* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2004 m
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
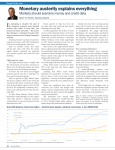
ECONOMIC AND MONETARY UNION Bachelor studies, 2013/14 academic year, autumn semester, Vilnius University, Institute of Political Science and International Relations. Lecturer: Assoc. Prof., Dr. Stasys Kropas, [email protected], phone: 8 685 00624 Time and location: Monday 16.45-18.15; Vokiečių 10, room 102. Subject Outline: This course gives a brief overview of the movement towards the creation of an Economic and Monetary Union. It also deals with theoretical considerations of the pros and cons of the creation of the common currency area and its impact on social welfare states, European models of society and regime changes. Moreover, it considers the historical experience of the monetary unions and impact of the EMU on the process of monetary integration in the other parts of the world. It then describes the structure of the European monetary authorities and, in particular, of the European Central Bank. It also considers implications for other areas of economic policies, such as fiscal, labor markets and structural policies. Also, the process of the EU enlargement in relation to the accession of new member states to the euro area is discussed. Finally, recent shock effects on euro zone and it member states also the reform measures toward complete monetary union are presented . Aims and objectives: The aims of this course is to: introduce students to the organizational and institutional structure of the Economic and Monetary Union; equip students with the theoretical arguments relevant to the debate about EMU; provide students with the relevant information and knowladge to enable them to analize, understand and follow debates on current EMU issues; allow students to develop economic concepts and analysis skills that will enable them to form opinions on the future of European integration. Literature: The basic textbook: Paul de Grauwe. Economics of Monetary Integration. Oxford University Press, Ninth Editon, 2012. Purchase of this book recommended. Earlier editions of this book also could be used for a studies. All other sources are easily accessible by internet. Some of them contains direct links from this program. Course requirements: 40% written exam, 40% a term paper, 20% periodic in-class reports of work-inprogress and performance in seminars. Basic knowlage of macroeconomy is required. Plan of the semester: No. Topics 1. Introduction to class. Discussion on the course outline and the work for the coming course 2. Lessons from monetary unions in the past and present 3. The long and winding road to EMU: -The European payments union: between international financial diplomacy and integration -Revival of European interests in monetary cooperation and the SNAKE experience -The political economy of the European Monetary System 4. Costs and benefits of monetary union L, S L Hours 2 L,S 2 L,S 2 L,S 2 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. S S S S S S 2 2 2 2 4 2 The fragility of incomplete monetary union The structure of the ESCB Monetary policy in the euro area Fiscal policy The euro and financial markets Macroeconomic and structural policies. Labour market 1 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Role of the payments systems The euro as an international currency Enlargement and the European integration process. ERMII Assessment of the functioning of the EMU Final discussion. Reserve, final exam Total L,S S S S 2 2 2 2 2 32 Topics to be discussed: 2. Lessons from monetary unions in the past and present International monetary system at current juncture. How international monetary system is going to be reformed and why? What are main lessons from monetary unions in the past? Specific features of the EMU compare with other monetary unions in the past and present. Does the move towards regional monetary stability is a reasonable response to global turbulences? Monetary integration tendencies in different parts of the world. Topic for discussion: How Asian regional monetary integration is proceeding? - Paul De Grauwe, 90-99. - IMF, 2013. WEST AFRICAN ECONOMIC AND MONETARY UNION (WAEMU) Staff Report on Common Policies for Member Countries, IMF Country Report, April. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/2013/cr1392.pdf - IMF, 2010. EASTERN CARIBBEAN CURRENCY UNION (ECCU). Staff Report for the 2010 Discussion on Common Policies of Member Countries, September 17, Washington. