* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 40
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
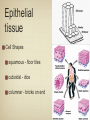
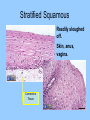
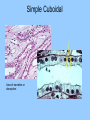
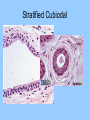
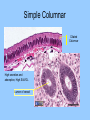
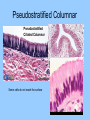
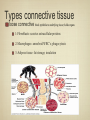
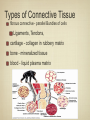
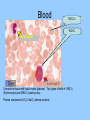
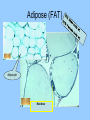
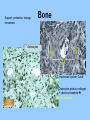
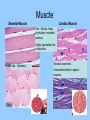
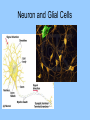
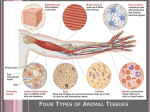
Histology The study of tissues Homeostasis • Maintenance of a constant internal environment. • We Don’t Like Stress. • Physiology identifies and studies the mechanisms of homeostasis. • Controlled by Two Systems – A. – B. Levels of Organization Cells Tissues organs organ system organism Tissues groups of cells with a common structure and function Four categories epithelial connective muscle nervous Epithelial tissue location: outside of body, line organs and cavities Function: barrier, absorption or secretion – Glandular secretory portion of gland 2 types simple - one layer stratified - multiple layers “pseudostratified” appears stratified due to cells of various lengths Epithelial tissue Cell Shapes squamous - floor tiles cuboidal - dice columnar - bricks on end Simple Squamous Leaky to allow diffusion/osmosis. Capillaries, alveoli. May be keratinized on body surfaces. Connective Tissue Basement Membrane Stratified Squamous Readily sloughed off. Skin, anus, vagina. Connective Tissue Simple Cuboidal Area of secretion or absorption. Stratified Cubiodal Simple Columnar Ciliated Columnar High secretion and absorption, High SA/VOL Lumen of vessel Pseudostratified Columnar Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Some cells do not reach the surface Connective Tissue MOST ABUNDANT TYPE OF TISSUE. binds and supports other tissues, TRANSPORT, FRAMEWORK, STORE ENERGY cells create a matrix/ web of fibers living web of fibers.] 3 kinds of fibers collagenous fiber - made of collagen Elastic fibers - Elastin Protein reticular fibers - Thin collagen fibers [Matrix non- Types connective tissue loose connective binds epithelia to underlying tissue; holds organs 1-Fibroblasts- secretes extracellular proteins 2-Macrophages- amoeboid WBC’s; phagocytosis 3-Adipose tissue- fat storage; insulation Types of Connective Tissue fibrous connective - parallel Bundles of cells Ligaments, Tendons, cartilage - collagen in rubbery matrix bone - mineralized tissue blood - liquid plasma matrix Collagen Tough, somewhat flexible protein. Provides the toughness of meats. Very strong, resists longitudinal stress (tensile strength). Underlies epithelial tissue. Elastic fibers Long threads of elastin. Easily returns to original shape (rubberband). This is from an aorta. Also found in skin and lungs. Small, unbranched. Secreted by fibroblasts. Nuclei of Fibroblast Loose Connective Tissue (areolar) • Loose web of fibers (all 3) • Fills space between organs (Styrofoam peanuts). Gel-like matrix. • Composed of elastin (elasticity), collagen (strength), reticular fibers (support/form). • Edema: excess interstitial fluid absorbed by LCT Dense Connective tissue Fibrous Connective Tissue. Bundles of collagenous fibers. Secreted by fibroblasts. Non-elastic. Resists pulling forces Fxn: strong attachment between structures (tendons & ligaments) Nuclei of Fibroblast Hyaline Cartilage Elastic cartilage Chondrocyte Large amount of collagen, embedded in chondroitin sulfate. Provide rigid support. Nose, ear, trachea, interverterbral disks. Reduces friction on ends of long bones, absorbs shock Blood R.B.C’s W.B.C. Neutrophil Eosinophil Connective tissue with liquid matrix (plasma). Two types of cells RBC’s (Erythrocytes) and WBC’s (Leukocytes) Plasma composed of H2O, NaCl, plasma proteins Adipose (FAT) Adipocyte Nucleus Support, protection, storage, movement. Bone Osteocytes Haversian System/ Canal Osteocytes produce collagen + calcium phosphate hydroxyapatite Muscle Tissue long cells called muscle fibers capable of contracting when stimulated 3 types Smooth - involuntary Skeletal - voluntary cardiac - walls of heart Muscle Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Fxn: Motion, Heat production, maintain posture. Highly specialized for contraction Aka. Voluntary Striated, branched. Intercalated disks to speed impulse. Smooth Muscle aka: visceral, unstriated. Surround hollow structures (stomach, blood vessels, intestine, bladder. Nervous tissue neuron or nerve cell specialized to transmit nerve impulses Dendrites: transmit impulses from tips to rest of neuron Axons: transmit impulses toward another neuron or effector Neuron and Glial Cells Nervous Tissue Neuromuscular Junction Create a presentation: use microscope pictures Show the All types of epithelial: simple squamous, simple cuboidal, stratified squamous, simple columnar tell what they are where they would be located SHow types of connective tissue and what they do: adipose, cartilage, loose connective, ground bone (no longer a ground bone slide) show the 3 kinds of muscle tissue and how to tell them apart: Skeletal, cardiac, smooth Show a neuron - what are the axons and dendrites? - Use a web picture • Organ systems…... • Digestive-food processing • Circulatory-internal distribution • Respiratory-gas exchange • Immune/Lymphatic-defense Regulation of Internal Environment Interstitial fluid: internal environment of vertebrates; exchanges nutrients and wastes Homeostasis: “steady state” or internal balance Negative feedback: change in a physiological variable that is being monitored response counteracts the initial fluctuation; i.e., body temperature i.e., uterine contractions at childbirth Positive Feedback Positive feedback: physiological control mechanism in which a change triggers mechanisms that amplify the change; Metabolism: sum of all energy-requiring biochemical reactions Size vs. Metabolic Rate Inverse relationship Small = high metabolic rate Large = low metabolic rate Endotherms: bodies warmed by metabolic heat Ectotherms: bodies warmed by environment • Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): minimal rate powering basic functions of life (endotherms) • Standard Metabolic Rate (SMR): minimal rate powering basic functions of life (ectotherms) Countercurrent exchange Counter Current Common process in multiple systems Heat exchange example