* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Governing of Colonies to French and Indian War Teacher Notes
Slavery in the colonial United States wikipedia , lookup
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
Shipbuilding in the American colonies wikipedia , lookup
Queen Anne's War wikipedia , lookup
Peace of Paris (1783) wikipedia , lookup
Colonial South and the Chesapeake wikipedia , lookup
Cuisine of the Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
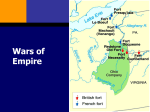
Topic/Person/Event Describe It British Incoherent, Administration of inefficient, its American and unfocused British policy colonies As a result of English Civil War, for one example Creation of the Dominion of New England to gain more political control over colonies (fails) “Salutary Neglect” Glorious Revolution places William and Mary on the throne Britain is lax in its administration of its colonies Colonies develop a measure of self-governance Significance/Impact Colonies developed a habit of selfgovernance (However, while the king no longer had the power to veto acts of Parliament, the governors of royal colonies enjoyed this power, as well as wide-ranging powers to appoint and remove officials and to grant pardons.) Colonies are used to: taxing themselves, voting on colonial issues, colonial representation Example Colonial assemblies (the lawmaking branch of the government) were elected by a popular vote of the citizens Often modeled after Parliament, took control of colony’s budget as well as voting on taxes. Glorious Revolution House of Burgesses, Other colonial assemblies Topic/Person/Event Describe It Mercantilism Theory of economics The main aspect of mercantilism was that there was a finite amount of gold and silver in the world, and the best way for a nation to gather it was to earn it Significance/Impact Colonies were seen to be a way that Great Britain could increase its total wealth through its raw resources Colonies not allowed to manufacture goods Example Navigation Acts supported the theory of mercantilism Direct Trade Routes Triangle Trade Routes Colonies provide raw resources AND Colonies provide Britain buyers for their manufactured goods Navigation Acts (Before French & Indian Wars) Trade restrictions that required an increasing number of British sailors on British ships transporting British goods to British ports In short: Britain would control all trade Too expensive for Britain to enforce Navigation Acts Colonies enjoy a little bit of smuggling to make some money on the side Attempt to gain back control by Charles II through Lords of Trade Rum is smuggled to other nations directly instead of going through British controlled shipping Topic/Person/Event Describe It French and Indian Primarily between French & English European War powers with Indian allies (1756–1763) France created trading posts, not self(Known as Seven sustaining colonies. Years War in As a result, a preponderance of males were Europe) sent, and they often integrated into the tribes of Native Americans by taking Indian brides. War begin when This allowed them to have some strong Indian British colonists allies. crossed into the However, the French were small in number Ohio River Valley, compared to the British numbers (colonies). which both England and France claimed British had Indian allies, too—particularly those who were enemies of the tribes that were In response, the supporting the French. French erected forts in western Spain was in decline as a presence in No. Pennsylvania to America since their settlements here never prevent further became prosperous incursions. Significance/Impact Fight over dominance of North America George Washington Sent to fight in French & Indian War Gains experience in war Begins to earn respect Primary Source: First Political Cartoon By Benjamin Franklin First political cartoon in colonies Urged colonies to unite against the French in 1754 Would become popular again twenty years later urging colonies to unite against British policies Example British are victorious See image on p. 180 Topic/Person/Event Describe It Albany Congress Convened to discuss Franklin’s Plan of Union Significance/Impact Forerunner to the Articles of Confederation. Example British Victorious Britain took all of France’s North American provinces from the Mississippi east to the Appalachian mountains and all of Spanish Florida and Canada. Great Britain now controlled all of the landmass east of the Mississippi River. Plan called for creation of a confederation of the colonies Peace of Paris of 1763 Ends French and Indian War Britain was hoping to obtain the Louisiana Territory as well, but through a secret treaty, France gave the land to Spain so that it would not be taken by Britain. Britain at End of French and Indian Wars Great Britain has double the amount of land (all the way to the Mississippi) Britain begins to manage its colonies more aggressively Proclamation of 1763 Sugar Act British displeased by the colonists’ refusal to stop trading with the enemy while the Redcoats were fighting a war the colonists had started. Enforcement of Navigation Acts Stamp Act Britain faced a massive national debt that demanded payment. Topic/Person/Event Describe It Pontiac’s Rebellion Widespread Indian attacks erupted along the new frontier in 1763 under the leadership of Ottawa chieftain named Pontiac Angered that their land had been ceded to the British by the French without their approval, they fought to regain it. Significance/Impact Great Britain wanted to keep the colonists out of the newly acquired lands to: ● prevent another war from erupting and ● prevent adding further to the burdensome debt. Focus Questions: Why did New England suffer more than other regions of North America during the wars of the eighteenth century? What were the long-term financial, military, and political consequences of the wars between France and Britain? How did the British Empire administer the economy of its colonies? How were colonial governments structured, and how independent were they of the mother country? How did the presence of the French to North America affect Britain and its colonies? What were the causes of the French and Indian War? How did victory in the Seven Years’ War affect the British colonies in North America? Example