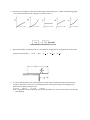
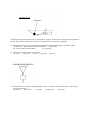
MULTIPLE CHOICE ITEMS First Term AP Physics Chapters 1-8 (2009) 1. A railroad flatcar of mass 2,000 kilograms rolls to the right at 10 meters per second and collides with a flatcar of mass 3,000 kilograms that is rolling to the left at 5 meters per second. The flatcars couple together. Their speed after the collision is (A) 1 m/s (B) 2.5 m/ s (C) 5 m/ s (D) 7 m/ s (E) 7.5 m/ s 2. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t = 0 does the object again pass through its initial position? (A) Between 0 and 1 s (B) 1 s (C) Between 1 and 2 s (D) 2s (E) Between 2 and 3 s 3. Which of the following is true for a system consisting of a mass oscillating on the end of an ideal spring? (A) The kinetic and potential energies are equal to each other at all times. (B) The kinetic and potential energies are both constant. (C) The maximum potential energy is achieved when the mass passes through its equilibrium position. (D) The maximum kinetic energy and maximum potential energy are equal, but occur at different times. (E) The maximum kinetic energy occurs at maximum displacement of the mass from its equilibrium position 4. A ball of mass m is suspended from two string of unequal length as shown above. The tensions T1 and T2 in the strings must satisfy which of the following relations? (A) Tl = T2 (B) T1 > T2 (C) T1 < T2 (D) Tl + T2 = mg (E) T 1-T2 = mg 5. Each of five satellites makes a circular orbit about an object that is much more massive than any of the satellites. The mass and orbital radius of each satellite are given below. Which satellite has the greatest speed? Mass Radius (A) ½m R (B) m ½R (C) m R (D) m 2R (E) 2m` R 6. From the top of a high cliff, a ball is thrown horizontally with initial speed vo. Which of the following graphs best represents the ball's kinetic energy K as a function of time t ? 7. When the frictionless system shown above is accelerated by an applied force of magnitude the tension in the string between the blocks is 8. (A) 2F (B) F (C) 2 F 3 (D) 1 F 2 (E) 1 F 3 A 5-meter uniform plank of mass 100 kilograms rests on the top of a building with 2 meters extended over the edge as shown above. How far can a 50-kilogram person venture past the edge of the building on the plank before the plank just begins to tip? (A) 0.5 m (B) 1 m (C) 1.5 m ( D) 2 m (E) It is impossible to make the plank tip since the person would have to be more than 2 meters from the edge of the building. 9. An asteroid moves in an elliptic orbit with the Sun at one focus as shown above. Which of the following quantities increases as the asteroid moves from point P in its orbit to point Q ? (A) Speed (B) Angular momentum (C) Total energy (D) Kinetic energy (E) Potential energy 10. A person pushes a box across a horizontal surface at a constant speed of 0.5 meter per second. The box has a mass of 40 kilograms, and the coefficient of sliding friction is 0.25. The power supplied to the box by the person is (A) 0.2 W (B) 5 W (C) 50 W (D) 100 W (E) 200 W 11. Two planets have the same size, but different masses, and no atmospheres. Which of the following would be the same for objects with equal mass on the surfaces of the two planets? I. The rate at which each would fall freely II. The amount of mass each would balance on an equal-arm balance III. The amount of momentum each would acquire when given a certain impulse (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 12. A body moving in the positive x direction passes the origin at time t = 0. Between t = 0 and t = 1 second, the body has a constant speed of 24 meters per second. At t = 1 second, the body is given a constant acceleration of 6 meters per second squared in the negative x direction. The position x of the body at t = 11 seconds is (A) +99m (B) +36m (C) - 36 m (D) - 75 m (E) - 99 m 13. Three forces act on an object. If the object is in translational equilibrium, which of the following must be true? I. The vector sum of the three forces must equal zero. II. The magnitudes of the three forces must be equal. III. All three forces must be parallel. (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and III only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 14. A 2-kilogram block rests at the edge of a platform that is 10 meters above level ground. The block is launched horizontally