* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Risk and Return
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
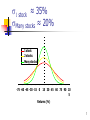
CHAPTER 6 Risk, Return, and the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) 1 Topics in Chapter 6 Basic return measurement Types of Risk addressed in Ch 6 Stand-alone (total) risk Portfolio (market) risk Relationship between risk and return: CAPM/SML 2 Investment Returns Returns may be: actual or expected. Returns can be expressed in: dollars or percentage. Returns include changes in asset value. 3 What is investment risk? Risk exists any time returns are not known with certainty. Why is risk important? 4 Stand-Alone Risk Stand-alone (total) risk is the risk facing an investor (firm) who owns only one asset. Measures of stand-alone risk: Standard deviation Variance Coefficient of variation (CV) 5 Adding Stocks to a Portfolio What happens to the risk of a one-stock portfolio as additional randomly selected stocks are included? 6 s1 stock ≈ 35% sMany stocks ≈ 20% 1 stock 2 stocks Many stocks -75 -60 -45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45 60 75 90 10 5 Returns (%) 7 Risk vs. Number of Stock in Portfolio sp Company Specific (Diversifiable) Risk 35% Stand-Alone Risk, sp 20% Market Risk 0 10 20 30 40 2,000 stocks8 Stand-alone risk = Market risk + Diversifiable risk Market risk is that part of a security’s stand-alone risk that cannot be eliminated by diversification. Firm-specific, or diversifiable, risk is that part of a security’s stand-alone risk that can be eliminated by diversification. 9 Beta Market risk is measured by beta. Beta indicates: A stock’s contribution to the risk of a diversified portfolio The stock’s volatility relative to the market: beta > 1.0 high risk beta = 1.0 average risk beta < 1.0 low risk 10 Using a Regression to Estimate Beta To estimate a stock’s beta, plot the stock’s returns on the Y axis and market returns on the X axis. The slope of the line of best fit as estimated through regression is the stock’s beta coefficient, or b. 11 Use the SML to calculate an asset’s required return. The Security Market Line (SML) is part of CAPM. The equation for the SML is: ri = rRF + (RPM)bi ri is the required return on security i rRF is the risk-free interest rate RPM is the risk premium on the market bi is the beta for security i 12