* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit1
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
MTS system architecture wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
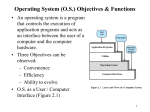
1 STUDY MATERIAL DEPARTMENT : SOFTWARE SYSTEMS CLASS : II M.Sc SUBJECT : OPERATING SYSTEMS UNIT :I Syllabus: Objectives of an operating system. Operating system as a resource manager, operating system as a user computer interface, ease of evolution. The evolution of the operating system. Definition for Operating System: Program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between the user of computer and the hardware. Objectives : Convenience : Make computer more ease to work. Efficiency : Resources in efficient manner. Ability to evolve : Permit effective development , testing , and introduction of without interfering the service. new system function Three Aspects of Operating System: Operating System as a user / computer interface , Operating System as Resource Manager , Ease Of Evolution Operating System as a user / computer interface : User of these Application – End User He can view the system in terms of Applications Application is a Program Developed by a Programmer To help the application programmer, a set of system programs are provided called as Utilities. This is used for calling frequently used functions , management of files ,and for Control of I/O devices. Most important system program is Operating System. Operating System hides the details of hardware from the programmer . End User Application Program Utilities Operating System Hardware Services Of Operating System: 2 i)Program Creation: Editors and Debuggers are the utility Programs accessible through the OPERATING SYSTEM. ii)Program Execution : Instruction and data must be loaded into main memory , I/O devices and file must be initialized and other resources must be prepared which are governed by OPERATING SYSTEM. iii)Access To I/O devices : Each I/O device , peculiar set of instructions , control SYSTEM . signals are governed by OPERATING iv)Controlled Access to files: In the file Cases , control with addition to the storage format on I/O devices are governed by OPERATING SYSTEM . It also provide security in case of Multi User mode. v) System Access: In an shared or public mode , OPERATING SYSTEM provide Protection Mechanism to the resources and Resolve Conflict in use of A resource. vi)Error Detection and Response: During running , Varity of errors can occurred so the Operating System to make the response that clears the error with least impact on running Application. The response may range from ending a program that cause error , or to retrying the operation , to simply reporting the error in the application. vii) Accounting: Operating System has the statistics about available resources , which is useful for future Up gradation. Other Services are Communication, Resource Allocation etc., Operating System As a Resource Manager: Operating System is also a Program, and the key difference is that it directs the processes in the use of other system resources. This Program is Executed by the Processor. Processor releases its control to the process and regain its control after the process has finished the job. This allocation is managed by the Kernel or nucleus where most frequently used functions of operating system are present which are kept in main memory. In allocating Resources it has to follow the below steps ; 1.Status (Free or Allocated) , 2.Priority among the Process, 3.Allocate the Processor to the Process(Relinquish the Control), 4.Deallocate the Process (Regain its Control). Ease Of Evolution: Hardware Upgrades and New Type of Hardware Evolution of Paging Mechanism , Evolution of Graphic or Window mode Terminals. New Services: Fixes Due to the user request , new kind of services are evolved by the operating System. : 3 Unexpected errors are found and some fixes are made. Evolution of Operating System: Serial Processing Simple Batch System Multi Programming Environment Time Sharing Environment Serial Processing: No concept of Operating System. Programs are in Machine Code. If error occurs program comes to halt state. There are switches and lights , input (Program in Machine Code)is given to the switches And output is sent to printer through the switches. If any error occurs light will glow. Programmer correct the error by checking Registers ,Memory etc., and then proceed the above step to get the output . Scheduling: Reserving the Machine time for Processing ----- Scheduling. If Process time for a process < Reserved time –Processor put as idle. If Process time for a process > Reserved time –Process is stopped without completion. Setup Time: For a Process to be completed, then some basic steps to be done ; Loading Complier(Program) + Source Program to then Memory. Compiling the Source Program so that source Program is converted to Object Program , which has to be saved in memory. Linking has to be done so that Object Program is linked with the Built in Functions. So for the above process some amount of time will be consumed. This amount of time is consumed is called as setup time. If any error occurs while running, then we have to startup from the first which make to consume large amount of time. Due to this two cases , we are moving to the Batch Processing Environment. Simple Batch Systems: First of this kind is developed for General Motors by IBM in mid of 1950’s . Monitor the heart of this kind. User submit his job to