* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math II - Unit 1 – Basics
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
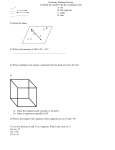
Unit 1 – Geometry Basics Math II - Task Checklist Undefined terms Draw, name, label, and identify: point, line, segment, plane, ray, angle Apply the correct notation for figure names Classify figures as collinear, non-collinear, coplanar, non-coplanar, parallel, intersecting, “on”, “through”, skew, etc. Apply the properties of figures and measurement of segments and angles Algebraic proofs and properties Solve multi-step equations by showing all steps Check answers algebraically and graphically Apply and identify properties of equality (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, distributive, symmetric, transitive, substitution, etc.) Write the steps to solving an equation as a two-column proof Parallel lines Understand similarities and differences of parallel and skew lines Classify special angle pairs (alternate interior, alternate exterior, consecutive interior, corresponding, linear pair, vertical angles) Know and apply the relationship between special angle pairs and parallel lines to set up equations to solve for variables and angles (i.e. congruent, supplementary, etc.) Know and apply the relationship between segment lengths associated with multiple parallel lines through the same transversal Midpoint Know and apply the midpoint formula Find the midpoint of a segment given the endpoints Find a missing endpoint given the midpoint and one endpoint Result should be an ordered pair in the form of (x, y) Distance Know and apply the distance formula Find the distance between two points Exact = as a radical, reduced if possible Approximate = as a rounded decimal Partition a directed line segment Identify the beginning and endpoints of a directed line segment Calculate the needed ratio (i.e. 2:3 has 5 parts (2+3), so the ratio would be ⅖ of the whole) Calculate the x-distance and y-distance and multiply by the ratio to find new measurement Segment Addition Draw and label an appropriate diagram Create and solve an equation to represent the segment addition relationship Substitute values to find all individual segment lengths Angle Addition Draw and label an appropriate diagram Create and solve an equation to represent the angle addition relationship Substitute values to find all individual angle measures