* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s second law of motion
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Moment of inertia wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
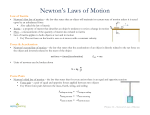
CLASS 9 PHYSICS CHAPTER-FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION. Q. Define force Force is the physical cause which can change or tends to change the state of a body , speed and direction of motion and size and shape of a body. Newton’s first law of motion: Q: State Newton’s first law of motion. Newton’ first law states that every body continuous to be in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless an external force acts upon it. Q : Define Inertia. Inertia is the tendency of undisturbed objects to stay at rest or keep moving with same velocity. Q: Name the factor on which inertia of a body depends. Inertia depends on the mass of the body. Q: Explain why some of leaves may get detached from a tree, if the branches are vigorously shaken. This is because of inertia of rest. Initially the braches and the leaves where in the state of rest. When the branches are shaken, the leaves try to remain at rest and they get detached from the branches. Q: When a carpet is beaten with the stick, the dust will come out .why? This is because of inertia of rest. Initially the carpet and dust particles where at the state of rest. While the carpet is beaten with the stick, the dust particles tend to remain at rest and gets detached from the carpet. 1|Page Q: When a bus suddenly start moving immediately, the passengers in the bus will fall backward. Why? This is because of inertia of rest. Initially the passengers and bus were at the state of rest. When the bus suddenly moves, the passengers tend to remain at rest and they fall backward. Q: The passengers in a moving bus tend to move forward when brakes are applied suddenly, why? This is because of inertia of motion. Initially the bus and the passengers were moving. When brakes are applied suddenly to stop the bus, the passengers tend to remain in motion and so they fall forward. Q: Why is it dangerous to jump out of moving vehicle? This is because of inertia of motion. Initially the vehicle and person were moving. When he suddenly jumps out of the moving vehicle, the body shows the tendency to remain in motion. So he will fall forward there by injuring himself. Q: Why is it advised to tie the luggage with a rope on the roof of buses? This is done to avoid the sliding of the luggage from the roof of the bus. When a fast moving bus applies brakes suddenly, the luggage is likely to fall forward due to inertia of motion. Conversely when a stationery bus accelerate suddenly, luggage lightly to fall backward due to inertia of rest. To prevent such situation, it is advisable to tie the luggage with a rope. Newton’s second law of motion:Q: Define momentum of a body. What is its SI unit? The momentum of a body is defined as the products of its mass and velocity. P = m x v, where p is the momentum of the body. The S I unit of momentum is kgm/s. Q: State Newton’s second law of motion. 2|Page Newton’s second law of motion states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of force. Q: Define one newton force. One newton force is defined as the amount of force which produces an acceleration of 1m/s2 in a body of mass1 kg. Mathematical formulation of second law of motion or derive the equation F = ma. Suppose an object of mass “m” is moving along a straight line with an initial velocity “u”. Let the force “F” acts on it and changes its velocity to “v” in time “t” Let the uniform acceleration acting on the body be “a” The initial momentum p1= mu The final momentum p2 = mv By Newton’s second law the rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to force, That is Fα (p2---- p1 )/ t Fα(mv-mu)/t Fαm(v-u)/t Fα ma F = kma, k is a constant, if k=1 then F= ma That is force is the product of mass and acceleration. 3|Page THIRD LAW OF MOTION To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples. 1. When a boatman wants to move away from the shore ,he pushes the shore with his oar(action) The shore pushes the boat away with an equal and opposite force (reaction) 2. When a man fires a bullet from a gun, a force is exerted on the bullet (action) and the gun experiences a recoil (reaction) 4|Page 5|Page