* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 22
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
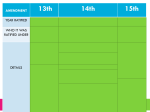
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Forty acres and a mule wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 22 The southern economy and social structure collapsed as a result of the Civil War. o Banks and businesses were ruined by inflation. o Lack of effective transportation and factory systems. Lack of slaves crushed agriculture. o Livestock was minimal due to scavenging throughout the war. o Took 5 years for a large cotton crop to yield after the war. Collapse of planter aristocrats. o Humbled by poverty and worthless land. o $2 billion investment in slaves gone with emancipation. “Freedom” for blacks o Responses to emancipation: o Loyalty to plantation master prompted some slaves to resist the liberating Union armies. o Violence on day of liberation by Union armies. o Joining Union troops in pillaging. New names, Mr. and Mrs. Abandonment of cotton clothing for silk and satin. Many left just because they could or to find loved ones. o Emancipation strengthened the black family units. o Formalized marriages. o Sought existing black communities for protection and mutual assistance. Exodusters = 1878-1880 25,000 from LA, TX, and MS poured in to Kansas. Black Church formed the bed rock of the black community. o Baptist grew from $150,000 to $ 500,000 in 20 years. o Methodist grew from by 300,000 in 10 years. o Gave rise to benevolent organizations and mutual aid societies. Education- demand was high and there were not enough black teachers. o Helped by northern, white women who were former abolitionists. o 200,000 learned to read. Freedmen’s Bureau o Primitive welfare agency that provided food, clothing, medical care, and education. Included both former slaves and white refugees. o Led by former Union General Oliver Howard. o President Johnson tried to end the program for many years. He vetoed the continuance of the program. o The program expired in 1872. Andrew Johnson o Championed poor whites over the planter aristocracy. o Running mate of Lincoln because he was a Democrat and Southern. o Favored states’ rights. o Did not understand the North, was distrusted by the South, a Democrat who was not accepted by the Republicans, a president who was never elected. o Wrong man in the wrong place at the wrong time. Civil Rights Bill o 1866, passed in retaliation of Johnson vetoing the Freedmen’s Bureau renewal. o Offered black citizenship and tried to offset the Black Codes. o Vetoed by Johnson. Overturned by Congress with a 2/3rd’s majority vote. o Turned into the Fourteenth Amendment. Passed just in case Southerners someday won back control of Congress and repealed the bill. The amendment did the following: Granted civil rights to blacks. Citizenship for blacks. Former Confederate officers could not hold office. Denied Confederate debts. Would not allow Southern states to come back in to the Union without ratification of the amendment. President Johnson advised the southern states to reject the amendment. Fifteenth Amendment o Gave black men the right to vote. o Angered white women. They felt they too deserved basic civil rights. KKK- “Invisible Empire of the South” o Founded in TN in 1866. o Members wanted to keep black men from voting by using means of terror and intimidation. o End results turned to flogging, mutilation, and murder (lynching). Force Acts passed in response to KKK. o Banned Klan membership o Prohibited the use of intimidation to prevent blacks from voting. o Gave the U.S. military the authority to enforce the acts. Black Codes were designed to regulate the affairs of blacks. o Varied in severity from state to state. MS was the harshest, GA the most lenient. o Aimed to ensure a subservient labor force. o Blacks could not serve on a jury, punished or fined for not working, etc. o Gateway to sharecropping. Sharecropping- black and white farmers rented land and homes from a plantation owner in exchange for a certain “share” of each year’s crop. o Land owners manipulated the system to keep tenants in perpetual debt and unable to leave. Lincoln’s 10% Plan: o 10% of a state’s prewar voters took loyalty oath, which led to setting up a new state government. o Seen as too lenient by members of his own party. o Lincoln wanted to make the process of unification uncomplicated and quick. o Led to Wade-Davis Bill. Wade-Davis Bill: o 50% of a state’s prewar voters took loyalty oath. o Pocket-vetoed by Lincoln. Pocket veto =The indirect veto of a bill received by the President within ten days of the adjournment of Congress, effected by retaining the bill unsigned. o Revealed factions in the Republican Party and Congress: split in to moderate and radical. Moderates tended to side with Lincoln. Congressional Reconstruction: moderate and radical. o Radicals feared restoration of the planter aristocracy just like Johnson. o Radicals also wanted to make the South pay for the sins of the war. o Radicals demanded citizenship and even suffrage. o Radicals were against rapid restoration of the Southern states. Wanted to apply federal power to bring about drastic social and economic transformation before letting the states back in. o Moderates did not like the federal government involved directly in individual’s lives. Thaddeus Stevens and Charles Sumner: radical Republicans. o Labored for black equality. o Favored land redistribution. o Johnson’s Plan for Reconstruction: o He went with Lincoln’s 10% idea which divided him with Congress. o Didn’t want the Fourteenth or Fifteenth Amendments. o Wished for the states to handle the issues of social integration of blacks. Impeachment: o Tenure of Office Act- Senate approval for Cabinet members being hired and fired. Johnson fired Edwin Stanton without Senate approval. Johnson was acquitted by one vote. Angered radical Republicans most. Alaska was sold by Russia to the U.S. for $7.2 million. o Deal made by Secretary of State, William Seward. o Many Americans were against the purchase at first. “Seward’s Folly”, “Icebox” Americans were too focused on Reconstruction and the economy. They favored saving money and not acquiring land.