* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cold War Goes Global Packet #39 S. Gerhardt Global II DO
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Austria wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Marshall Plan wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
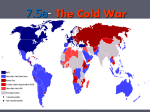
The Cold War Goes Global S. Gerhardt Packet #39 Global II DO NOW: Eastern Side of the Berlin Wall The Two Sides of the Berlin Wall Look at the two sides of the Berlin Wall. What can you conclude? Western Side of Berlin Wall OBSERVATION/ANSWER NOTES: ESSENTIAL VOCABULARY NOTES NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) North Atlantic Treaty Organization Military alliance formed by the US, Great Britain, France, Belgium , Italy, Denmark, Iceland, Norway and Canada. Members agreed that an attack on one would be considered one on ALL Warsaw Pact: Soviet and Eastern European response to NATO The pact was also for strengthening the Soviets hold on Eastern Europe Berlin Airlift: The Soviets blocked the Allies access to the allied occupied zones of Berlin (June 1948) Allies organized supplies to be flown in on airplanes to be given out to residents of West Berlin The Soviets were humiliated when this airlift was proved to be successful and they lifted the blockade on Berlin in May 1949 Stalin’s Successors Hold the Line Stalin died in 1953 Nikita Khrushchev emerged as the new Soviet leader He closed Stalin’s prison camps and eased censorship Cuban Missile Crisis: Fidel Castro came to power in 1959 and wanted to reform the country He sought support from the Soviets 1962, Soviet Union sent missiles to Cuba. President Kennedy responded by imposing a blockade of Cuba preventing further shipments Containing Communism: Containment = Holding back the spread of Communism Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan Truman Doctrine: Allowed for American military aid to any country threatened by Communism US gave $400 million dollars in aid to Greece and Turkey to fend off Communists Marshall Plan: Proposed European aid program (1947) US gave money to Western European countries to stop them from becoming Communist Marshall Plan was a great success and extended American influence in Western Europe The purpose of both the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan was to (1) support the construction of the Iron Curtain (2) increase membership in the United Nations (3) prevent the spread of communism (4) attempt to solve world hunger The Marshall Plan was designed to stop the spread of communism by providing (1) government housing to refugees (2) military assistance to Vietnam (3) funds for economic recovery in war-torn European nations (4) nuclear weapons to North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) members In the 1950s, what was the status of most countries in Eastern Europe? (1) members of the Common Market (2) participants in the Marshall Plan (3) allies of the United States (4) satellites of the Soviet Union Which group of countries became Soviet satellites after World War II? (1) France, Spain, Great Britain (2) Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary (3) Switzerland, Austria, Belgium (4) Turkey, Greece, Italy The use of the Marshall Plan in Western Europe after World War II strengthened the forces of (1) democracy (3) isolationism (2) communism (4) autocracy The primary purpose of the United Nations is to (1) control world grain prices (2) promote democratic governments (3) resolve conflicts between nations peacefully (4) unite all nations militarily through alliances During the Cold War, nations that adopted a policy of nonalignment believed they should (1) be exempt from United Nations decisions (2) restrict trade with neighboring countries (3) reject international environmental treaties (4) follow a course independent of the superpowers The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was initially formed to (1) promote religious freedom (2) defend Western Europe from Soviet aggression (3) isolate member nations from the rest of the world (4) stop the flow of immigration between member nations The purpose of the Marshall Plan after World War II was to (1) promote the spread of militarism (2) force the losing nations to help areas destroyed in the war (3) rebuild national economies to stabilize governments (4) strengthen the alliances that had won the war The Truman Doctrine, Korean War, crisis in Guatemala, and Soviet invasion of Afghanistan were all (1) reasons for the Industrial Revolution (2) examples of Japanese imperialism (3) events of the Cold War (4) causes of World War II