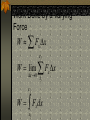* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Work and Energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
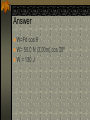
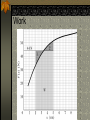
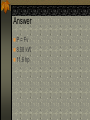
Work and Energy Conservation Law Work and Energy Work is a force applied to an object that causes the point of application of the force to move through some distance Energy is the capacity of an object to do work Unit: Joules Energy and work are scalar quantities Work Is work a dot product or a cross product? W Fd cos Example problem A man cleaning a floor pulls a vacuum cleaner with a force of magnitude F= 50.0 N at an angle of 30.0º with the horizontal. Calculate the work done by the force on the vacuum cleaner as the vacuum cleaner is displaced 3.00m to the right. Answer W=Fd cos θ W= 50.0 N (3.00m) cos 30º W = 130 J Work a Scalar Product Work is the dot product of Force and Displacement W F d Work Done by a Constant Force A particle moving in the xy plane undergoes a displacement as shown below in a constant force as given below acts on the particle. A) Calculate the magnitude of the displacement and that of the force. B) Calculate the work done on the object. d (2.0i 3.0 j )m F (5.0i 2.0 j ) N Answer d x2 y2 d (2.0) 2 (3.0) 2 d 3.6m F Fx2 Fy2 F (5.0) 2 (2.0) 2 F 5.4 N W F d W (5.0i 2.0 j ) (2.0i 3.0 j ) W (5.0i 2.0i) (5.0i 3.0 j ) (2.0 j 2.0i) (2.0 j 3.0 j ) W 10 0 0 6 16 J Work Done by a Varying Force Imagine a particle undergoes a very small displacement Δx The Fx is approximately constant over this small displacement. Work done can be expressed as W Fx x Graph of a Varying Force Force Force vs. displacement 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Series1 1 2 3 4 Displacement 5 6 Work Done by a Varying Force W Fx x xf W lim Fx x x 0 xf W xi F dx x xi Work Integration Work Video Power Power is the rate of doing work or of transferring energy. dw P dt Power Units Power is measured in joules per second. 1 J/s = Watt 1 hp = 746 W 1 kWh = 3.6 x 106W Power and Force If force F causes a particle to undergo a displacement ds, the work done is dW=F•ds. Since ds/dt is v the power is given by the following formula: dW P dt F ds P dt P F v Problem Consider a car traveling at a steady speed of 60 km/h (16.7 m/s). It encounters a frictional force (rolling and air drag) of 520 N. At what power level does the engine deliver energy to the wheels? Answer P = Fv 8.68 kW 11.6 hp