the Operator. Operator batches all the jobs and load it as input to the monitor. Monitor send its control to the first job . After Processing of first job , control is branch back to the monitor. Monitor: Resident monitor , part of the monitor resides in main memory. Rest of monitor consists of utilities and common functions that are loaded as subroutines to the user program at the beginning of any job that requires them. Monitor send its control to the first job which is in main memory. After Processing of first job , control is branch back to the monitor. Results are sent to the Printer. Processor: Processor first executes set of instructions , so that monitor fetch a job. After that Processor executes the set of instruction in the user program until it ends or error occurs. Control is passed to a job , that is it fetches an instruction from the user program and executes it. Control is passed to the Monitor , that is it fetches an instruction from the monitor Program and executes it. Job Setup: 4 Job Control Language (JCL) , special type of language which provide instructions to the monitor. For Example , if user submits a program(Fortran) with data cards and job control instructions denoted by $ at the beginning. If following tasks are done for specific card has been read $FTN card load Fortran complier from its tape. Compiler transfer Source Code to the Object Code and store in memory. If it is stored in memory , then it is termed as compile , load and go If it is stored in tape ,$LOAD card is required. $LOAD card is read by monitor and invokes loader , which stores the object program into main memory that is in the place of compiler. Input instruction cause the monitor to fetch the data from data cards until next JCL card has been read. Hardware features: Memory Protection : Protection is given to the memory where Monitor resides. Timer: Timer is to prevent a single job to monopolize the system. Privileged Instruction: To secure the resources such as I/O devices Some set of instructions can be executed only by the Monitor. If any user try to execute these set of instruction , then error occurs and stops current execution. These set of instruction are called as Privileged Instruction. Interrupts: Flexible for to release and to regain its control to the or from the process or job. Multi Programming Batch System: In Simple Batch System , if any process is waiting to get control over some I/O devices , then processor is to wait for some time until the process has received the control .(Refer to the example ) To avoid that we are moving to the new concept that is, if a process is waiting for some event had to occur, processor can send its control to the next job which is waiting for the processor control. This concept is called as Multiprogramming or Multitasking . Run Run Wait Wait Time UniProgramming Program A Run Wait Run Run Program B Combined Wait Run Wait Run Run Wait Wait Run Run Wait Time Multi Programming with Two Programming 5 In the above figure , if Program A is waiting for a control of I/O device , then Program B is receive the Processor control . Comparison between Simple Batch and Multi Batch Systems: Time taken by each job to complete its task are; Job 1 = 5 min Job 2 = 15 min Job 3 = 10 min In simple Batch System , Job2 has to wait for 5min until job1 has been finished. Job 3 has been wait for 20 min so that job1 & job 2 has been over ( 5 + 15).So that total time to process all the three jobs are 30 min. But in Multiprogramming batch system when job1 is over , 1/3 of job2 and ½ of job3 has been completed . so that total time taken by the processor to complete all the task is 15 min. So total time taken by the processor in multi programming mode is less than the time taken by the processor in simple batch system. Time Sharing System: Processor’s time is shared among all the process . For example , if a machine with 32K of main memory , with the 5K of resident monitor. User program and data are loaded into 27K of main memory. A system clock generates interrupt at the rate of 0.2 seconds. When interrupt occurs , control is regained by the processor and sent its control to the next process. Assume that there are four jobs , Job1 = 15K Job 2 = 20K Job 3 = 5 K Job 4 = 10 K Monitor loads job1 and transfer its control to it. Monitor if wants to load job 2 which needs more memory , so that job 1 is written out into the disk first , then job 2 is loaded. Monitor if wants to load job 3 which has need less memory , so that part of job 2 is written out into the disk first to avoid disk write time , then job 3 is loaded. Monitor if wants to load job 1, so that part of job 2 , and job 3 are written out into the disk first , then job 1 is loaded. Monitor if wants to load job 4 which has need less memory , so that part of job 2 and part of job 1 is written out into the disk first to avoid disk write time , then job 4 is loaded. Monitor if wants to load job 2, so that job 1 is written out into the disk first and missing portion of job 2 is loaded into the memory , 32K 32K 25K Job 2 Job1 5K 5K Monitor Monitor 6 32K 32K 25K 25K Job 2 (Job 2) 20K 10K Job 1 Job 3 5K 5K Monitor 0 Monitor 0 32K 32K 25K 25Kk (Job 2) 20K (Job 1) Job 2 15K Job 4 5K 0 5K Monitor Monitor Monitor 0 Questions: Services Provided By the Operating System. Evolution Of Operating System. Comparison of Serial , simple batch ,Multi Programming and Time Sharing System. Hardware facilities available in Simple Batch System. How Operating System work as a Resource Manager.