from the edge of the platform with an initial speed of 3 meters per second. Air resistance is negligible. The time it will take for the block to reach the ground is most nearly (A) 0.3 s (B) 1.0 s (C) 1.4 s (D) 2.0 s (E) 3.0 s 15. A horizontal force F is used to pull a 5-kilogram block across a floor at a constant speed of 3 meters per second. The frictional force between the block and the floor is 10 newtons. The work done by the force F in 1 minute is most nearly (A) 0 J (B) 30 J (C) 600 J (D) 1,350 J (E) 1,800 J 16. A diver initially moving horizontally with speed v edives off the edge of a vertical cliff and lands in the water a distance d from the base of the cliff. How far from the base of the cliff would the diver have landed if the diver initially had been moving horizontally with speed 2v? (A) d (B) 2d (C)2d (D)4d (E) can’t be determined without knowing the height of the cliff 17. Two bodies of masses 5 and 7 kilograms are initially at rest on a horizontal frictionldess surface. A light spring is compressed between the bodies, which are held together by a thin thread. After the spring is released by burning through the thread, the 5 kilogram body has a speed of 0.2 m/s. The speed of the 7 kilogram body is (in m/s) (A) 1 12 (B) 1 7 (C) 1 35 (D) 1 5 (E) 7 25 Questions 18-19: A block oscillates without friction on the end of a spring as shown above. The minimum and maximum lengths of the spring as it oscillates are, respectively, xmin and xmax. The graphs below can represent quantities associated with the oscillation as functions of the length x of the spring. 18. Which graph can represent the total mechanical energy of the block-spring system as a function of x ? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D (E) E 19. Which graph can represent the kinetic energy of the block as a function of x ? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D (E) E 20. Mars has a mass 1/10 that of Earth and a diameter 1/2 that of Earth. The acceleration of a falling body near the surface of Mars is most nearly (A) 0.25 m/s2 (B) 0.5 m/s2 (C) 2 m/s2 (D) 4 m/s2 (E) 25 m/s2 21. A uniform rope of weight 50 newtons hangs from a hook as shown above. A box of weight 100 newtons hangs from the rope. What is the tension in the rope? (A) 50 N throughout the rope (B) 75 N throughout the rope (C) 100 N throughout the rope (D) 150 N throughout the rope (E) It varies from 100 N at the bottom of the rope to 150 N at the top. 22. To weigh a fish a person hangs a tackle box of mass 3.5 kilograms and a cooler of mass 5 kilograms from the ends of a uniform rigid pole that is suspended by a rope attached to its center. The system balances when the fish hangs at a point 1/4 of the rod’s length from the tackle box. What is the mass of the fish? (A) 1.5 kg (B) 2 kg (C) 3 kg (D) 6 kg (E) 6.5 kg Questions 23-24 A ball swings freely back and forth in an arc from point I to point IV, as shown above. Point II is the lowest point in the path, III is located 0.5 meter above II, and IV is I meter above II. Air resistance is negligible. 23. If the potential energy is zero at point II, where will the kinetic and potential energies of the ball be equal? (A) At point II (B) At some point between II and III (C) At point III (D) At some point between III and IV (E) At point IV 24. The speed of the ball at point II is most nearly (A) 3.0 m/s (B) 4.5 m/s (C) 9.8 m/s (D) 14 m/s (E) 20 m/s 25. When an object of weight W is suspended from the center of a massless string as shown above. The tension at any point in the string is (A) 2Wcos (B) ½Wcos (C) Wcos (D) W/(2cos) (E) W/cos 26. An object weighing 4 newtons swings on the end of a string as a simple pendulum. At the bottom of the swing, the tension in the string is 6 newtons. What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the object at the bottom of the swing? (A) 0 (B) 0.5 g (C) g (D) 1.5 g (E) 2.5 g 27. A truck traveled 400 meters north in 80 seconds, and then it traveled 300 meters east in 70 seconds. The magnitude of the average velocity of the truck was most nearly (A) 1.2 m/s (B) 3.3 m/s (C) 4.6 m/s (D) 6.6 m/s (E) 9.3 m/s 28. A projectile is fired with initial velocity vo at an angle 0 with the horizontal and follows the trajectory shown above. Which of the following pairs of graphs best represents the vertical components of the velocity and acceleration. v and