* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chemical change
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Microplasma wikipedia , lookup
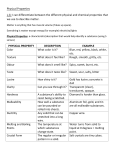
Cornell Notes Paper Topic: Changes in Matter Date: 11/6/14 Source: ItC, 20-27 Main Topics Detailed Notes What happens to a substance in a physical change? Physical change – alters the form or appearance of matter but does not turn any substance in the matter into a different substance (example – butter turned into a sculpture looks different but is still butter, snow melting) changes of state are physical changes – ice into water, water into water vapor, water turning into ice…the water looks different but is not a new material sugar water – when dissolved, sugar disappears but no new substance is created. When water evaporates, sugary crust is left in the pan – dissolving is a physical change other physical changes – bending, crushing, breaking, and chopping any change that alters only the shape or form of matter is a physical change methods of separating mixtures – filtration, distillation (both are physical changes) What happens to a substance in a chemical change? chemical change – a change in matter that produces one or more new substances o ex - a single substance breaking down into two or more other substances (hydrogen peroxide breaking into water and oxygen) o ex - two or more substances combine to form different substances (photosynthesis – several compounds combined with energy, produce new substances) o ex - vapors from glue react with sweat/body chemicals to form a white powder o ex – Luminol reacts with blood – creates a new substance that glows in the dark Cornell Notes Paper Topic: Changes in Matter Main Topics Examples of chemical change Conservation of mass (the law of conservation of mass (LoCoM) How are changes in energy and matter related? Date: 11/6/14 Source: ItC, 20-27 Detailed Notes ex - burning of natural gas on a stove. When burned, methane combines with oxygen in the air to create carbon dioxide and water vapor. Both substances have different properties than methane. Other processes that result in chemical changes – o combustion - rapid combining of fuel with oxygen – creates heat, light, new substances o electrolysis – electricity breaks compounds into elements or simpler compounds – ex. breaking water into hydrogen and oxygen o oxidation - combining a substance with oxygen – when iron rusts o tarnishing - combining of bright metal with sulfur – creates dark coating on metal – tarnishing of brass LoCoM - matter is not created or destroyed in any chemical or physical change ex - figure 5 on page 25 – new substances created, but same atoms are simply rearranged Energy = the ability to do work or cause change KEY CONCEPT – every chemical and physical change in matter includes a change in energy! o Bending a paperclip takes energy o ice melting absorbs energy from surrounding matter o candle wax burning gives off energy as light and heat *** Like matter, energy is conserved in a chemical change – it is never created or destroyed – can only be transformed from one type to another Cornell Notes Paper Topic: Changes in Matter Main Topics Temperature and thermal energy Transforming chemical energy Date: 11/6/14 Source: ItC, 20-27 Detailed Notes Temperature – measure of how hot or cold something is Thermal energy – total energy of the motion of all of the particles in an object – thermal energy flows from warmer to cooler matter o ex - particles moving quickly bang into particles nearby in a chain reaction Temperature and thermal energy are not the same thing! But they are related. Thermal energy is released or absorbed when matter changes – ex. ice absorbs thermal energy from its surroundings when it melts leaving the surroundings feeling cold endothermic change – a change in which energy is absorbed (melting of ice) exothermic change – change in which energy is released (combustion) Chemical energy – energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms o CE is stored in foods, fuels, cells of your body – we gain CE from the foods we eat o burning fuel transforms CE and releases it as thermal energy o energy can change into other forms of energy