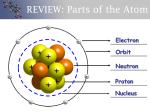
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 Study Guide Key
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Name:______________________________________________________Date:________Period:________ Study Guide: Periodic TableKEY 1. What is periodic law? A pattern of repeating physical and chemical properties that starts at the beginning of each period on the periodic table. Periodicity occurs only when the atoms are arranged in order of atomic number. 2. How did Moseley improve upon Mendeleev’s periodic table? Moseley organized the elements by increasing atomic number instead of increasing atomic mass. This fixed the inconsistencies in Mendeleev’s initial table. 3. Label the following periodic table with the group numbers (both overall numbers AND the main group element numbers. i.e., the boron family is overall group 13 but 3A for main group elements). 1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A 1 17 18 2 13 14 15 16 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 4. Identify each element as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. a. Fluorine (F): _nonmetal________________________________________________ b. Germanium (Ge):_Metalloid____________________________________________ c. Zinc (Zn):__Metal_________________________________________________ d. Phosphorous (P): __Nonmetal___________________________________________ e. Lithium (Li):__Metal_______________________________________________ 5. Give two examples of elements in each group and write the number of valence electrons. a. Alkali Metals:___Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr____________________________________ b. Alkaline Earth Metals: _Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra___________________________ c. Transition Metals:_Any d-block element such as Cu ,Zn, Ag, Zr, Mn______ d. Halogens:__F, Cl, Br, I At_________________________ e. Noble Gases:_He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn__________________________ 6. Write the symbol for the elements in the following locations. a. period 3, Group IIIA __Al___________________________________________ b. period 1, Group VIIIA ___He_________________________________________ c. period 4, Group IIA __Ca____________________________________________ d. period 6, Group VA __Bi____________________________________________ 7. How many 1A: 1 2A: 2 3A: 3 4A: 4 Valence electrons are in each group of the main group elements? 5A: 5 6A: 6 7A: 7 8A: 8 8. Find the Element Write the symbol of the element or elements that fit each description a. A halogen in period 3 Cl b. The inner transition metal with the lowest atomic number La c. A metal in group 5A Bi d. All the transition metals with an atomic number that is a multiple of 5 Mn, Zn, Zr, Rh, Re, Hg, Db, Ds e. The electron configuration ends with 4s2 Ca 9. Why do elements in the same family generally have similar properties? Because elements in the same group/family have the same number of valence electrons. 10.What trend in atomic radius occurs down a group on the periodic table? What causes this trend? Atomic Radius increases down a group on the periodic table. This is due to adding energy levels as you go down a group, as well as increased electron-electron repulsions due to an increased number of inner electrons. As a result, the electrons push each other away to a greater extent. 11. What is the trend in atomic radius across a period in the periodic table? What causes this trend? Atomic radius decreases going left to right across a period. This is due to an increased number of protons/nuclear charge to the valence electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus. 12.Circle the atom in each pair that has the largest atomic radius. a. Al or B d. O or F b. Na or Al e. Br or Cl c. S or O f. Mg or Ca 13. Define ionization energy. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom. 14.What trend in ionization energy occurs down a group on the periodic table? What causes this trend? Ionization energy decreases down a group on the periodic table. The reason for this is shielding—as you move down a group the number of inner electrons increases as more energy levels are added. The greater number of inner electrons blocks the attractive forces between the nucleus and the valence electrons. This means that valence electrons are not held as tightly by the atom, thus requiring less energy to remove the electrons. 15. What is the trend in ionization energy across a period in the periodic table? What causes this trend? Ionization energy increases left to right across a period. The reason for this is that more energy is required to remove an electron due to the increased attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons. 16. Circle the atom in each pair that has the greater ionization energy. a. Li or Be d. P or Ar b. Ca or Ba e. Cl or Si c. Na or K f. Li or K 17.How does ionization energy affect the trend in reactivity in the alkali metals and the alkaline earth metals? Since ionization energy decreases going down a group (due to shielding, see explanation above) it is easier to remove an electron for alkali metals and alkaline earth metals as you go down a group. As a result, alkali metals and alkaline earth metals are more reactive as you go down a group. In addition, metals form cations (they lose electrons to form an ion) because the alkali metals have 1 valence electron and the alkaline earth metals have 2 valence electrons. It is easier to lose 1 or 2 valence electrons to form a full outer shell versus gain 7 or 6 valence electrons. 18. Define electronegativity. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to pull electrons towards itself in a covalent bond. Think of it like a tug of war. 19.What is the trend in electronegativity down a group on the periodic table? What causes this trend? Electronegativity decreases as you go down a group on the periodic table. This reason for this is the shielding effect. The inner electrons block the nucleus attraction on valence electrons, so there is less ability to pull electrons towards the atom. In addition, there are more electron-electron repulsions so electrons are more likely to be repelled than attracted. 20.What is the trend in electronegativity across a period on the periodic table? What causes this trend? Electronegativity increases as you go left to right across a period. This is because of the increased nuclear charge (attractive force from the nucleus due to an increased number of protons). There is a greater attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons, making the atom better able to pull other electrons towards it. 21. Circle the atom in each pair that has the greater electronegativity. a. Ca or Ga d. Ba or Sr b. Br or As e. Cl or S c. Li or O f. O or S 22. How does electronegativity affect the trend in reactivity in the halogens? The reactivity of halogens decreases as you go down the group. This is due to the fact that halogens are going to gain 1 electron to form an ion due to the fact it is easier to gain 1 electron to get a full outer shell than it is to lose 7 electrons. Since electronegativity decreases down a group, it is more difficult for the halogens to attract electrons since there is more shielding by the inner electrons. The code letters A to Z have been assigned to the first 26 elements in the periodic table. The code letters do not represent the chemical symbols, nor have the letters been assigned in alphabetical order. These letters are presented in groups and your assignment is to arrange these elements in the proper periodic form, according to the information given pertaining to certain members of the group. The best way to start is to find which group each family belongs, and then arrange the elements within the group. The following elements belong together in groups: NDG WASO BRL QTJ HUM ZPY EVFX KIC The following clues are given 1. M has a total of 8 electrons 2. W’s electron configuration of1s22s22p63s23p6 3. S is a noble gas 4. R is an alkaline earth metal 5. X has an electronegativity less than V 6. D has the smallest atomic mass in its group 7. S only has electrons in the 1s orbital 8. L is an alkaline earth metal 9. Z is a halogen 10. U has an ionization lower than H 11. A has more neutrons than O 1A 2A 3A 12. I has one more proton than B 13. K is a metal 14. T has the smallest atomic radius in its group 15. E is a gas 16. Atom F contains 11 electrons 17. J is a metalloid 18. R has an atomic number smaller than B but larger than L 19. P has the smallest radius in its family 20. Z has higher ionization energy than Y 4A 5A 6A 7A E S V L F R C D N K X 8A B G I T M P O Q H Z W J U Y A Name:________________________________________________Date:____________Hour:___________