* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
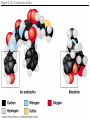
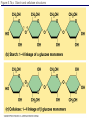
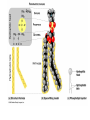
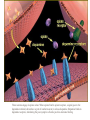
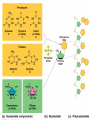
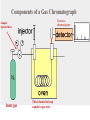
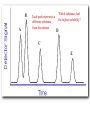
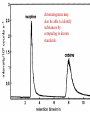
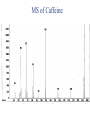
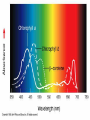
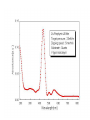
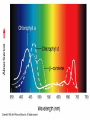
Chapter 5: Organic Analysis Figure 2.19 A molecular mimic Objective: You will be able to explain the basic properties and functions of carbohydrates Organic vs. Inorganic Organic contains Carbon AND Hydrogen 4 Types of organic compounds Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Readily available source of energy Serve as raw material for synthesis of other molecules Used as a structural component One type is called a monosaccharide What do all monosaccharides have in common? Paired Activity Create a unique monosaccharide based on the criteria discussed. After you have built your molecule, write down what YOU think makes it unique. Figure 5.4 Linear and ring forms of glucose Figure 5.7b,c Starch and cellulose structures Cellulose–laced missiles AIM 9-L/M "SIDEWINDER" CH2O H O OH H H OH H OH H H NH C O CH3 (a) The structure of the chitin monomer. gure 5.10 A–C What popular drug is created from carbohydrates? Objective: You will be able to state the properties of lipids and proteins Lipids All are hydrophobic Three types: Triacylglycerols (fats) Phospholipids Steroids FATS Triacylglycerol or fat is made up of 3 fatty acids and one glycerol Are significant to forensics because many substances are stored in fats PCB’s Marijuana, Cocaine, etc… Because they are stored, there affect may be long lasting 3D lipids Proteins Made up of a specific sequence of amino acids Each protein has its own specific number of amino acids and in its own unique order This sequence will lead to a specific shape that will give the protein its function Ex. Enzymes, hormones Proteins Proteins have many functions in the body A key function is that they act as chemical messengers Many of the illegal drugs cause their affect because they act as messengers Overview of cell signaling EXTRACELLULAR FLUID 1 Reception CYTOPLASM Plasma membrane 2 Transduction 3 Response Receptor Activation of cellular response Relay molecules in a signal transduction pathway Signal molecule Figure 11.5 Drugs that act as messengers Opiates Morphine Heroin These chemicals help reduce pain Three neurons engage in opiate action. When opiates bind to opiate receptors, a signal goes to the dopamine terminal (shown here as part of another neuron) to release dopamine. Dopamine binds to dopamine receptors, stimulating the post-synaptic cell and a positive emotional feeling Nucleic Acids DNA Stores genetic information Double stranded Is transcribed to synthesize proteins __________________________________________ RNA Translates DNA and carries out protein synthesis Single stranded Paired Activity Use DNA kits to build DNA Create a key for the parts Hints Yellow is for covalent bonds between the sugar and the phosphate Look at number of bonds for each part You have enough to create 6 nucleotides on each side Objective: You will be able to describe the theory of chromatography. Analyzing Organic Compounds Quality versus quantity Quality identifies exactly what it is Quantity may be important because larger amounts of illegal substances may carry longer jail time Many times substances are in fact mixtures Drug dealers may “cut” the drugs This requires a different technique to identify the substance Chromatography This technique has the ability to purify substances It rips each component from mixture and separates it single components Theory of chromatography Chemical substances partially escape into surroundings when: Dissolved in a liquid Absorbed into a solid Dissolved in liquid Dissolved on a solid Gas chromatography TLC Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) Separation of mixture is done by using a stationary solid phase (paper) and moving liquid phase Still based on solubility of each substance in the liquid Substances that are highly soluble move faster Analyzing the TLC sample A measurement of how far each component of a substance would then be taken This will determine the RF value of a substance A substances RF value can be used to HELP determine what it is Not unique and other substances may have same RF value A direct comparison can also be made by running a known sample versus and unknown Activity: We need to find out who wrote that note!!! Work with your group to develop a method to determine whose pen was used. You need to: Give the names of the suspects State which method you are going to use Describe the “science” behind the method Provide an outline of steps you are going to use Gas Chromatography Can separate substances because of differences in solubility in a liquid Force air to continuously move in one direction Gas phase is moving phase, liquid phase is stationary phase The chemical race High solubility means it wants to stay in liquid This makes the highly soluble substance move slower Objective:You will be able to explain how GC can be used for the quantitative and qualitative analysis of compounds. Do Now: Read “Gas Chromatography” on p. 123 and only first paragraph on 124 Differentiate between the two types of columns used in GC Activity Work in pairs to create a parts list for the gas chromatography machine Make sure you draw each part and give its function Use the diagram on p. 136 to help you Gas Chromatography Uses a stationary liquid phase and a moving gas phase Can separate substances because of differences in solubility in a liquid High solubility means it wants to stay in liquid The chemical race Force air to continuously move in one direction Gas phase is moving phase, liquid phase is stationary phase Need large enough area so that the molecules can be fully separated The GC Machine Sample is placed into the injector and travels through the column Carrier gas is typically nitrogen or helium Column is heated to keep substance being tested in a gaseous state As each substance in the sample emerges from the column, it enters a detector Here it is ionized by a flame that creates an electric signal This signal creates a chart called a chromatogram Components of a Gas Chromatograph Creates a chromatogram Sample injected here Inert gas This is heated to keep sample in gas state Chromatograms Chromatograms are plotted based on retention time Usually has a series of peaks which represents each substance from a mixture Qualitative analysis done by comparing retention time with known samples Not 100% reliable because two substances may have same retention time Quantitative analysis is done by viewing how high the peak is B A Each peak represents a different substance from the mixture Which substance had the highest solubility? D C E Mixture of material in marijuana chromatograms may also be able to identify substances by comparing to known standards. Material must be a gas to enter GC Some material like paint, fibers and plastics cannot be readily dissolved into a liquid to go into the GC machine A technique called pyrolysis heats these materials so they decompose into gaseous materials These materials are then injected into the GC machine Objective: You will be able to explain how the mass spectrometer can be used to specifically identify a substance. Do Now: Read the chapter summary on p. 142-143 Give three things that you learned the best in this chapter Mass Spectrometer As the gas leaves the GC, it enters the MS Within the MS, a beam of electrons is shot at the substance breaking it down into fragments These fragments pass through an electric field which separates them by their masses The fragment masses are then recorded on a graph Each substance breaks down into its own characteristic pattern MASS MS of Caffeine Objective: You will be able to discuss the various properties of light Do Now: Read “Electrophoresis” on p. 131-132 How are the processes of electrophoresis and TLC similar? Different? What is electrophoresis used for? Pair Work Read page 136-137 (The Spectrophotometer) Explain how a spectrophotometer works by giving the function of the: Radiation source Monochromator Sample cell Detector and Recorder Explain how samples are prepared Objective: You will be able to explain how the ultraviolet, visible and infrared spectrophotometer can be used in qualitative analysis. Do Now: Read “Absorption of electromagnetic radiation” on p. 135-136 How does spectrophotometry work? Relate energy requirement to absorption