* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Veltassa ® - Patiromer Literature Review
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Potassium iodide wikipedia , lookup
List of comic book drugs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
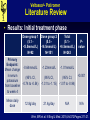
Veltassa® - Patiromer Manufacturer: Relypsa Inc. FDA Approval Date: October 21, 2015 Veltassa®- Patiromer Objectives • At the end of this presentation participants will be able to: 1. Appropriately recommend Veltassa® - Patiromer 2. Effectively educate patients on the purpose, proper use and potential adverse effects of Veltassa® - Patiromer Veltassa®- Patiromer Clinical Application • Indications: • Treatment of hyperkalemia • Place in therapy: • Patients who are receiving RAAS therapy and have hyperkalemia Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Clinical Application • Contraindications: • Known hypersensitivity to patiromer or any of its components • Precautions: • Hypomagnesemia • Worsening of gastrointestinal motility Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Clinical Application • Black Box warnings • Patiromer binds to many orally administered medications, which could decrease their absorption and reduce their effectiveness • Administer other oral medications at least 6 hours before or 6 hours after patiromer • Choose patiromer or the other oral medication if adequate dosing separation is not possible Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Clinical Application • Pregnancy: • Patiromer is not absorbed systemically following oral administration and maternal use is not expected to result in fetal risk • Lactation: • Patiromer is not absorbed systemically by the mother, so breastfeeding is not expected to result in risk to the infant Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Drug Facts • Pharmacology: • A cation exchange polymer that increases fecal potassium excretion through binding of potassium in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in a reduction of serum potassium levels Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Drug Facts • Pharmacokinetics: • • • • A– D– M– E– N/A N/A N/A N/A • In radiolabeled ADME studies in rats and dogs, patiromer was not systemically absorbed and was excreted in the feces Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Drug Interactions • Drug Interactions – Object Drugs: • No formal drug studies have been conducted in humans • In in vitro binding studies, patiromer was shown to bind about half of the oral medications that were tested • Administer other oral medications at least 6 hours before or 6 hours after patiromer Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Adverse Effects • Common Adverse Effects: • Constipation (7.2%) • Hypomagnesemia (5.3%) • Diarrhea (4.8%) • Nausea (2.3%) • Common Laboratory Abnormalities: • Hypomagnesemia < 1.4mg/dL (9%) • Hypokalemia < 3.5mEq/L (4.7%) Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Monitoring Parameters • Efficacy Monitoring: • Serum potassium at least weekly until desired serum potassium target range • Toxicity Monitoring: • Serum potassium • Serum magnesium Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Prescription Information • Dosing: • 8.4g by mouth daily; may titrate > 1 week intervals to a max dose of 25.2g • Administer with food 6 hours apart from oral medications • Mix the powder with water and consume all of the powder • Cost: – $714 - $1071 • UpToDate.com – accessed 3/13/15 Veltassa® [package insert]. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Patiromer in Patients with Kidney Disease and Hyperkalemia Receiving RAAS Inhibitors • Purpose: To assess the safety and efficacy of patiromer in patients with chronic kidney disease and hyperkalemia that are receiving at least one RAAS inhibitor Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Design: multinational, single-blind, two-phase study • Conducted at sites in: Eastern Europe, European Union, United States Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Initial treatment phase: • N = 243 (4 weeks) • 5.1 - <5.5mmol/L – mild hyperkalemia (4.2g of patiromer twice daily) • 5.5 - <6.5mmol/L – moderate-to-severe hyperkalemia (8.4g of patiromer twice daily) • The dose could be adjusted to reach and maintain a target potassium level Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Randomized withdrawal phase: • N = 107 (8 weeks) • > 5.5mmol/L at baseline of the initial treatment phase and if their potassium level was within 3.8 - <5.1mmol/L at the end of the initial treatment phase • Randomized in 1:1 ratio to continue the same daily dose they were receiving at the end of the initial treatment phase or to receive placebo Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria • 18 – 80 years old • Had stage 3 or stage 4 CKD (15 - <60 mL/min/1.73m2) • Serum potassium of 5.1 <6.5mmol/L at two screenings • Receiving a stable dose of one or more RAAS inhibitors for >28 days • Doses of antihypertensives had to be stable for >28 days • Potassium-related EKG changes • Severe GI disorders • Uncontrolled or unstable arrhythmias • Recent cardiac surgery • Kidney or heart transplant • ACS • TIA or stroke within the past 2 months • T1DM • >180 or <110 systolic BP • >110 or < 60 diastolic BP Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Initial treatment phase baseline characteristics: • 58% male • 64 years old • 98% white • 57% T2DM • Serum potassium 5.6mmol/L • eEGF 35.4 mL/min/1.73m2 • 54% using a non-RAAS-inhibitor diuretic • 70% using ACE inhibitor • 38% using an ARB • 44% receiving maximal dose of RAAS inhibitor Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Results: Initial treatment phase Dose group 1 Dose group 2 (5.1 (5.5 <5.5mmol/L) <6.5mmol/L) N=92 N=151 Primary Endpoint: Mean change in serum potassium from baseline to week 4 Mean daily dose Total (5.1 <6.5mmol/L) N=243 -0.64mmol/L -1.23mmol/L -1.01mmol/L (95% CI, -0.74 to -0.54) (95% CI, -1.31 to -1.15) (95% CI, -1.07 to -0.94) 12.8g/day 21.4g/day N/A Pvalue <0.001 N/A Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Results: Initial treatment phase • 76% of patients had serum potassium within target range (3.8 – <5.1mmol/L) at end of week 4 • To note, this phase 3 trial and the phase 2 trial both used BID dosing, yet the FDA approved once daily dosing based off of the total daily dose given to patients in the trials Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Results: Withdrawal treatment phase Patiromer Placebo P-value Start of phase to week 4 of the phase median change in serum potassium 0mmol/L 0.72mmol/L <0.001 >1 serum potassium >5.5mmol/L through week 8 15% 60% <0.001 >1 serum potassium >5.1mmol/L through week 8 43% 91% <0.001 Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Adverse Events Initial Treatment Withdrawal Treatment Placebo (N=52) Patiromer (N=55) >1 Adverse event 47% 50% 47% Constipation 11% 0% 4% Diarrhea 3% 0% 4% Nausea 3% 0% 4% Hypomagnesemia 3% N/A N/A Anemia 3% N/A N/A Headache N/A 8% 4% Chronic renal failure 3% N/A N/A Supraventricular extrasystoles N/A 2% 4% >1 Serious adverse event 1% 2% 0% Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Literature Review • Conclusions: • Patients with chronic kidney disease who were taking RAAS inhibitors and who had hyperkalemia, treatment with patiromer was associated with reductions in serum potassium levels and maintenance of normal potassium levels Weir, MR et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;Vol372:Pages 211-21. Veltassa®- Patiromer Summary • Veltassa, patiromer, is a potassium binder indicated to treat hyperkalemia. It is not to be used as emergency treatment for life-threatening hyperkalemia because of its delayed onset of action. • Black box warning for patiromer binding to other oral medications. The administration of other oral medications should be given 6 hours before or 6 hours after the administration of patiromer. • Patiromer has 3 different doses (8.4 g, 16.8 g, 25.2 g once daily) that can be adjusted at > 1 week intervals based on the patient’s serum potassium levels. • Most common adverse drug effects include: constipation, hypomagnesemia, diarrhea, and nausea. Veltassa®- Patiromer References 1. https://www.veltassa.com 2. Veltassa package insert. Relypsa Inc. Oct. 2015. 3. Bakris, GL et al. Effect of patiromer on serum potassium level in patients with hyperkalemia and diabetic kidney disease: The AMETHYST-DN Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015 Jul 14;314(2):151-61. 4. Weir, MR et al. Patiromer in patients with kidney disease and hyperkalemia receiving RAAS inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jan 15;372(3):21121.