* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Conservation - Miss Jones 8th Grade Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
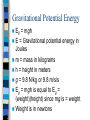
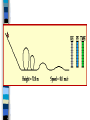
Energy Notes Energy Is the ability to do work (no energy = no work) Unit for measurement is the joule (J) Energy has no direction Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy – made up of potential and kinetic energy Example: Ball rolling down a ramp Potential Energy – energy of position or stored energy (case of chemical bonds) Kinetic Energy – energy of motion Potential Energy Potential energy is energy waiting to be released either due to position (boulder on top of a hill) or chemical make up (exothermic/endothermic bonds) Gravitational potential energy is based on height (think roller coaster) Gravitational Potential Energy Eg = mgh E = Gravitational potential energy in Joules m = mass in kilograms h = height in meters g = 9.8 N/kg or 9.8 m/s/s Eg = mgh is equal to Eg = (weight)(height) since mg is = weight Weight is in newtons Kinetic Energy Energy of motion Ek = ½ mv2 Ek = Kinetic energy in Joules m = mass in kilograms v = velocity in m/s According to order of operations you must square your velocity before multiplying mass. Some people find it easier to think of the equation as Ek = (mv2)/2 Other forms of energy Thermal (heat) energy – internal motion of atoms. The faster they move the more energy they produce Chemical energy – chemical changes that bond atoms together (photosynthesis, cellular respiration and fire) Nuclear energy – nucleus undergoes fusion or fission to release energy Electromagnetic energy – moving electrical charges (light energy). Examples include radio waves, microwaves, visible light Sound energy - vibrations Work W=F x W = work in joules F = force in newtons x = change in displacement (same direction) in meters Law of Conservation of Energy Energy may not be created or destroyed. All forms of energy can be converted into other forms. –Kinetic and potential energy conversions are among the most common. Thermal energy and conservation No system is perfect or efficient Some of the useful energy is transformed to thermal energy Energy pyramid from life science