* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformers and Electromagnetic Waves Practice Problems
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
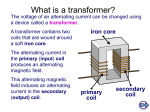
Transformers and Electromagnetic Waves Practice Problems AP Physics Name: Period: Transformers 1. Explain in your own words how a transformer works. What happens to cause a transformer to output electricity? 2. What uses do transformers have? Where are some places where you might find transformers. 3. Which coil, primary or secondary, has more windings in a step-up transformer? Explain. [A step up transformer has a higher voltage output from the secondary coil than is input to the primary coil.] 4. In an ideal transformer, how does the power put out by the secondary coil depend on the power put into the primary coil? 5. An ideal transformer steps 8.0 V up to 2000 V. The 4000 turn secondary coil carries 2.0 A. a) How many turns are in the primary coil? b) What is the current in the primary coil? 6. The primary coil of an ideal transformer is connected to a 120 V source and draws 10 A. The secondary coil has 800 turns and produces a current of 4.0 A. a) What is the voltage across the secondary coil? b) How many turns are in the primary coil? 7. An ideal transformer has 840 turns in its primary coil and 120 turns in its secondary coil. The primary draws 2.50 A at 110 V. a) What is the current through the secondary coi? b) What is the voltage output of the secondary coil? 8. The circuit components inside an electronic device operate at 20 V and 0.50 A. The power adapter for the device contains a transformer with 300 turns in its primary coil that is used to convert 120 V household electricity to the proper voltage. a) How many turns must the secondary coil have? b) How much current is in its primary? Electromagnetic Waves 9. What new idea did James Clerk Maxwell add to the understanding of electricity and magnetism? 10. According to Maxwell, what are electromagnetic waves? How does an electromagnetic wave work? 11. How does one create an electromagnetic wave? 12. What are the different classes of electromagnetic waves? How do they differ from each other? 13. A simple wire antenna is connected to a battery. Will the antenna emit an electromagnetic wave? Explain.