* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Federal Budget and Economic Policy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
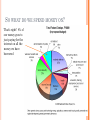
FEDERAL BUDGET AND ECONOMIC POLICY SO WHAT DO WE SPEND MONEY ON? That’s right! 8% of our money goes to just paying for the interest on all the money we have borrowed TYPES OF SPENDING Mandatory Spendingprograms that require that the federal government pay back the contributions previously taxed from the citizens Discretionary Spendingspending on programs like defense, roads, schools, and running the government DISCRETIONARY SPENDING Of discretionary spending, National Defense is clearly the largest expenditure. PAST PRESIDENTIAL ECONOMIC PROGRAMS Trust Busting/Progressivism T. Roosevelt Early 1900’s These efforts were results of the late 1800’s Populist votes and growing demands for industrial reforms New Deal FDR 1930’s Massive help from government programs was needed and became key social efforts. Fair Deal H.Truman 40’s Early efforts at civil rights equality began in federal programs such as the military & housing New Frontier J.Kennedy 60’s Civil rights laws get passed. Early forms of affirmative action and environmental plans. Great Society L.Johnson 60’s Vast attempts were made to rebuild inner cities, give jobs, and provide assistance. Price Controls New Federalism R.Nixon 70’s Rapid inflation was met with attempts to stop price increases through mandates Whip Inflation Now (WIN) G. Ford 70’s More federal attempts at stopping rapid price increases were required but did not help. Reaganomics/TrickleDown Supply Side/Devolution R. Reagan 80’s The goals were to cut federal programs and business regulations. Tax cuts in the name of econ expansion were central programs. TWO SCHOOLS OF ECONOMIC THOUGHT Laissez-Faire, Supply-side policies, Reaganomics Allows the private sector to compete and run the economy on their own Taxes should be low, profit motives should be rewarded, and helping the rich conduct more business will help the middle class and poor find more jobs. Trickle down Economics/Voodoo Economics Reduce regulations on business and business will be able to create more jobs (and therefore wealth) for poorer TWO SCHOOLS OF ECONOMIC THOUGHT Keynesian Named after economist John Maynard Keynes New Deal type policies Argues that when the economy stalls and falls into recessions/depressions, Congress should lower taxes and create jobs. When the economy overheats and suffers from inflation, congress should raise taxes and cut jobs. Assumption is that laissez-faire policy leaves the nation vulnerable to drastic cycle swings. Monetary Policy When the economy is in recession, government should force lower interest rates (the Fed does that) and buy bonds from the public (like the Bailout) Most conservatives also believe in this intervention 9 REQUIREMENTS FOR A MARKET ECONOMY 1. Establishing Law and Order 2. Defining Rules of Property 3. Enforcing Contracts 4. Governing Rules of Exchange 5. Setting Market Standards 6. Providing Public Goods 7. Creating a Labor Force 8. Ameliorating Externalities 9. Promoting Competition PROPERTY AND PUBLIC GOOD To provide public goods often the government must seize private property, called expropriation. The governmental power that the government claims in order to expropriate is called eminent domain. HOW DOES THE GOVERNMENT PROMOTE OR DISCOURAGE ACTIVITIES Categorical Grants-in-Aid- A way for the Federal government to lure states into promoting policies (ex: highway funds for lowering BAC level of drunk drivers) Subsidies- Government grants of cash or other valuable items to promote activities desired by the government. (ex: My house!, agriculture subsidies to promote farming and keep food prices low) Taxes- usually done at the state level, called sin taxes. (ex: cigarette taxes, alcohol taxes) MONETARY POLICY Federal Reserve System- (the Fed) 12 Banks that facilitate exchanges of cash, checks, and credit; it regulates member banks; and it uses monetary policies to fight inflation and deflation. Discount Rate- the interest on loans given by the Fed to member banks. Reserve Requirement- the proportion of money that the Fed requires member banks hold in their vaults (ex: 5% of the banks holdings) Open-market operations- the buying and selling of Treasury Securities to absorb or release dollars. Federal Funds Rate- the interest rate that banks can charge one another on loans. TAXES Progressive- Taxation that hits the upper income brackets more heavily. (Ex: Federal Income Tax) Regressive- Taxation that hits the lower income brackets more heavily. (Ex: social security) Why is income tax progressive? Policy of redistribution- an objective of the graduated income tax whereby revenue is raised in such a way as to reduce the disparity of wealth between the lowest and the highest income brackets.