* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ALAMO HEIGHTS INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT ALAMO
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
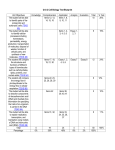
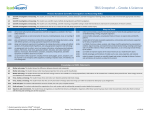
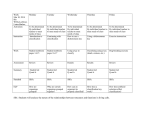
ALAMO HEIGHTS INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT ALAMO HEIGHTS HIGH SCHOOL Biology Scope and Sequence 1st NINE WEEKS Unit: “The Nature of Science” Approximate Time Frame: 5 Days TEKS (2) The student uses scientific methods and equipment during laboratory and field investigations. Student Expectations (A) know the definition of science and understand that it has limitations Key Concepts Safety Lab Equipment Metric Measurement (B) know that hypotheses are tentative and testable statements that must be capable of being supported or not supported by observational evidence (C) know scientific theories are based on natural and physical phenomena and are capable of being tested by multiple independent researchers. (D) distinguish between scientific hypotheses and scientific theories (E) plan and implement experimental investigations F) collect and organize qualitative and quantitative data and Resources and Activities Experimental Lab Design Graphing Scientific Method Procedures, Theory, Law Commercial Products Activity Metric Measurement Lab w/ Graphing Scientific Method Lab w/ Graphing make measurements with accuracy G) analyze, evaluate, make inferences, and predict trends from data (H) communicate valid conclusions supported by the data through methods such as lab reports, labeled drawings, graphic organizers, journals, summaries, oral reports, and technology-based reports Unit: “Ecology” Approximate Time Frame: 5 Days TEKS Student Expectations Key Concepts (12) The student knows that interdependence and interactions occur within an environmental system. (A) interpret relationships, including predation, parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, and competition among organisms -Populations -Ecosystems -Energy Flow (food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids) -Biological Communities -The Environment (B) compare variations and adaptations of organisms in different ecosystems (C) analyze the flow of matter and energy through trophic levels using various models, including food chains, food webs, and ecological pyramids Resources and Activities Population Dynamics Lab w/ Graphing Biome Design Project (D) recognize that longterm survival of species is dependent on changing resource bases that are limited (E) describe the flow of matter through the carbon and nitrogen cycles and explain the consequences of disrupting these cycles (F) describe how environmental change can impact ecosystem stability Unit: “Biochemistry” Approximate Time Frame: 9 Days TEKS (9) The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms. Student Expectations (A) compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (C) identify and investigate the role of enzymes (D) analyze and evaluate the evidence regarding formation of simple organic molecules and their organization into long complex molecules having information Key Concepts -Nature of Matter -Water and Solutions -Chemistry of Cells -Energy and Chemical Reactions Resources and Activities pH Lab Macromolecule Testing Lab Enzyme Activity Lab Unit: “Cellular Biology” Approximate Time Frame: 10 Days TEKS Student Expectations (5) The student knows how an organism grows and the importance of cell differentiation. (B) examine specialized cells, including roots, stems, and leaves of plants; and animal cells such as blood, muscle, and epithelium Key Concepts Cellular Structure -Microscopes -Cell Theory -Prokaryotes -Eukaryotes -Organelles Resources and Activities Introduction to the Microscope Lab Cell Type Comparison Lab Cells Flipbook (11) The student knows that biological systems work to achieve and maintain balance. (A) describe the role of internal feedback mechanisms in the maintenance of homeostasis (7) The student knows evolutionary theory is a scientific explanation for the unity and diversity of life. (G) analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell Cellular Transport -Passive Transport -Active Transport Osmosis and Diffusion Lab Plasmolysis Lab Unit: “Cellular Energetics” Approximate Time Frame: 12 Days TEKS (9) The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms. Student Expectations (B) compare the reactants and products of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in terms of energy and matter Key Concepts -Photosynthesis Overview -Photosynthesis Equation -Respiration Overview -Respiration Equation -ATP Resources and Activities Plant Pigment Lab Photosynthesis Lab 2nd NINE WEEKS Unit: “Cellular Reproduction” Approximate Time Frame: 7 Days TEKS Student Expectations (5) The student knows how an organism grows and the importance of cell differentiation. (A) describe the stages of the cell cycle, including deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms Key Concepts -The Cell Cycle -Mitosis -Cancer -Meiosis Resources and Activities Chromosome Manipulative Activity Cell Division Lab (D) recognize that disruptions of the cell cycle lead to diseases such as cancer Unit: “Genetics” Approximate Time Frame: 14 Days TEKS Student Expectations (6) The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics (B) recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms (F) predict possible outcomes of various genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses, dihybrid crosses and nonMendelian inheritance (G) recognize the significance of meiosis to sexual reproduction Key Concepts -Mendel’s Studies -Laws of Heredity -Punnett Squares -Patterns of Heredity Resources and Activities Punnett Square Activities Inheritance Lab Unit: “Molecular Biology” Approximate Time Frame: 18 Days TEKS Student Expectations Key Concepts (5) The student knows how an organism grows and the importance of cell differentiation. (C) describe the roles of -DNA Structure DNA, ribonucleic acid -DNA Function (RNA), and -DNA Replication environmental factors in cell differentiation (6) The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics (A) identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA (C) explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA (D) recognize that gene expression is a regulated process (E) identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of these changes (H) describe how techniques such as DNA fingerprinting, genetic modifications, and chromosomal analysis are used to study the genomes of organisms -Protein Synthesis -RNA -Transcription -Translation -Mutations Resources and Activities DNA Model Activity DNA Extraction Lab Protein Synthesis Activity Mutation Activity GATTACA Movie 3rd NINE WEEKS Unit: “Evolution” Approximate Time Frame: 10 Days TEKS Student Expectations Key Concepts (7) The student knows evolutionary theory is a scientific explanation for the unity and diversity of life. (A) analyze and evaluate how evidence of common ancestry among groups is provided by the fossil record, biogeography, and homologies, including anatomical, molecular, and developmental -History of Life -Age of Earth -Chemicals of Life -Cellular Evolution -Life to Land (B) analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning any data of sudden appearance, stasis, and sequential nature of groups in the fossil record (C) analyze and evaluate how natural selection produces change in populations, not individuals (D) analyze and evaluate how the elements of natural selection, including inherited variation, the potential of a population to produce more offspring than can survive, and a finite supply of environmental resources, result in differential reproductive success Resources and Activities Progression of Life on Earth Activity Natural Selection Lab Population Genetics Lab -Theory of Evolution -Darwin -Natural Selection -Evidence of Evolution -Speciation -Adaptations -Primate Evolution Darwin Video Human Evolution Video (E) analyze and evaluate the relationship of natural selection to adaptation and to the development of diversity in and among species (F) analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination Unit: “Taxonomy” Approximate Time Frame: 5 Days TEKS Student Expectations (8) The student knows that taxonomy is a branching classification based on the shared characteristics of organisms and can change as new discoveries are made. (A) define taxonomy and recognize the importance of a standardized taxonomic system to the scientific community (B) categorize organisms using a hierarchical classification system based on similarities and differences shared among groups (C) compare characteristics of taxonomic groups, including archaea, bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals Key Concepts -Classification -Taxonomy -7 Levels of Taxa -Scientific Names -Phylogeny -6 Kingdom Overview Resources and Activities Taxonomy Activity Phylogenic Application Lab Unit: “Microorganisms and Fungi” Approximate Time Frame: 20 Days TEKS Student Expectations Key Concepts (11) The student knows that biological systems work to achieve and maintain balance. (C) summarize the role of microorganisms in both maintaining and disrupting the health of both organisms and ecosystems -Viral Structure -Viral Reproduction -Viral Diseases -HIV AIDS -Bacterial Structure -2 Bacteria Kingdoms -Bacteria Reproduction -Pathogenic Bacteria -Antibiotics -Importance of Bacteria Resources and Activities HIV Simulation Lab Bacteria Cultivation Lab Introduction to Protist Lab Introduction to Fungus Lab -Protist Structure and Adaptations -Fungus Structure and Adaptations Unit: “Plants” Approximate Time Frame: 6 Days TEKS (10) The student knows that biological systems are composed of multiple levels. Student Expectations (B) describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of transport, reproduction, and response in plants (C) analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and relate the levels to each other and to the whole system Key Concepts -Evolution of Plants -Vascular Tissue -Gymnosperms -Angiosperms -Plant Reproduction -Adaptations Resources and Activities Plant Growth Lab Stomata Lab Transpiration Lab Flower Dissection Lab 4th NINE WEEKS Unit: “Animals” Approximate Time Frame: 15 Days TEKS (10) The student knows that biological systems are composed of multiple levels. Student Expectations (A) describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in animals Key Concepts -Basic Characteristics -Invertebrate vs. Vertebrate -Arthropods -Spiders -Insects -Reproduction Resources and Activities Invertebrate Comparison Activity Worm Comparison Dissection Arthropod Comparison Dissection Mollusk and Echinoderm Dissection (C) analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and relate the levels to each other and to the whole system Unit: “Humans” Approximate Time Frame: 15 Days TEKS (10) The student knows that biological systems are composed of multiple levels. Student Expectations Key Concepts (A) describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in animals -Body Structure -Systems -Reproduction and Development (C) analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and relate the levels to each other and to the whole Resources and Activities Vertebrate Comparison Dissection Frog Dissection Human Body Portfolio Unit: “Research and Technology Application” Approximate Time Frame: 8 Days TEKS (3) The student uses critical thinking, scientific reasoning, and problem solving to make informed decisions within and outside the classroom. Student Expectations (A) in all fields of science, analyze, evaluate, and critique scientific explanations by using empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and experimental and observational testing (B) communicate and apply scientific information extracted from various sources (C) draw inferences based on data related to promotional materials for products and services (D) evaluate the impact of scientific research on society and the environment (E) evaluate models according to their limitations in representing biological objects or events (F) research and describe the history of biology and contributions of scientists Key Concepts Topic of student choice from the entire year Resources and Activities Independent Research Project