* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review for Quiz 1 20..
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
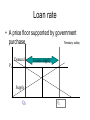
Review for Quiz 1 (Everything through Chapt 5) Peter Berck 2016 Env. Econ. 1 Supply and Demand • • • • • • • • • • • • • Supply and Demand demand vs. quantity demanded supply vs. quantity supplied movements along vs. shifts of S & D price ceiling, price floor Excess supply/demand market & individuals' demand curves horizontal summation specific tax tax incidence elasticity of demand and supply complementary vs. substitute goods normal and inferior goods Tax example 3 2.5 2 S D D - .6 P 1.5 1 0.5 0 -0.5 0 Ps = 0.25 Q Pd = 3 – .4 Q 2 4 6 Q t= .6 8 10 D-1(Q) – t = S-1(Q) Pd - t = Ps Tax • Incidence • Flat and vertical supply curve Loan rate • A price floor supported by government ?treasury outlay purchase. Demand Excess supply PL Supply QD QL Consumer Theory • • • • • consumption bundle* *=learn the definition Preferences* budget line or budget constraint* indifference curve* properties of indiff. curves – (1) slope down (2) don't cross (3)"moon" shaped • derivation of demand curves – Why tangency of budget line & indiff curve – Change price Demand Curve Price of Wine is 8 50 40 High P Wine 30 Medium P 20 Low P 10 0 0 50 Bread 100 Normal & Inferior Again • What happens to q demanded with increased income? Pareto Improvement* • When at least one party to a deal is made better off and no parties are made worse off the deal is said to be Pareto improving. • Examples of market trades that are pareto improving • Examples of market trades that are NOT pareto improving What Goes Wrong With Markets • Reasons for – No ownership; open access* – Externalities* – Public Goods (non-rival; non-excludable)* – Insufficient weight on future – Government Failure • Give examples of each Surplus,EV,CV • • • • • Total Willingness to Pay* Amount Paid Consumer Surplus* Surplus from a public good Define EV* and CV* for a price change. • Willingness to Accept and Willingness to pay questions. • When are they EV and when are they CV