* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Government Basics PPt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
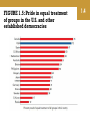
Introducing Government in America 1 1 Intro: https://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=lrk4oY7UxpQ&index=1&list= PL8dPuuaLjXtOfse2ncvffeelTrq vhrz8H Essential Question: What are the key functions of government and explain why they matter? Government What is government? How should we govern? (Democratic-Republic) What should government do? Maintain a national defence Provide public goods and services Preserve order Socialize the young Collect taxes 1.1 Afghanistan 1.1 National defense is a key public service. The United States spends over $650 billion a year on national defense. As we learn from the caption, these troops are guarding the road in Afghanistan against explosive devices planted by Taliban insurgents. 1.1 Which of the following is not a duty of government? a. Collecting taxes b. Proving for national defense c. Promoting religion d. Preserving order 1.1 1.1 Which of the following is not a duty of government? a. Collecting taxes b. Proving for national defense c. Promoting religion d. Preserving order 1.1 Politics 1.2 What is politics? the activities associated with the governance of a country or other area, especially the debate or conflict among individuals or parties having or hoping to achieve power. Who gets what, when, and how Political participation More than just voting Attending a rally Writing a letter FIGURE 1.1: Political apathy among young and old Americans, 1972–2008 1.2 FIGURE 1.2: Age and political knowledge, 1972 and 2008 1.2 FIGURE 1.3: Election turnout rates of young and old Americans, 1972–2010 1.2 Politics Single-issue groups e.g., abortion Single-issue groups consist of voters so concerned with one issue that members often cast their votes on the basis of that issue only, ignoring a politician’s stand on everything else. 1.2 1.2 Which is true of single-issue groups? a. They increase voter participation. b. They negatively affect voter turnout. c. They vote just for politicians who support their issue. d. They force politicians to consider compromises. 1.2 1.2 Which is true of single-issue groups? a. They increase voter participation. b. They negatively affect voter turnout. c. They vote just for politicians who support their issue. d. They force politicians to consider compromises. 1.2 Essential Question: How do citizens impact public policy and how do policies impact people? Policymaking System People Shape Policy Politics Impact People 1.3 FIGURE 1.4: The policymaking system 1.3 People Shape Policy Linkage institutions Parties, elections, interest groups, media Connect people to the policy makers Policy agenda Issues that attract attention Political issue Result of people disagreeing about the problem Policymaking institutions Congress Presidency Courts 1.3 Politics Impact People Public policy Statute Presidential action/executive action Court decision Budgetary choice Regulation Policies should be effective –address the problem designed to solve Policies must have a goal 1.3 Table 1.1: Types of public policies 1.3 1.3 Which of the following is an example of public policy? a. Personal conviction b. Parental rule c. Congressional statute d. Religious edict 1.3 1.3 Which of the following is an example of public policy? a. Personal conviction b. Parental rule c. Congressional statute d. Religious edict 1.3 Democracy in America Essential Question: Identify the key principles of democracy and outline theories regarding how it works in practice. Democracy in America 1.4 Traditional Democratic Theory Three Contemporary Theories of American Democracy Challenges to Democracy American Political Culture and Democracy A Culture War Traditional Democratic Theory Key principles of the democratic process Equality in voting- one person, one vote Effective participation – adequate and equal opportunities Enlightened understanding- free press and speech are important Citizen control of the agenda- everyone has a voice Inclusion-of all citizens Majority rule and minority rights Representation – should reflect the ideas and beliefs of the constituency 1.4 Three Contemporary Theories of American Democracy Pluralism Groups of minorities working together Elitism Power is held by the wealthy Hyperpluralism Too many groups try to control policy 1.4 Challenges to Democracy Increased complexity of issues – people are not well informed Limited participation in governmentthe young do not participate Diverse political interests - Policy gridlock Escalating campaign costs- $$ and politics is an ongoing challenge 1.4 American Political Culture and Democracy 1.4 Political culture based on American creed Liberty Egalitarianism Individualism Laissez-faire Populism FIGURE 1.5: Pride in equal treatment of groups in the U.S. and other established democracies 1.4 A Culture War? Polarization of liberal and conservative political culture – intense commitment to a candidate, a culture, or an ideology- separating one group definitively away form another Is it happening? Testing a crisis of values Loss of traditional values (religion, family, education) Less patriotism – love for country Irreconcilable differences- (gay marriage, abortion) 1.4 1.4 Which of the following illustrates hyperpluralism? a. Use of the court system to try to set policy b. Decrease in patriotism c. Reliance on Congress to limit special interests d. Diversity in political interests 1.4 1.4 Which of the following illustrates hyperpluralism? a. Use of the court system to try to set policy b. Decrease in patriotism c. Reliance on Congress to limit special interests d. Diversity in political interests Interest groups may turn to the courts instead of Congress, turning the court system in a battleground. 1.4 Scope of Government in America 1.5 How Active Is American Government? Politicians constantly debate whether the scope of government responsibilities is too vast, just about right, or not comprehensive enough. This debate concerns whether the goals that are agreed to be important are best achieved through government action or rather through means other than government. 1.5 The political debate over programs that help lowincome individuals continues. Do such programs expand the scope of government too much? Or do they help people to get by during hard times? How Active Is American Government? Gross domestic product (GDP) • The gross domestic product is the total value of all goods and services produced annually by the United States. The federal government spends about one-third of this, or $3.7 trillion a year, implementing public policies, and it employs about 24 million Americans. Americans expect government to solve problems Unemployment, terrorism, illegal immigration, energy, education, lack of access to health care 1.5