* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concepts For Micro Theory
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
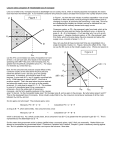
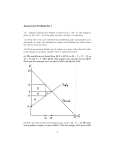
Concepts For Micro Theory Supply and Demand demand vs. quantity demanded supply vs. quantity supplied movements along vs. shifts of S & D price ceiling, price floor economic shortage/surplus market & individuals' demand curves horizontal summation specific tax tax incidence elasticity of demand and supply Consumer Theory consumption bundle preferences budget line indifference curve properties of indiff. curves slope down don't cross "moon" shaped tangency of budget line & indiff curve normal vs. inferior goods complementary vs. substitute goods derivation of demand curves endowment Farm Programs deficiency payments loan program (CCC) food stamp program surplus and profit dead weight loss The Firm Cost Curves and Profit Maximizing Output economic profits cost function, C(Q) marginal cost fixed vs. variable costs c = vc + fc ac = avc +afc producer's supply curve mc above avc why does p = mc? increasing, decreasing and constant costs u-shaped costs diagram short-run vs. long-run supply long-run competitive equilibrium profits are zero p = mc S=D Deriving Cost Curves from Isoquants production function returns to scale isoquant isocost = expenditure lines tangency gives chosen inputs derive cost curve derive (conditional) factor demand Monopoly marginal revenue for competitive firm causes of monopoly profit-maximizing P & Q for monopoly barriers to entry why MR=MC gives max profit What's Wrong With Monopoly deadweight loss of monopoly regulation of public utility Market Failure and Welfare Willingness to Pay Surplus Deadweight loss Competition maximizes profits plus surplus allocation Pareto efficiency efficiency versus income distribution Public Good A competitive Equilibrium is a Pareto Optimum Pollution Technology Based Effluent Standard Isoquant diagram price that achieves same level of pollution Major Water/Land/Air legislation and programs Clean Air Act. National Goals State Plans to meet goals; stricter standards in dirtier places Technology Based Effluent Standards --TBES--(Best Practicable, Available, Conventional Technology) Point Source--TBES for new sources, existing sources in dirty areas, toxics Non-point Source--rules for cars but not yet for trucks, trains, and boats RECLAIM Acid Rain CERCLA--Superfund Fund to pay for cleanup of old wastes Ability to sue for Natural Resource Damages You Touched It, You're Responsible Taxes vs. Standards: who gets the money/efficiency Right amount of pollution: Between firms, between firms and consumers. Diagram read from both sides price of clean air/water is too low results in too much of polluting input (isoquant diagram) results in too much output private marginal cost understates social mc Property rights in Water Appropriative: first in use, first in right Equal sharing Need for trade to get efficient allocations Coase Theorem is pollution independent of assignment of property rights transaction costs with high enough transactions costs it could be best to let the polluter pollute The smoker and asthmatic: does income matter? do property rights attenuate pollution Fishery Increased growth = interest rate Open access