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/2011/cr1130.pdf - Buiter, W. H. 2010. Economic, Political, and Institutional Prerequisites for Monetary Union among the Members of the Gulf Cooperation Council. In Currency Union and Exchange Rate Issues: Lessons for the Gulf States, edited by R. MacDonald and A. Al Faris. Cheltenham, UK and Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar, 29–69. - Yung Chul Park, Chi-Young Song, 2011. Prospects for Monetary Cooperation in East Asia,ADBI Working Paper Series, No. 314, October. http://www.adbi.org/files/2011.10.21.wp314.prospects.monetary.cooperation.east.asia.pdf 3. The long and winding road to EMU The European payments union: between international financial diplomacy and integration. Why EPU? The experience of inter-war period and Marshall Plan as precursors for the establishment of the EPU. The EPU system: institutions and principle. The EPU and intra-European trade: problems and EPU’s contribution to finding of solutions. The US role in fostering the European integration. Revival of European interests in monetary cooperation and the SNAKE experience. The external dimension in late 1960s and early 1970s: the failure of the Bretton Wood’s system. The monetarist vs. economist approach to monetary integration. The Werner’s Plan and the establishment of the SNAKE. Why did the SNAKE fail and what did it achieve? The political economy of the European Monetary System. Towards the establishment of the EMS: the issue of macroeconomic policy convergence. The institutional and operational framework of the EMS. The Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM): credibility, disinflation and convergence. The Black Wednesday: a vindication of the British view? The crisis of the EMS: reasons and implications. Topic for discussion: The SNAKE’s failure was due to the fact that it was a half-way between flexible exchange rates and monetary union. Do you agree? 2 Baldwin R., Wyplosz C., Economics of European Integration, second edition, McGraw-Hill education, 2004, 293-346 p. 4. Costs and benefits of monetary union. The Dolour’s report. From Keynesianism to monetarism. Optimal currency area properties: mobility of labour and other factors of production, price and wage flexibility, economic openness, diversification in production and consumption, similarity in inflation rates, fiscal integration, and political integration. European Monetary Union: costs and benefits. Different preferences of countries about inflation and unemployment; differences in labour market institutions; differences in legal system different fiscal systems, seignorage problem. Elimination of transaction costs, welfare gains from less uncertainty, benefits of international currency, economic growth and trade effects. How to create a monetary union? shock vs. gradualism; the institutional structure; economic conditions for an optimum currency area. Price and wage rigidities, labour mobility, shocks and labour market flexibility, nominal and real depreciation. Why convergence requirements? How to organize relations between “ins” and “outs”? Topic for discussion: Costs and benefits for Lithuania to join euro zone. Please, discuss. Paul De Grauwe, 23-81; 133-150; 5. Fragility of incomplete monetary union . Fixed exchange rate regimes as incomplete monetary union. The many dimensions of political union. The theory of optimal currency areas and political union. How does political integration affect the optimality of a monetary union? Topic for discussion: Assessment of the currency board regime from the point of view of incompleteness. Paul De Grauwe, 105-132. 6. The structure of the ESCB. The European monetary institute. European central bank: centralization vs. decentralized approach; credibility vs accountability. The design of the ECB: The Maastricht Treaty; why has a German model prevailed? Independence and accountability. Financial resources. The structure and voting procedures of the ECB. Eurosystem. The institutional context of the European Union. The interaction of the ECB with other European institutions. Bank supervision and financial stability in Euro Area. EU level macro-prudential oversight. European Systemic Risk Board. How important is the adoption of the EU Constitution for efficient functioning of the EMU? The eurosystem and the Fed. Topics for discussion: The extent to which the ECB is independent depends on four factors: institutional, functional, financial and personal independencies. Discuss with reference to the Maastricht