* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Teacher Copy: World Religions Notes (Hinduism, Buddhism
Buddha-nature wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Triratna Buddhist Community wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist ethics wikipedia , lookup
Gautama Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist philosophy wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Dhyāna in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in Cambodia wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Sanghyang Adi Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Myanmar wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Pre-sectarian Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
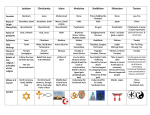
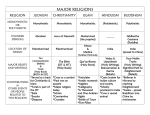
Hinduism Monotheistic or Polytheistic Origin Founder Name of God Polytheistic and Monotheistic depending on group Indian Subcontinent Around 3000 BCE No known founder Brahman (Creator); Vishnu (restores/protects universe); Shiva (destroys universe) & … 1,000s of gods Name of Follower Hindu Key teacher/ Religious Example Brahmans (priests) and the gods in their many forms Place of worship Religious Text Key Doctrine Temple Brahmans (priests) Vedas (oldest) Customs Afterlife belief Major groups Reincarnation- soul is reborn into another person/animal depending on karma Karma- consequences (good or bad) Goal is to gain good karma and be released from reincarnation Four goals to life: o fulfilling one's purpose o prosperity o enjoyment o enlightenment Not eating meat Enforcing social classes – in India (Caste System) Shrines for gods in the home Use yoga and meditation to help reach enlightenment Diwali- Holiday in Oct/Nov that celebrates victory of good over evil Ganges River in India is very important- rivers are life sources Reincarnation- reborn into a life you have earned in your previous live Monotheistic groups (Vishnu or Shiva as main gods) Polytheistic groups Buddhism Monotheistic or Polytheistic Origin Polytheistic and Monotheistic- depends on group Indian Subcontinent Around 500 BCE Founder Siddhartha Gautama/Buddha Name of God Depends of branch: No creator Buddha is god or savior Hindu gods Buddhist Name of Follower Key teacher/ Religious Example Place of worship Religious Text Key Doctrine Customs Siddhartha Gautama/Buddha Shrine temples Depends on branch Mahayana Buddhism: Sutras Theravada Buddhism: Tripitaka life is suffering (because of worldly desires) reincarnation to escape suffering you must follow the Eightfold Path (how to lead a good life) Goal- reach nirvana (state of bliss) and end reincarnation 3 Jewels of Buddhism: o The Buddha (your example) o Dharma (path you follow) o Buddhist Community (helps you) Afterlife belief Major groups Celebrating Buddha – using his statue Use yoga and meditation to help reach enlightenment Use shrines at home to worship Losar: The Tibetan New Year Celebration, time to visit temples or shrines to show commitment to religion Sangha Day: Celebrates Buddhist Community Reincarnation Theravada- You find your own way to enlightenment Mahayana- Bodhisattvas help you find your way Confucianism Monotheistic or Polytheistic Origin Founder Name of God Neither- way of life, not a religion China Around 600 BCE Confucius (551-479BCE) None Name of Follower Confucian Key teacher/ Religious Example Confucius Place of worship Religious Text None Analects Key Doctrine People are teachable, improvable and perfectible Important traits: o human goodness o behave correctly o Wisdom o Trustworthiness o Respect elders Customs Respecting Important relationships: o Leader vs. follower o Parent vs. child o Husband vs. wife Focuses on living correctly- combined with other religious customs of Hinduism, Buddhism, and Daoism Afterlife belief Major groups None Often combined with other religions