a, respectively, of the projectile as functions of time t? 29. In which of the following situations would an object be accelerated? I. It moves in a straight line at constant speed. II. It moves with uniform circular motion. III. It travels as a projectile in a gravitational field with negligible air resistance. (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III. 30. A ball falls straight down through the air under the influence of gravity. There is a retarding force F on the ball with magnitude given by F = bv, where v is the speed of the ball and b is a positive constant. The magnitude of the acceleration a of the ball at any time is equal to which of the following? (A) g - b (B) g – (bv/m) (C) g + (bv/m) (D) g/b (E) bv/m 31. The figure above shows a rough semicircular track whose ends are at a vertical height h. A block placed at point P at one end of the track is released from rest and slides past the bottom of the track. Which of the following is true of the height to which the block rises on the other side of the track? (A) It is equal to h/2 (B) It is equal to h/4 (C) It is equal to h/2 (D) It is equal to h (E) It is between zero and h; the exact height depends on how much energy is lost to friction. 32. If Spacecraft X has twice the mass of Spacecraft Y, then true statements about X and Y include which of the following? I. On Earth. X experiences twice the gravitational force that Y experiences. II. On the Moon, X has twice the weight of Y. III. When both are in the same circular orbit, X has twice the centripetal acceleration of Y. (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 33. Two pucks are attached by a stretched spring and are initially held at rest on a frictionless surface, as shown above. The pucks are then released simultaneously. If puck I has three times the mass of puck II, which of the following quantities is the same for both pucks as the spring pulls the two pucks toward each other? (A) Speed (B) Velocity (C) Acceleration (D) Kinetic energy (E) Magnitude of momentum 34. Which of the following is true when an object of mass m moving on a horizontal frictionless surface hits and sticks to an object of mass M > m, which is initially at rest on the surface? (A) The collision is elastic. (B) All of the initial kinetic energy of the less massive object is lost. (C) The momentum of the objects that are stuck together has a smaller magnitude than the initial momentum of the less-massive object. (D) The speed of the objects that are stuck together will be less than the initial speed of the less massive object. (E) The direction of motion of the objects that are stuck together depends on whether the hit is a head-on collision. Questions 35-36 A rock of mass m is thrown horizontally off a building from a height h, as shown above. The speed of the rock as it leaves the thrower’s hand at the edge of the building is v0. 35. How much time does it take the rock to travel from the edge of the building to the ground? a. 36. hv o b. h v0 c. hv 0 g d. 2h g e. 2h g What is the kinetic energy of the rock just before it hits the ground? a. mgh b. ½ mv02 c. ½ mv02 - mgh d. ½ mv02+mgh e. mgh-½ mv02 37. A weight lifter lifts a mass m at constant speed to a height h in time t. What is the average power output of the weight lifter? (A) mg (B) mh (C) mgh (D) mght (E) mgh /t 38. A block of mass 3m can move without friction on a horizontal table. This block is attached to another block of mass m by a cord that passes over a frictionless pulley, as shown above. If the masses of the cord and the pulley are negligible, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the descending block? (A) Zero (B) g/4 (C) g/3 (D) 2g/3 (E) g ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~END OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PART~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ AP Physics Term 1 Multiple Choice Section Covers Material in Chapters 1-8 ~ This test has 38 Multiple Choice Items ~ You will have 48 minutes to complete this section ~ Correct responses earn +1 point ~ Incorrect responses and items left blank earn no credit ~ You may write in this test booklet – make marks on answer sheet ~ Do not open until told to begin ~ When told to stop, promptly put pencil down ~ You will receive a notice when 5 minutes are left ______________________________________________________ Your name