Treaty and ESCB/ECB protocol; Why and how ECB is different from the other central banks in the world? - Paul De Grauwe, 151-173. -The ECB’s relations with European Union institutions and bodies: trends and prospects, ECB Monthly bulletin, January 2010. -Rotation of voting rights in the Governing Council of the ECB, ECM Monthly bulletin, July 2009. -The European Central Bank - History, role and functions, October 2004, ECB. http://www.ecb.int/pub/pdf/other/ecbhistoryrolefunctions2004en.pdf 3 7. Monetary policy in the euro area The relation between economic, monetary and political integration: the triangle between Market, Money and the State. The “impossible trinity”: capital mobility, fixed exchange rates and monetary autonomy cannot be reconciled. Why price stability? Implications for monetary policy in the euro zone: ECB strategies and instruments. Asymmetries in the transmission mechanism and optimal monetary policies. Decision making process of the Euro system. The monetary policy instruments of the Euro system: open market operations, standing facilities, minimum reserves. Elements of liquidity management. Eligible counterparties and assets. Cross-border use of collateral: the CCBM. Unconventional policy measures. Outright monetary operations. Topic for discussion: Should the price stability remain the only main goal of the ECB? - Paul De Grauwe, 191-221. -The implementation of monetary policy since August 2007, ECB Monthly bulletin, July 2009. -The ECB’s monetary policy stance during the financial crisis, ECB Monthly bulletin, January 2010. -Price stability and growth, ECB Monthly bulletin, May 2008. -The Monetary Policy of the ECB, 2nd edition, January 2004 http://www.ecb.int/pub/pdf/other/monetarypolicy2004en.pdf 8. Fiscal policy Implications for fiscal policies in the euro zone: fiscal discipline vs. stabilization. How to ensure fiscal discipline. Fiscal policy and economic growth. Role of the Stability and growth pact. Community budget. Risks of default and bailout in a monetary union. The reform of the stability and growth pact. Topics for discussion: -The Stability and growth past is necessary to avoid moral hazard and destabilisation of the euro zone economy. Discuss. - German debt is the gold standard in Europe. - Paul De Grauwe, 207-230. -One monetary policy and many fiscal policies: ensuring a smooth functioning of EMU, ECB Monthly bulletin, July 2008. -Artis M., Buti M., 2000: Close to Balance or in Surplus: A Policy Maker’s Guide to the Implementation of the Stability and Growth Pact. – Journal of Common Market Studies, 38(4) November. - Ensuring fiscal sustainability in the euro area – ECB Monthly Bulletin, July, 2011. -The Relationship Between Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policies in Euro Area. – ECB Monthly Bulletin, February, 2003. 9. The euro and financial markets EMU and financial integration in Europe. Why financial integration is important in a financial sector in the euro zone? Stability of the financial system. Indicators of the level of financial market integration. Obstacles for further integration. Role of the euro system in the field of supervision of the financial sector. EU framework for crisis management. New supervisory architecture in Europe. Europe Financial Stability Fund. European Stability Mechanism. Banking union. Topics for discussion: It falls to the bond market to provide the discipline that the stability pact could not and the ECB will not; The political and economic implications of the creation of banking union. 4 - Paul De Grauwe, 231-245. -Financial integration in Europe, ECB, April 2013. http://www.ecb.int/pub/pdf/other/financialintegrationineurope201304en.pdf; - What kind of European monetary union? J .PISANI-FERRY, A. SAPIR, N.VÉRON, G. B. WOLFF, BRUEGEL, JUNE 2012. http://www.bruegel.org/publications/publication-detail/publication/731-whatkind-of-european-banking-union/; -A Roadmap towards a Banking Union. COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL, EUROPEAN COMMISSION, Brussels, 2012. