* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 22 Planet Earth
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
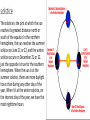
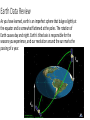
Chapter 22 Planet Earth Key Words – define these words on your paper as you read the following chapter. Sphere Axis Rotation Revolution Ellipse Equinox Solstice Earth’s Shape Space probes and artificial satellites have sent back images that show Earth is sphere-shaped. A sphere is a round, three dimensional object whose surface at all points is the same distance from its center. Tennis balls and basketballs are examples of spheres. But people had evidence of Earth’s true shape long before cameras were sent into space. Around 350 B.C., the Greek astronomer and philosopher Aristotle reasoned that Earth was spherical because it always casts a round shadow on the moon during an eclipse. Only a spherical object always produces a round shadow. If Earth were flat, it would as a flat shadow. If the earth were flat It’s shadow would be Flat. Physical Properties of Earth Diameter (pole to pole) Diameter (equator) Circumference (poles) Circumference (equator) Mass Density Average distance from the sun Period rotation (1 day) Period of Revolution (1 year) 12,714 km 12,756 km 40,008 km 40,075 km 5.98 X 10 g 5.52 g / cm3 149, 600, 000 km 23 hr. 56 min 365 day, 6 hr., 9 min. 27 Today we know that Earth is sphere-shaped, but is not a perfect sphere. It bulges slightly at the equator and is some-what flattened at the poles. The poles are located at the north and south and of Earth’s axis. Earth’s axis is the imaginary line around which the Earth spins. The spinning of Earth on its axis, called rotation, causes day and night to occur. Earth’s Rotation As Earth rotates, the sun comes into view at daybreak. Earth continues to spin, making it seem that the sun moves across the sky until it appears to set at night. During the night, your area of Earth has spun away from the sun. Because of this, the sun is no longer visible. Earth continues to steadily rotate, and the sun eventually comes into view the next day. One complete rotation takes about 24 hours, or one day. How many rotations does Earth complete during on year? It completes about 365 rotations during its journey around the sun. Earth’s Magnetic Field Convection currents inside Earth’s mantle power the movement of tectonic plates. Scientists hypothesize that movement of material inside Earth also generates a magnetic field. The magnetic field of Earth is much like that of a car magnet. Earth has a North and South magnetic pole, just as a bar magnet has opposite magnetic poles at its ends. Magnetic North When you observe a compass needle pointing toward the north, you are seeing evidence of Earth’s magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic axis, the line joining its North and South magnetic poles, does not align with its rotational axis. The magnetic axis is inclined at an angle of 11.5 degrees to the rotational axis. If you followed a compass needle pointing north, you would end up at the magnetic north pole rather than the geographic (rotational) north pole. Earth’s magnetic field and other physical properties affect us every day. Seasons / Earth’s Revolution Earth’s rotation causes day and night to occur. Another important motion of Earth is the revolution, or yearly orbit around the sun. just as the moon is a satellite of Earth, Earth is a satellite of the sun. if Earth’s orbit were a circle, and the sun were at the center of the circle, Earth would maintain a constant distance from the sun. however, this is not the case. Earth’s orbit is an ellipse, and elongated closed curve. The sun is off set from the center of the ellipse. Because of this the distance between Earth and the sun changes during Earth’s yearlong orbit. Earth gets closest to the sun – 147 million km away – on January 3. The farthest point in Earth’s orbit is about 152 million km away from the sun and is reached on July 4. is this elliptical orbit causing the changing temperatures on Earth? If it were, you would expect the warmest days in January. You know this isn’t the case in the northern hemisphere. Something else is causing the change. Even though Earth is closest to the sun in January, the over all amount of energy Earth receives from the sun changes little through the year. However, the amount of energy any one place on earth receives can vary quite a bit. Earth’s Tilted Axis Earth’s axis is tilted 23.5 degrees from a line perpendicular to its orbit. This tilt causes the seasons. Daylight hours are longer for the hemisphere tilted toward the sun. think of how early it gets dark in the winter compared with the summer. The hemisphere tilted toward the sun receives more hours of sunlight than the hemisphere tilted away from the sun. Another effect of Earth’s tilt is that the sun’s radiation strikes the hemisphere tilted toward it at a higher angle than it does the other hemisphere. Because of this, the hemisphere tilted toward the sun receives more electromagnetic radiation per unit are than the hemisphere tilted away. a summer season results when the sun is in the sky longer and its electromagnetic radiation strikes Earth at a higher angle. Just he opposite occurs during winter. Equinoxes and Solstices Because of the tilt of Earth’s axis, the sun’s position relative to Earth’s equator constantly changes. Most of the time, the sun is North or South of the equator. Two times during the year, however, the sun is directly over the equator. Equinox When the sun reaches an equinox, it is directly above Earth’s equator, and the number of daylight hours equals the number of night time hours all over the world. At that time, neither the northern nor the southern hemisphere is tilted toward the sun. In the norther hemisphere, the sun reaches the spring equinox on March 20 and 21 and the fall equinox on September 22 or 23. in the southern hemisphere, the equinoxes are reversed. These dates are the first days of spring and fall. solstice The solstice is the pint at which the sun reaches its greatest distance north or south of the equator. In the northern hemisphere, the sun reaches the summer solstice on June 21 or 22, and the winter solstice occurs on December 21 or 22. just the opposite is true for the southern hemisphere. When the sun is at the summer solstice, there are more daylight hours than during any other day of the year. When it’s at the winter solstice, on the shortest day of the year, we have the most nighttime hours. Earth Data Review As you have learned, earth is an imperfect sphere that bulges slightly at the equator and is somewhat flattened at the poles. The rotation of Earth causes day and night. Earth’s tilted axis is responsible for the seasons you experience, and our revolution around the sun marks the passing of a year. Review 1. Which earth motions causes night and day? 2. Why does summer occur in Earth’s norther hemisphere when Earth’s north pole is tilted toward the sun? 3. the physical properties of Earth lists Earth’s distance from the sun as an average. Why isn’t there one exact measurement of the this distance? 4. What causes seasons on Earth? 5. What causes winter? 6. What effect on seasons does the sun being closest to Earth in January have?