* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Full_India
Vaishnavism wikipedia , lookup
C. P. Ramaswami Iyer wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Mahabharata wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
Dharmaśāstra wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Pratyabhijna wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
Tamil mythology wikipedia , lookup
Dayananda Saraswati wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
LGBT themes in Hindu mythology wikipedia , lookup
Hindu deities wikipedia , lookup
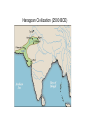
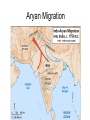
Ancient India India: Modern Map Monsoon Map Harappan Civilization (2500 BCE) Aryan Migration The Aryans • Light Skinned nomads who entered India from the North in 1500 BCE. • The Aryans spoke a language called Sanskrit and counted their worth in cows. • The Aryans conquered dark skinned, town-dwelling Dasas when they entered India • The Aryans had a rigid class (or caste) system, which determined how people lived their lives (jobs, socializing….). The Caste System Ganges River, Varanasi Bodhgaya, India Origins of Hinduism • No founder • No single sacred text • Collection of practices and beliefs • Evolved over time Sacred Texts of Hinduism The Vedas: Brought to the Indian subcontinent by the Aryans. The Vedas are four collections of prayers and instructions for performing rituals. The Rig Veda is the most important, which includes Purusa. Mahabharata: A great epic Indian story that explains the struggles that took place in India as the Aryans moved South. One part is the Bhagavad Gita, about a warrior prince about to go to war; chariot driver is Krishna, god in human form. Ramayana: The great epic story of Rama and Sita, which stresses the importance of dharma. Vedas • • • • Prayers Rituals Existed orally Written in Sanskrit around 300 BCE The Vedas Rama and Sita, with Hanuman, from the Ramayana Krishna and Arjuna, from the Bhagavad Gita Sources of Authority: Upanishads • Philosophical commentary on Vedas begun around 8th C. BCE • Means “sitting near;” told in dialogues • Explore the relationship between humans and gods • Conclusion: Atman the same as Brahman Major Beliefs of Hinduism • Reincarnation: The process in which people are reborn into new bodies when they die. • Karma: System that determines whether someone reincarnates into a higher or lower caste. • Dharma: • Samsara: One’s obligations in life—helps to determine karma—depends on caste Cycle of birth, death, and re-birth • Moksha: Goal of Hinduism—end of samsara—when the soul (atman) becomes one with the one true reality Goal of Life: Moksha • Understand Ultimate Reality, pierce through maya (illusion) • Free oneself from samsara (cycle of rebirth) Paths to Moksha • Bhakti-yoga: path of devoting oneself to God • Raja-yoga: path of meditation and proper knowledge • Karma-yoga: path of acting correctly not for the result of action Hindu Pantheon • Thousands of Gods/Goddesses—flexibility of worship • All part of the Ultimate Reality, Brahman • Individual human soul, Atman, also part of this Ultimate Reality • Main Gods: Brahma, Vishnu, Shiva Brahma, the Creator Vishnu, the Preserver Siva/Shiva, the Destroyer Siva/Shiva, as ascetic Ganesh Mother Goddesses: Shakti Durga slaying a demon Kali Hindu Temple, Madras Puja: Worship Sadhus White Temple, Jaipur Hindu Temple, Trimbukeshwar Bathers, Ganges River