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2012:0510:FIN:EN:PDF 10. Macroeconomic and structural policies. Labour market Decentralized institutional framework for economic policy decision making in the EU. Does entering the euro zone mean the loss of useful instruments of macro policy? Euro exchange rate policy. Employment policies. Microeconomic and structural policies. Concept of macro financial stability. Macroeconomic Dialogue. Product market reforms and the completion of the single market programme. How to ensure optimal outcome of different mix of economic policies? Annual cycle of the coordination of economic policies. European Semester. Europe-2020 strategy. Euro Plus Pact. Topic for discussion: Euro is and always has been a one-sided coin. It has given Europe a common monetary policy, matched or mismatched with a dozen different policies on the other side. Discuss. -Measures taken by euro area governments in support of the financial sector, ECB Monthly bulletin, April 2010. - Annual report on structural reform. European Commission, – http://europa. eu.int/comm/economy_finance/epc/epc_reports_en.htm. -The reform of economic governance in the euro area – essential elements. ECB monthly bulletin, March 2011. 11. Role of the payments systems Changing role of the central banks in the field of payments systems. Real time payment systems. Why there is a need to ensure of the adequate public interest in the field of retail payments systems in the EMU? Effectiveness of the TARGET system; Target 2; SEPA. Securities settlement systems. Deliveryversus- payment principal. Electronic money and institutions. Topic for discussion: TARGET and SEPA systems: similarities and differences. Please discuss. -Payment systems and market infrastructure oversight report, ECB, July 2008 -Ten years of TARGET and the launch of TARGET2, ECB Monthly bulletin, November 2008. - The Role of the Eurosystem in Payment and Clearing Systems. – Monthly Bulletin, April 2002. - Role of the Eurosystem in the Field of Payment System Oversight. – ECB, Monthly Bulletin, June 2000. 12. The euro as an international currency International use of the euro. Benefits and costs of international use of the euro. Conditions for the euro to become an international currency. International euro representation. EMU and international policy coordination. Reserve currencies. Topics for discussion: 5 The euro is not likely to be a significant reserve currency. Discuss. “Emergence of the euro as a counterpart to the dollar is a longer-term rather than crisis-driven process”. Discuss. - Paul De Grauwe, 258-264. -The international role of the euro, ECB, July, 2013. http://www.ecb.int/pub/pdf/other/euro-internationalrole201307en.pdf?57a2383cd54ffc15111284c46a7a5601 -The external representation of the EU and EMU, Monthly Bulletin, ECB, May 2011. 13. Enlargement and the European integration process. ERMII. The EU’s official framework for enlargement. Economic criteria for the membership of the EU. How the new member states can enter the euro area. The ERMII. The Balassa-Samuelson effect. Euroisation: a viable choice? Benefits and the costs of the monetary union and the openness of the country. How long will real convergence process may take? Case studies: Lithuania’s application for convergence in 2006: lessons to be drown; How Latvia succeeded to fulfil convergence requirements? - Paul De Grauwe, 88-93; 133-150. -Schadler S., Drummond P., Kuijs L., 2005: Adopting the Euro in Central Europe. – Challenges of the Next Step in European Integration, Occasional Paper No. 234, Washington. IMF. -Gulde A., Kahkonen J., Keller P., 2000: Pros and cons of Currency Board Arrangements in the Led-up to EU Accession and Participation in the Euro Zone. – Discussion Paper, No. 1, IMF, Washington. 14. Assessment of the functioning of the EMU Political and institutional developments. The impact of the euro on the eurozone and its economic performance. Major risks for the EMU sustainability. Product market reforms and the completion of the Single Market Programme. How/ weather the euro project will be completed? Topics for discussion: -The euro’s success within limits? -How euro will survive crises? Discuss. -EMU@10: successes and challenges after 10 years of Economic and Monetary Union, EUROPEAN ECONOMY, 2/2008 - The First Ten Years. ECB monthly bulletin. 10th anniversary of the ECB. 1998-2008. Frankfurt Main, 2008. -Economic Crisis in Europe: Couses, Consequencies and Responses. European Commission, European Economy, 2009, N7. -Completing the Euro. A road map towards fiscal union in Europe. Report of the “Tommaso PadoaSchioppa Group”, Notre Europe, 2012,June. http://www.eng.notre-europe.eu/011-3317-Completing-the-EuroA-road-map-towards-fiscal-union-inEurope.html; -A blueprint for a deep and genuine economic and monetary union. Launching a European Debate. COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION, Brussels, November, 2012. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2012:0777:FIN:EN:PDF 6