* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Theory, Isotopes and Radioactive Decay
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
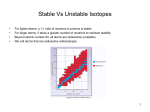
ATOMIC THEORY, ISOTOPES AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY Section 7.1 WHAT IS (DEFINE) Radioactivity Radiation Isotopes Decay RADIOACTIVITY Deals with non-normal matter, something that behaves irregularly. Matter that can give off something Matter that is changing, and cause radio interference within the nuclei of its (Electromagnetic). atoms RADIATION Is what is given off (emit) and causes the interference. They are the high-energy, short wave particles and rays of energy. ISOTOPES Any element, same # of protons, with a different # of neutrons and overall mass. Stability ≈ Decay (excess neutrons): neutron proton TYPES OF DECAY Normal Radioactive Implies to breakdown, To decay by emitting fall apart and become radiation. smaller. Something is High-energy, short changing form wavelength particles & (composition). Decay is a rays process. WHAT ARE (DEFINE): THE 3 MAIN TYPES OF RADIATION FOUND IN THE DECAY PROCESS ALPHA An Alpha particle is the nucleus of a Helium atom. It has 2 protons and 2 neutrons. BETA Beta particle is an electron Caused from a neutron decay GAMMA A gamma particle is a high-energy, short wavelength ray (like light). Caused from changes in energy (between levels or states) RADIATION TYPES (PENETRATION) Think of Alpha (α), Beta (β) and Gamma (γ) as letters A, B, C that equal changes according to size. A = Biggest = α B = Next = β C = Smallest = γ RADIATION TYPES (REPULSION) Think of Alpha (α), Beta (β) and Gamma (γ) in terms of charges (attract and repel). α = Positive (+2) β = Negative (-1) γ = No Charge RADIATION TYPES 1. The sum of the mass numbers on each side of the equation does not change (stays the same) Don’t Forget to Balance!!!! 2 RULES FOR WRITING NUCLEAR EQUATIONS 2. The sum of the atomic charges (in the nucleus) on each side of the equation does not change (stays the same) Isotope Tables Radioactive decay & Nuclear Equations 1. Show what happens when Plutonium 242 decays by alpha emission. 2. Show what happens when Uranium 238 decays by alpha emission. 3. Show what happens when Carbon 15 decays by beta emission. 4. Show what happens when Hydrogen 3 decays by beta emission.