* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download abnormalities of p wave
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
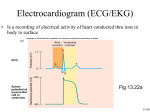
Fourth stage اسم الدكتور Medicine Lec-1 1/1/2014 The 12 leads stndard ecg Normal ECG Abnormal ECG The 12 leads stndard ecg *6 standard limb leads (orianted on the frontal plane of the heart) -bipolar limb leads Lead I :RA(-)to LA(+) Lead II :RA(-)to LF(+) Lead III :LA(-)to LF(+) -augmented unipolar limb leads 1 lead AVR : RA(+) to (LA&LF) (-) lead AVL : LA(+) to (RA&LF) (-) lead AVF : LF(+) to (LA&RA) (-) *6 unipolar (+) chest leads Orianted on the horizental plane of the heart) -leads v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6 V1: right 4th intercostal space V2: left 4th intercostal space V3: halfway between v2 and v4 v4: left 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line V5: horizontal to v4, anterior axillary line V6: horizontal to v5, mid-axillary's line. *leads II,III,AVF: record changes from inf. Border of the heart. *v1-v2 : record changes from the RV *v3-v4 : record changes from the intervent. Septum. *v5-v6 -I-AVL: record changes from LV P wave: the sequential activation (depolarization) of the right and left atria. qrs complex: right and left ventricular depolarization (normally the ventricles are activated simultaneously). st-t wave: ventricular repolarization. u wave: origin for this wave is not clear - but probably represents "afterdepolarizations" in the ventricles 2 PR interval: time interval from onset of atrial depolarization (p wave) to onset of ventricular depolarization (QRS complex) QRS duration: duration of ventricular muscle depolarization QT interval: duration of ventricular depolarization and repolarization RR interval: duration of ventricular cardiac cycle (an indicator of ventricular rate) PP interval: duration of atrial cycle (an indicator of atrial rate) measurements Sensivity :10mm = 1mv =2 large sq vertically Paper speed :25mm/sec Each large 5mm sq=0,2s Each small 1mm sq=0,04 H.R =1500/r-r interv.in 1mm ssq =300/r-r interv. In 5mm l sq P-r interv.=0,12-0,2 sec Qrs duration=0,06-0,10 sec Qt interv.=/< 0,4 sec Reading & interpriting ecg Methods of reading &interpreting the ecg 1.determine the cardiac rate 2.determine the cardiac rhythem 3.determine the axis of the heart 4.examine the p wave 5.asses the pr interval 6.examine the qrs complex 7.examine the st segment 8.examine the t wave 3 9.examine the u wave Examination of p wave *represent sequencial right &left atria activation *duration >0,12 s. *amplitude >2,5 mm *best studied in lead ii abnormalities of p wave 1.p mitral (l a. Hypertrophy) *broadening of p wave *m shape configeration 2. P pulmonal (r atr. Hypertrophy) *peaked p wave 3. Inverted p wave(nodal rhythem) 4. Absent p wave (AF , VT ,SA block) 5.inverted p in lead I (wrong connection, dextrocardia) assesment of pr interval From beginning of p to beginning of qrs *normal 0,12-0,2 sec. Abnormalities of pr inerval Short pr interval(>0,12s) *preexcitation syndromes - wolff parkinson white syndrome - Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome *AV junctional rhyth. *ectopic atrial rhyth. Prolonged pr (<0,2 sec.) *rhaumatic fever *first degree heart block . *drugs *electrolyte disturbance 4 QRS complex Normal 0,06-0,10 s Abnormalities of qrs 1- qrs widening Boundle branh block(bbb): *RBBB -normal varient -rt ventricle pathology -congenital heart disease (atrial septal defect) -coronary artery disease *LBBB -coronary artery disease -hypertension. -aortic valve disease -cardiomyopathy RBBB -wide qrs complex -rsr pattern or m shape in v1 -slurred s in v5 v6 -inverted t in v1 LBBB -wide qrs complex -small q in v1 -m shape qrs in v6 5 2- increase voltage Ventricular hypertrophy: *LVH -hypertension -hypertrophic cardiomyopathy -aortic stenosis *RVH -pulmonary stenosis -pulmonary hypertension *LVH -increase r in v5-6 - increase s in v1-2 sum. <35 s sq -LV strain pattern (st,t inversion in: i,avl,v5-v6) *RVH -increase r voltage in v1-v2 -deep s in v5-6 -RV strain pattern (st,t inversion in v1-2 ) 3- Abnormal Q wave Myocardial infarction *inferior mi: pathological q wave in leads ii, iii ,avf *anterior mi: pathological q wave in leads i,avl,v1-6 6 St segment Start from s wave till the beginning of t wave Abnormalities of st segment 1.st elevation St elevation convex upward *acute mi *prinzmetal angina *ventricular aneurysm *normal variant St elevation concave upward: pericarditis Other causes (lbbb,hyperkalemia) 2. St depression IHD *subendocardial ischemia *non q wave mi *reciprocal changes in acute mi Non-ischemic causes *vh, bbb, digoxine, hypokalemia, mvp, cns diseases 7 T wave Most labile wave in ecg Amplitude >5mm Abnormalities of t wave t inversion *mi *ischemia *pericarditis *myocarditis *cns dis *vh (strain pat.) *digoxine *mvp Peaked t wave *anxiety *hyperkalemia U wave Represent after depolarization of ventricles. Normal u has same polarity of t, amplitude 1/3 of t abnormalities of u wave Prominent upright u *bradycardia *hypokalemia *quinidine *mvp *cns diseases inverted u wave: IHD, LVH 8 axis of the heart Normal :(-30 )to (+110) *>-30 :left axis deviation *<+110:right axis deviation LAD : LI up L II,L III down RAD : L II down LII,III up 9