* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exchange Rate Determination
Survey
Document related concepts
International status and usage of the euro wikipedia , lookup
History of the euro wikipedia , lookup
Bretton Woods system wikipedia , lookup
History of monetary policy in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Currency War of 2009–11 wikipedia , lookup
Reserve currency wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
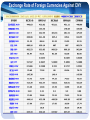
经济学导论 ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS UNIT Eight Foreign Exchange And Exchange Rate Contents 1 Foreign Exchange Regimes 2 Exchange Rate Determination 3 Flow Theory 4 Monetary Theory 5 Portfolio Balance Theory Words & Usage Transaction 交易;事物 A transaction is a piece of business, for example, an act of buying or selling something. Broker 经纪人,掮客 A broker is a person whose job is to buy and sell securities, foreign money, real estate, or goods for other people. Words & Usage Regime 制度;政体 A regime is the way that something such as an institution, company, or economy is run, especially when it involves tough or severe action. Peg 钉住;固定 If a price or amount of something is pegged at a particular level, it is fixed at that level. Words & Usage Portfolio 证券资产;资产组合 In finance, a portfolio is the combination of investments that a particular person or company owns. Proposition 主张;陈述 A proposition is a statement or an idea that people can consider or discuss to decide whether it is true. What is Foreign Exchange? Definition: The exchange of one currency for another, or the conversion of one currency into another currency. Foreign exchange also refers to the global market where currencies are traded virtually around-theclock. The term foreign exchange is usually abbreviated as "forex" and occasionally as "FX." Most Traded Currencies What is Exchange Rate Definition : Rate at which one currency may be converted into another. The exchange rate is used when simply converting one currency to another (such as for the purposes of travel to another country), or for engaging in speculation or trading in the foreign exchange market. There are a wide variety of factors which influence the exchange rate, such as interest rates, inflation, and the state of politics and the economy in each country. Exchange Rate of Foreign Currencies Against CNY Foreign Exchange Regimes Fixed Exchange Rate 固定汇率制 The value of a currency is pegged by the central bank. Flexible Exchange Rate 浮动汇率制 The value of a currency is determined by market forces without intervention by the central bank. Managed Exchange Rate 管理汇率制 The central bank would intervene in the foreign exchange market to smooth out fluctuations in the value of a particular currency but without seeking to maintain an absolutely constant value for a long period of time. Current Exchange Rate System The United States allows the dollar to float against other major currencies. Most countries in Europe have adopted a single currency, the euro. Some developing countries have attempted to keep their currencies’ exchange rates fixed against the dollar or another major currency. Exchange Rate Determination The value of a foreign currency is determined by demand and supply. Flow Theory 流动理论 Monetary Theory 货币理论 Portfolio Balance Theory 资产结合平衡理论 Flow Theory Exchange rate adjusts itself to make the flow supply of a currency equal to the flow demand for the currency. USA’s export in 2014: USD16,234 billion USA’s import in 2014: USD23,451 billion International Payments: interest, profit, loans. Shortcoming: It doesn’t explain how the net flows associated with international loans are determined. Monetary Theory Exchange rate adjusts itself to make the stock of a currency demanded equal to the stock supplied. The quantity of a currency is determined by the behavior of banking system and the actions of the central bank. Shortcoming: the theory is too narrow without considering a broader asset aggregate. Portfolio Balance Theory Exchange rate adjusts itself to make the stock of all financial assets denominated in units of that currency demanded equal to the stock supplied. USD supply=USD-denominated financial liabilities USD-denominated securities issued by government and firms; USD-denominated liabilities of Reserve; USD-denominated liabilities of the banks , etc. 名义汇率 名义汇率(nominal exchange rate) 指一个人可以用一国通货交换另一国通货的 比率。 当一种通货升值时,就可以说它是“坚挺”的, 因为它可以购买更多的外国通货。 当一种通货贬值时,就可以说它是“疲软”的。 真实汇率 真实汇率 (real exchange rate) 指一个人可以用一国的物品与服务交换另一国的物品与服务 的比率。 真实汇率公式: 名义汇率 X 国内价格 真实汇率= 国外价格 真实汇率=(e X p)/p P代表国内消费物价指数;P代表国外消费物价指数;e代表 本国通货与外国通货之间的名义汇率。 练习 如果一辆日本汽车的价格为50万日元,一辆类似的美国 汽车的价格为1万美元,并且1美元可以兑换100日元, 那么名义汇率与真实汇率分别是多少? 名义汇率=100/1 名义汇率 X 国内价格 真实汇率= =2/1 国外价格 100X10,000 = 500,000 购买力平价理论 根据购买力平价理论,一单位任何一种通货 应该能在所有国家购买等量的物品。这种理 论意味着两国通货之间的名义汇率应该反映 这两个国家的物价水平。因此,有较高通货 膨胀的国家的通货应该贬值,而有较低通货 膨胀的国家的通货应该升值。