* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
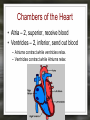
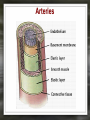
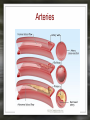
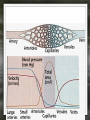
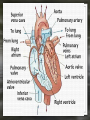
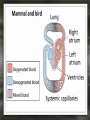
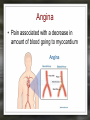
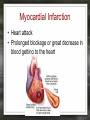
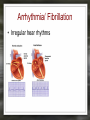
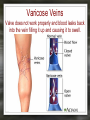
Notes: The Circulatory System The circulatory system is responsible for transporting materials through the entire body Functions of the Circulatory System • The circulatory system functions in the – Delivery of oxygen – Delivery of nutrient molecules – Delivery of hormones – Removal of carbon dioxide, ammonia and other metabolic wastes Parts of the Circulatory System • 3 parts of the Circulatory system: – Heart – Blood – vessels Fun Facts • The Heart is an amazing organ. It's job is to pump your blood and keep the blood moving throughout your body. • Your heart beats about 100,000 times in one day and about 35 million times in a year. During an average lifetime, the human heart will beat more than 2.5 billion times Notes: BLOOD Characteristics • Metallic (even in taste) • Slightly alkaline (pH 7.4) • Approximately 5 Liters Fun Fact • Your body has about 5.6 liters (6 quarts) of blood. This 5.6 liters of blood circulates through the body three times every minute. Functions – Medium of transport for oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste – Maintain – body temp, pH, and fluid volume – Prevent – blood loss, infections Make up of Blood Components of blood • Plasma – 55% of blood, fluid matrix, 90% water, non-living • Formed elements – 45% of blood, solid, living, produced by bone marrow – Erythrocytes (RBC) – Leukocytes (WBC) – Platelets Red Blood Cells • Red Blood Cells are responsible for carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide. • Red Blood Cells pick up oxygen in the lungs and transport it to all the body cells. Life Span of an RBC • Life-span of an erythrocyte is only 120 days, after which they are destroyed in liver and spleen. White Blood Cells (leukocytes ) • are larger than erythrocytes, They function in the cellular immune response. • White blood cells (leukocytes) are less than 1% of the blood's volume. Platelets • Platelets are blood cells that help stop bleeding. – When we cut ourselves we have broken a blood vessel and the blood leaks out. – To plug up the holes, the platelets start to stick to the opening of the damaged blood vessels. – As the platelets stick to the openings they attract more platelets, fibers and other blood cells to help form a plug to seal the broken blood vessel. Blood Types • A, B, AB, O (others are rare) – AB – universal recipient, least common – O – universal donor, most common Rh • Named for Rhesus Monkey • Rh+ - 85%, have antigens • Rh- - 15%, don’t have antigens • -woman and +man have will have problems with pregnancy Heart • Characteristics – Fist sized – Less than 1 pound – Behind and left of sternum – Surrounded by pericardium – sac filled with thin layer of fluid Heart - Layers • Epicardium – outermost, covered by fat • Myocardium – middle, actual cardiac muscle, contracts to pump blood • Endocardium – inner most, contact with blood, connective tissue replaceable Chambers of the Heart • Atria – 2, superior, receive blood • Ventricles – 2, inferior, send out blood – Atriums contract while ventricles relax. – Ventricles contract while Atriums relax Make up of the heart • Blood is brought back to the heart by veins & carried away from the heart by arteries Arteries Structure of a vein Arteries Capillaries • Capillaries are tiny blood vessels. Only 1 RBC fits though at a time • Capillaries are only 1 cell thick • Capillaries connect arteries to veins. Heart • Pulse rate – average number of heart beats in a minutes – 72 beats/min. is average for an adult • Circulation – path blood takes when moving through the body Circulation - pathways • Pulmonary – takes blood to and from lungs for gas exchange • Systemic – takes oxygenated blood to rest of the body and brings deoxygenated blood back to the heart Cardiac Cycle • All events associated with flow of blood in heart in one complete heart beat – Systole – contraction phase – Diastole – relaxation phase Angina • Pain associated with a decrease in amount of blood going to myocardium Myocardial Infarction • Heart attack • Prolonged blockage or great decrease in blood getting to the heart Heart Murmur • Valves not closing properly leading to a leak Arrhythmia/ Fibrillation • Irregular hear rhythms Varicose Veins Valve does not work properly and blood leaks back into the vein filling it up and causing it to swell. Healthy Heart • It is your job to keep your heart healthy & there are three main things you need to do: – Exercise on a regular basis. (walk, jog, run, bike, skate, jump, swim). – Eat Healthy. Stay away from high fat foods and have your cholesterol checked regularly – Don't Smoke! Don't Smoke! Don't Smoke! CW: Heart Anatomy & Flow of Blood AMAZING FACTS • One drop of blood contains a half a drop of plasma, 5 MILLION Red Blood Cells, 10 Thousand White Blood Cells and 250 Thousand Platelets. • You have thousands of miles of blood vessels in your body. Anywhere between 75,000 100,000 miles. The earths diameter is 25,000 miles. So your blood vessels could circle around the equator 3 to 4 times! • Keep your heart healthy...it's going to have to beat about 3 BILLION times during your lifetime!