* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.3 Solving Linear Equations
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Two-body Dirac equations wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli's principle wikipedia , lookup
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Exact solutions in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
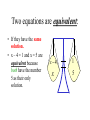
1.3 Solving Linear Equations An equation • Is a statement in which two expressions are equal. • A linear equation in one variable is an equation that can be written in the form ax+c=d 3 x9 7 15 A number is a solution of an equation if the statement is true when the number is substituted for the variable. Two equations are equivalent: • If they have the same solution. • x – 4 = 1 and x = 5 are equivalent because both have the number 5 as their only solution. x4 1 x 5 The following transformations, or changes, produce equivalent equations and can be used to solve an equation. Addition Property Add the same number to both sides: if a=b, then a+c=b+c Subtraction Property Subtract the same number from both sides: if a=b, then a-c=b-c Multiplication Property Multiply both sides by the same nonzero number: if a=b, then ac=bc. Division Property Divide both sides by the same nonzero number: if a=b, then a/c=b/c Solve an equation with a variable on one side: 3 x 9 15 7 9 9 73 7 ( ) x6( ) 37 3 x = 14 Write original equation Subtract 9 from each side Multiply both sides by 7/3 Simplify Solving an Equation with a Variable on Both Sides. 5n 11 7n 9 Write the original equation. 5n Subtract 5n from each side 5n 11 2n 9 9 9 20 2n 10 n Add 9 to both sides. Finally, divide both sides by 2. Using the Distributive Property Distributive property 4(3x 5) 2( x 8) 6 x Combine like terms. 12x 20 2x 16 6x 16x 20 16 16x 4 1 x 4 Solving an equation with fractions 1 1 1 Write original equation x x 3 4 6 “clear” the fractions by multiplying by the LCD 12. 1 1 1 12( x x ) 3 4 6 4x 3 12x 2 5 8x 5 x 8 Assignment 1.3