* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download prevention of malnutrition
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Overeaters Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Food safety wikipedia , lookup
Hunger in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics wikipedia , lookup
Stunted growth wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Food coloring wikipedia , lookup
Food studies wikipedia , lookup
Food politics wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
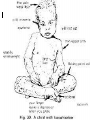
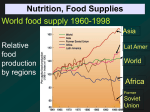
PREVENTION OF MALNUTRITION INTRODUCTION Food has nutrients which are required for protection of the body from diseases. According to 2011-2012 world population report – 925 million people are starving in the world. India’s population in 2011 – 1.21 billion. Karnataka’s population in 2011 – 6.1 crore. Cont…….. 37.6% - underweight children. 28.1% - undernourished. 55% - death of under five due to hunger. DEFINITION “A pathological state resulting from an absolute or relative deficiency or excess of one or more essential nutrients”. It may be an outcome of under nutrition, over nutrition or imbalance. CLASSIFICATION OF MALNUTRITION 1. Under nutrition - insufficient food is eaten. 2. Over nutrition – excessive quantity of food consumption. 3. Imbalance – disproposition among essential nutrients. 4. Specific deficiency – relative or absolute lack of an individual nutrient. ECOLOGY OF MALNUTRITION According to Jellief ecological factors are listed as:Conditioning influences Cultural influences Socio-economic factors Food production Health and other services Cont……… Conditioning influences:- The inter- relationship between malnutrition and infection such as diarrhoea, intestinal parasites, measles, whooping cough, malaria, TB are well documented. Cultural influences:- People choose poor diets when good ones are Cont……… available because of cultural influences which vary widely from country to country and from region to region. Food habits, customs, beliefs, traditions and attitude. Religion has powerful influence on the food habits of the people Cooking practices such as drawing water from rice, prolonged boiling, peeling of vegetables. Cont………. Child rearing practices, premature curtail of breast feeding, adoption. Socio-economic factors:Malnutrition is largely by the product of poverty, ignorance, insufficient education, lack of knowledge regarding the nutritive value of foods, inadequate sanitary environment, large family size. Cont………….. Food production:- The average Indian has 0.6 hectare of land surface compared to 5.8 hectare per head in the developed countries. The per capita available land for an average Indian is only 0.3 hectare. Health and other services:Improper organization and inadequate resources are the major factors responsible for malnutrition. REASONS FOR MALNUTRITION IN INDIA FOOD AVAILABILITY AND RELATED - - PROBLEMS:Low per capita food availability Low purchasing capacity of the masses Mal distribution of the available food Limited choice of food articles Problems of storage and distribution of food grains. Cont…….. - Protein gap versus “food gap” - Food gap and chronic starvation. POVERTY AND MALNUTRITION:- Low income of the masses - Poverty and malnutrition interaction. POPULATION PROBLEM AND MALNUTRITION:- Population explosion - Effect on food availability Cont…………. - Effects of uncontrolled fertility on nutrition SOCIAL FACTORS AFFECTING NUTRITIONAL STATUS:- Customs superstitions and taboos - Diet during illness - Castes and false social status - Food tastes and faculty cooling methods - Ignorance and lack of education - Alcohol and malnutrition. MALNUTRITION AND INFECTION CYCLE Loss of appetite mala absorption altered metabolism nutrient loss FOOD GAP INFECTION/ ILLNESS Wt loss growth retardation prone to infection mucosal damage PROTIEN ENERGY MALNUTRITION [PEM] PEM is a disease due to the deficiencies of protein and calories occur commonly among weaned infants and preschool children in India and other developing countries. PEM is divided into 3 groups: kwashiorkor nutritional marasmus Marasmus kwashiorkor KWASHIORKOR Its caused by deficiency of proteins in the diet. The important symptoms of the disease by deficiency of proteins in the diet muscle wasting, fatty liver, loss of appetite and diarrhoea, change in the colour the skin and hair and anemia. NUTRITIONAL MARASMUS This is caused by severe deficiency of proteins and calories in the diet. The important features of growth retardation and severe wasting of muscle and loss of subcutaneous fat. Eye lesions due to vitamin A deficiency and anemia may also be present. MARASMUS KWASHIORKOR Children suffering from this disease show the signs of both kwashiorkor and marasmus. FEATURES OF PEM FEATURES MARASMUS KWASHIORKOR Muscle wasting Obvious Hidden by edema and fat Edema None Present in lower legs, face, lower arms Fat wasting Loss of subcutaneous fat Fat often retained but not firm Weight for height Very low Weight ma be less than 60% of standard. Mental changes Quite Irritable CLASSIFICATION OF PEM According to ICMR classification NORMAL--- 80 % & Above Grade I ---- 70-80% Grade II----- 60- 70 % Grade III----- 50-60 % Grade Iv---- Below 50 % DIETARY MANAGEMENT OF PEM 1. PROTEIN ALLOWANCE Cereal & pulses protein about 4 to 5 gm per kg Animal protein 3 to 3.5 gm/kg NPU of cereals & pulses is only 60 percent CALORIES 160-180 KCAL /KG OF WEIGHT Younger child – 175 to 200 Older child – 150- 175 One year old –1oookcal After one year add 100 kcal/year TREATMENT OF PEM Adequate diet :- 125 -150 kcal & 3-4 gm of good quality of protein/kg of body weight/day. Treatment of infections Health education Rehabilitation Indicators Weight/height = weight of the child x100 weight of normal child at same age PREVENTIVE MEASURES HEALTH PROMOTION Measures directed to pregnant & lactating women Promotion of breast feeding development of low cost weaning foods measures to improve family diet Nutrition education conti Family planning & spacing of births Family environment 2) specific protection Childs diet should include protein & energy rich foods Immunization Food fortification Conti…. Early diagnosis & treatment period surveillance Early diagnosis f any lag in growth Early diagnosis and treatment of infections & diarrhea development of programmes for deworming of heavily infested children Rehabilitation Nutritional rehabilitation services Hospital treatment & follow up. Hyderabad mixture Whole wheat ( roasted )- --- 40 gm Bengal gram (roasted)---- 16 gm Ground nut (roasted) -----10gm Jaggery ----------------------20gm energy ----330kcal Protein ----11.3gm 86gm