* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 - Introduction
Communications in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Telephone exchange wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in India wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
National Broadband Plan (United States) wikipedia , lookup
Streaming television wikipedia , lookup
British telephone socket wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Telekom Malaysia wikipedia , lookup
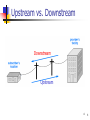
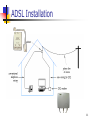
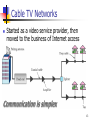
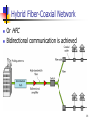
Access and Interconnection Technologies Asst. Prof. Chaiporn Jaikaeo, Ph.D. [email protected] http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~cpj Computer Engineering Department Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand Adapted from the notes by Lami Kaya, [email protected] © 2009 Pearson Education Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Access Technology Internet access technology A data communications system that connects an Internet subscriber to an ISP (Internet Service Provider) Such as a telephone company 2 Upstream vs. Downstream Most Internet users follow an asymmetric pattern a subscriber receives more data from the Internet than sending Downstream to refer to data traveling from an ISP in the Internet to a subscriber Upstream to refer to data traveling from a subscriber to an ISP 3 Upstream vs. Downstream Downstream Upstream 4 4 Narrowband vs. Broadband Both refer to access technologies Narrowband 128 kbps Broadband 1 Mbps Exact boundary is blurry 5 Narrowband Technologies Dialup telephone connections Leased line circuits (via modems) Fractional T1 data circuits ISDN 6 Broadband Technologies Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Cable modem Wireless access (GPRS, EDGE, 3G) T1 (or higher) data circuits 7 Local Loop Local loop describes the physical connection between a telephone company Central Office (CO) and a subscriber Consists of twisted pair and dialup call with 4 KHz of bandwidth It often has much higher bandwidth A subscriber close to a CO may be able to handle frequencies above 1 MHz 8 Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) DSL is one of the main technologies used to provide high-speed data communication services over a local loop the set is collectively referred to by the acronym xDSL 9 Bandwidth Division in ADSL 10 ADSL Installation 11 Recent DSL Technologies HDSL – High-bit-rate DSL VDSL – Very-high-bit-rate DSL SDSL – Symmetric DSL ADSL2 ADSL2+ See also Source: AWARE. ADSL2 and ADSL2+ The new ADSL standard. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_subscriber_line 12 Cable TV Networks Started as a video service provider, then moved to the business of Internet access 13 Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial Network Or HFC Bidirectional communication is achieved 14 Data Transfer over CATV Standard: DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) Division of coaxial cable band by Cable TV Theoretical downstream data rate is 30 Mbps Theoretical upstream data rate is 12 Mbps 15 Cable Modem 16 Cable Modem Transmission System Or CMTS 17 Fiber To The X Optical broadband network architectures Fiber-to-the-node Fiber-to-the-curb Fiber-to-the-building Fiber-to-the-home Source: Wikipedia 18 Wireless Technologies Imagine a farm or remote village many miles from the nearest city The twisted pair wiring used to deliver telephone service to such locations exceeds the maximum distance for technologies like ADSL Local loop technology may not work on all lines 19 Wireless Technologies 3G/4G (Third/Fourth Generation) cellular telephone services WiMAX Satellites 20 WiMAX Overview ISP Internet Backbone Cell-like WiMAX towers Line of sight transmission Non line of sight transmission Home WLAN 21 Broadcast Satellite Systems More BW than dialup Reach arbitrary locations Long delay Downlink is good, Uplink is expensive alternative uplink (dialup) 22